Abstract
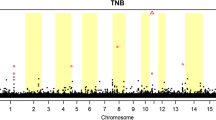
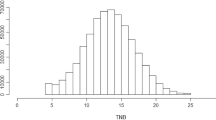
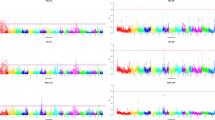
Maternal behavior around parturition is important to piglet survival. An extreme form of failure of maternal behavior, also called maternal infanticide, often occurs in some sows. This is defined as an active attack to piglets using the jaws, resulting in serious or fatal bite wounds within 24 h of birth. It leads to considerable economic losses to the pig industry and severe problems in pig welfare. In this study, maternal behaviors from 5 h before to 24 h after parturition were recorded in detail on 288 White Duroc × Erhualian intercross F2 sows over their three continuous farrowings. In the F2 population 12.8% gilts showed maternal infanticide in their first litter, while the incidences of maternal infanticide at their second and third farrowing reduced to 7.5% and 4.5%, respectively. All F2 sows were genotyped for 194 microsatellite markers spanning the whole pig genome. A whole genome linkage analysis was performed using the non-parametric linkage test by SimWalk2 software. The results identified that seven chromosome regions on SSC2, SSC6, SSC14, SSC15 and SSCX were significantly linked with maternal infanticide (P < 0.05). The quantitative trait loci (QTL) on SSC2 and SSCX achieved P < 0.01 significance level. The most promising QTLs, however, were detected on X chromosome where three peaks of negative logarithm of P-value located at marker SW980, SW2456 and SW1608. QTLs on SSC2 and SSCX from this experiment were consistent with published results from the Western commercial lines.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlstrom S, Jarvis S, Lawrence AB (2002) Savaging gilts are more restless and more responsive to piglets during the expulsive phase of parturition. Appl Anim Behav Sci 76:83–91. doi:10.1016/S0168-1591(01)00207-6
Ahmadiyeh N, Churchill GA, Shimomura K, Solberg LC, Takahashi JS, Redei EE (2003) X-linked and lineage-dependent inheritance of coping responses to stress. Mamm Genome 14:748–757. doi:10.1007/s00335-003-2292-x
Arnsten AFT (2004) Adrenergic targets for the treatment of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 174:25–31. doi:10.1007/s00213-003-1724-3
Barmada MM, O’Connell JR (2001) Model-free linkage analysis: performance under real-world conditions. Genet Epidemiol 21:S498–S503
Boks MP, Hoogendoorn M, Jungerius BJ, Bakker SC, Sommer IE, Sinke RJ, Ophoff RA, Kahn RS (2007) Do mood symptoms subdivide the schizophrenia phenotype? Association of the GMP6A gene with a depression subgroup. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B:707–711. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30667
Chen C, Gilbert CL, Yang G, Guo Y, Segonds-Pichon A, Ma J, Evens G, Brenig B, Sargent C, Affara N, Huang L (2008) Maternal infanticide in sows: incidence and behavioral comparisons between savaging and non-savaging sows at parturition. Appl Anim Behav Sci 109:238–248. doi:10.1016/j.applanim.2007.02.008
Dremencov E, Weizmann Y, Kinor N, Gispan-Herman I, Yadid G (2006) Modulation of dopamine transmission by 5HT2C and 5HT3 receptors: a role in the antidepressant response. Curr Drug Targets 7:165–175. doi:10.2174/138945006775515491
Gachon F, Fonjallaz P, Damiola F, Gos P, Kodama T, Zakany J, Duboule D, Petit B, Tafti M, Schibler U (2004) The loss of circadian PAR bZip transcription factors results in epilepsy. Genes Dev 18:1397–1412. doi:10.1101/gad.301404
Gilbert CL (2001) Endocrine regulation of periparturient behavior in pigs. Reprod (Cambridge, England) Suppl 58:263
Goes FS, Zandi PP, Miao K, McMahon FJ, Steele J, Willour VL, Mackinnon DF, Mondimore FM, Schweizer B, Nurnberger JI Jr, Rice JP, Scheftner W, Coryell W, Berrettini WH, Kelsoe JR, Byerley W, Murphy DL, Gershon ES, Bipolar Disorder Phenome Group, Depaulo JR Jr, McInnis MG, Potash JB (2007) Mood-incongruent psychotic features in bipolar disorder: familial aggregation and suggestive linkage to 2p11–q14 and 13q21–33. Am J Psychiatry 164:236–247. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.164.2.236
Green P, Falls K, Crooks S (1994) Cri-map version 2.4. Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis
Guo Y, Mao H, Ren J, Yan X, Duan Y, Yang C, Ren D, Zhang Z, Yang B, Ouyang J, Brenig B, Haley C, Huang L (2008) A linkage map of the porcine genome from a large scale White Duroc × Erhualian resource population and evaluation of factors affecting recombination rates. Anim Genet. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2052.2008.01802.x
Harris MJ, Gonyou HW (2003) Savaging behavior in domestic gilts: a study of seven commercial farms. Can J Anim Sci 83:435–444
