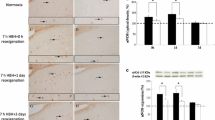
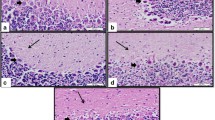
NO synthesis disturbances play an important role in the development of neurodegenerative damage in Alzheimer disease. We previously showed that adaptation to intermittent hypobaric hypoxia prevents cognitive disturbances in rats with experimental Alzheimer disease [6]. Here we evaluated the role of NO in cognitive disorders and development of adaptive protection during experimental Alzheimer disease. Adaptation to hypoxia in rats was performed in a hypobaric pressure chamber at a simulated altitude of 4000 m (4 h per day for 14 days). Alzheimer disease was simulated by bilateral injections of a toxic fragment of β-amyloid (25–35) into n. basalis magnocellularis. For evaluation of the role of NO in the development and prevention of memory disorders, the rats received intraperitoneally either NO-synthase inhibitor Nω-nitro-L-arginin (L-NNA, 20 mg/kg, every other day for 14 days) or NO-donor dinitrosyl iron complex (200 μg/kg daily for 14 days). NO-synthase inhibitor potentiated the damaging effect of β-amyloid, abolished the protective effect of adaptation to hypoxia, and produced memory disorders in rats similar to those observed during experimental Alzheimer disease. In contrast, the increase in NO level in the body provided by injections of the NO-donor produced a protective effect against memory disorders caused by β-amyloid similar to that induced by adaptation to hypoxia. We concluded that reduced NO production in the organism plays an important role in the development of cognitive disorders produced by injections of β-amyloid, while prevention of NO deficit by administration of NO-donors or nonpharmacological stimulation of NO synthesis can provide a protective effect in experimental Alzheimer disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. F. Vanin, Biochimia, 63, No. 7. 924–938 (1998).
E. B. Manukhina, F. Viegant, V. I. Torshin, et al., Proceeding of Russian Academy of Sciences, Ser. Biol., Vol. 31, No. 4, 382–395 (2004).
E. B. Manukhina, B. V. Smirin, and I. Yu. Malyshev, Ibid, 31, No. 4, 585–596 (2004).
S. Yu. Mashina, V. V. Aleksandrin, A. V. Goryacheva, et al., Byul. Exper. Biol. Med, 142, No. 8, 132–135 (2006).
M. G. Pshennikova, E. V. Popkova, and D. A. Podkidyshev, Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, No. 2, 50–55 (2007).
M. G. Pshennikova, E. V. Popkova, I. P. Khomenko, Byul. Exper. Biol. Med., 139, No. 5, 540–542 (2005).
V. Calabrese, T. E. Bates, and A. M. Stella, Neurochem. Res, 25, Nos. 9–10, 1315–1341 (2000).
M. Colosanti and H. Suzuki, Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 21, No. 7, 249–252 (2000).
C. A. Colton, M. P. Vitek, D. A. Wink, et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 103, No. 34, 12,867–12,872 (2006).
L. Corzo, R. Zas, S. Rodrhgues, et al., Neurosci. Lett., 420, No. 3, 263–267 (2007).
M. T. Gentile, C. Vecchione, A. Maffei, et al., J. Biol. Chem., 279, No. 46, 48,135–48,142 (2004).
C. Ghosh and D. K. Lahiri, J. Mol. Neurosci., 13, Nos. 1–2, 77–92 (1999).
U. Keil, A. Bonert, C. A. Marques, et al., J. Biol. Chem., 279, No 48, 50,310–50,320 (2004).
E. B. Manukhina, H. F. Downey, and R. T. Mallet, Exp. Biol. Med., 231, No. 4, 343–365 (2006).
E. Tarkowski , A. Ringqvist , K. Blennow, et al., Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord., 11, No. 6, 322–326 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 146, No. 10, pp. 371–375, October, 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manukhina, E.B., Pshennikova, M.G., Goryacheva, A.V. et al. Role of Nitric Oxide in Prevention of Cognitive Disorders in Neurodegenerative Brain Injuries in Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 146, 391–395 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-009-0315-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-009-0315-7