Kaabi B, Gelernter J, Woods SW, Goddard A, Page GP, Elston RC (2006) Genome scan for loci predisposing to anxiety disorders using a novel multivariate approach: strong evidence for a chromosome 4 risk locus. Am J Hum Genet 78:543–553. doi:10.1086/501072
Kent L, Emerton J, Bhadravathi V, Weisblatt E, Pasco G, Willatt LR, McMahon R, Yates JR (2008) X-linked ichthyosis (steroid sulfatase deficiency) is associated with increased risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, autism and social communication deficits. J Med Genet 45:519–524. doi:10.1136/jmg.2008.057729
Knap PW, Merks JWM (1987) A note on the genetics of aggressiveness of primiparous sows towards their piglets. Livest Prod Sci 17:161–167. doi:10.1016/0301-6226(87)90061-3
Lahdesmaki J, Sallinen J, MacDonald E, Scheinin M (2004) Alpha2Aadrenoceptors are important modulators of the effects of d-amphetamine on startle reactivity and brain monoamines. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1282–1293. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300428
Lange EM, Lange K (2004) Powerful allele sharing statistics for nonparametric linkage analysis. Hum Hered 57:49–58. doi:10.1159/000077389
McLean KA, Lawrence AB, Petherick JC, Deans L, Chirnside J, Vaughan A, Nielsen BL, Webb R (1998) Investigation of the relationship between farrowing environment, sex steroid concentrations and maternal aggression in gilts. Anim Reprod Sci 50:95. doi:10.1016/S0378-4320(97)00088-2
Nicolas LB, Pinoteau W, Papot S, Routier S, Guillaumet G, Mortaud S (2001) Aggressive behavior induced by the steroid sulfatase inhibitor COUMATE and by DHEAS in CBA/H mice. Brain Res 922:216–222. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(01)03171-7
Peripato AC, De Brito RA, Vaughn TT, Pletscher LS, Matioli SR, Cheverud JM (2002) Quantitative trait loci for maternal performance for offspring survival in mice. Genetics 162:1341–1353
Perlman WR, Webster MJ, Kleinman JE, Weickert CS (2004) Reduced glucocorticoid and estrogen receptor alpha messenger ribonucleic acid levels in the amygdala of patients with major mental illness. Biol Psychiatry 56:844–852. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.09.006
Quilter CR, Blott SC, Wilson AE, Bagga MR, Sargent CA, Oliver GL, Southwood OI, Gilbert CL, Mileham A, Affara NA (2007) Porcine maternal infanticide as a model for puerperal psychosis. Am J Med Gene B Neuropsychiatr Genet 144:862–868. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30529
Semba J (1998) Glycine therapy of schizophrenia; its rationale and a review of clinical trials. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi 18:71–80
Sinclair AG, Edwards SA, Hoste S, McCartney A (1998) Evaluation of the influence of maternal and piglet breed differences on behaviour and production of Meishan synthetic and European White breeds during lactation. Anim Sci (Penicuik, Scotland) 66:423–430
Sobel E, Lange K (1996) Descent graphs in pedigree analysis: applications to haplotyping, location scores, and marker-sharing statistics. Am J Hum Genet 58:1323–1337
van der Steen HA, de Groot PN (1992) Direct and maternal breed effects on growth and milk intake of piglets: Meishan versus Dutch breeds. Livest Prod Sci 30:361–373. doi:10.1016/0301-6226(92)90044-5
van der Steen HA, Schaeffer LR, de Jong H, de Groot PN (1988) Aggressive behavior of sows at parturition. J Anim Sci 66:271–279
Wang MW, Crombie DL, Hayes JS, Heap RB (1995) Aberrant maternal behavior in mice treated with a progesterone receptor antagonist during pregnancy. J Endocrinol 145:371–377
Waxman SG (2001) Acquired channelopathies in nerve injury and MS. Neurology 56:1621–1627
Webster MJ, Knable MB, O’Grady J, Orthmann J, Weickert CS (2002) Regional specificity of brain glucocorticoid receptor mRNA alterations in subjects with schizophrenia and mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 7:985–994. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001139
Whittemore AS, Halpern J (1994) A class of tests for linkage using affected pedigree members. Biometrics 50(1):118–127. doi:10.2307/2533202
Wood JN, Boorman JP, Okuse K, Baker MD (2004) Voltage-gated sodium channels and pain pathways. J Neurobiol 61:55–71. doi:10.1002/neu.20094
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program). Miguel Perez-Enciso is funded by grants AGL2007-65563-C02-01/GAN and PCI2006-A7-0523 (Spain). The authors are very greatful to Prof.Chris Haley for his very useful comments and suggestion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by Stephen Maxson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Guo, Y., Yang, G. et al. A Genome Wide Detection of Quantitative Trait Loci on Pig Maternal Infanticide Behavior in a Large Scale White Duroc × Erhualian Resource Population. Behav Genet 39, 213–219 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-008-9252-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-008-9252-x