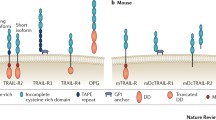
Abstract
Inducing apoptosis has become an important approach in the development of new anti-cancer treatments. Tumour necrosis factor apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) based therapies have emerged as one of the most promising examples of this as they selectively induce apoptosis in tumour cells. However, many primary tumours are inherently resistant to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis and require additional sensitisation. Here we review apoptotic and non-apoptotic TRAIL-signalling, and the therapeutic effects of TRAIL-based treatments both as monotherapy and in combination with sensitising agents.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81683-9
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K et al (1999) Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med 5:157–163. doi:10.1038/5517
Koschny R, Holland H, Sykora J et al (2007) Bortezomib sensitizes primary human astrocytoma cells of WHO grades I to IV for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res 13:3403–3412. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0251
Leverkus M, Sprick MR, Wachter T et al (2003) Proteasome inhibition results in TRAIL sensitization of primary keratinocytes by removing the resistance-mediating block of effector caspase maturation. Mol Cell Biol 23:777–790. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.3.777-790.2003
Ganten TM, Koschny R, Haas TL et al (2005) Proteasome inhibition sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells, but not human hepatocytes, to TRAIL. Hepatology 42:588–597. doi:10.1002/hep.20807
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A (1996) Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem 271:12687–12690. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.22.12687
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ et al (1995) Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 3:673–682. doi:10.1016/1074-7613(95)90057-8
Pan G, Ni J, Wei YF, Yu G, Gentz R, Dixit VM (1997) An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science 277:815–818. doi:10.1126/science.277.5327.815
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS et al (1997) TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J 16:5386–5397. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.17.5386
Screaton GR, Mongkolsapaya J, Xu XN, Cowper AE, McMichael AJ, Bell JI (1997) TRICK2, a new alternatively spliced receptor that transduces the cytotoxic signal from TRAIL. Curr Biol 7:693–696. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(06)00297-1
Sheridan JP, Marsters SA, Pitti RM et al (1997) Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science 277:818–821. doi:10.1126/science.277.5327.818
Wu GS, Burns TF, McDonald ER 3rd et al (1997) KILLER/DR5 is a DNA damage-inducible p53-regulated death receptor gene. Nat Genet 17:141–143. doi:10.1038/ng1097-141
Degli-Esposti MA, Dougall WC, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Smith CA, Goodwin RG (1997) The novel receptor TRAIL-R4 induces NF-kappaB and protects against TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, yet retains an incomplete death domain. Immunity 7:813–820. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80399-4
Degli-Esposti MA, Smolak PJ, Walczak H et al (1997) Cloning and characterization of TRAIL-R3, a novel member of the emerging TRAIL receptor family. J Exp Med 186:1165–1170. doi:10.1084/jem.186.7.1165
Lahm A, Paradisi A, Green DR, Melino G (2003) Death fold domain interaction in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 10:10–12. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401203
Merino D, Lalaoui N, Morizot A, Schneider P, Solary E, Micheau O (2006) Differential inhibition of TRAIL-mediated DR5-DISC formation by decoy receptors 1 and 2. Mol Cell Biol 26:7046–7055. doi:10.1128/MCB.00520-06
Wu GS, Burns TF, Zhan Y, Alnemri ES, El-Deiry WS (1999) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the mouse homologue of the KILLER/DR5 tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor. Cancer Res 59:2770–2775
Schneider P, Olson D, Tardivel A et al (2003) Identification of a new murine tumor necrosis factor receptor locus that contains two novel murine receptors for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). J Biol Chem 278:5444–5454. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210783200
Vitovski S, Phillips JS, Sayers J, Croucher PI (2007) Investigating the interaction between osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of NF-kappaB or tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand: evidence for a pivotal role for osteoprotegerin in regulating two distinct pathways. J Biol Chem 282:31601–31609. doi:10.1074/jbc.M706078200
Zauli G, Rimondi E, Nicolin V, Melloni E, Celeghini C, Secchiero P (2004) TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) blocks osteoclastic differentiation induced by RANKL plus M-CSF. Blood 104:2044–2050. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-03-1196
Cretney E, Takeda K, Yagita H, Glaccum M, Peschon JJ, Smyth MJ (2002) Increased susceptibility to tumor initiation and metastasis in TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-deficient mice. J Immunol 168:1356–1361
Finnberg N, Klein-Szanto AJ, El-Deiry WS (2008) TRAIL-R deficiency in mice promotes susceptibility to chronic inflammation and tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest 118:111–123. doi:10.1172/JCI29900
Grosse-Wilde A, Voloshanenko O, Bailey SL et al (2008) TRAIL-R deficiency in mice enhances lymph node metastasis without affecting primary tumor development. J Clin Invest 118:100–110. doi:10.1172/JCI33061
Diehl GE, Yue HH, Hsieh K et al (2004) TRAIL-R as a negative regulator of innate immune cell responses. Immunity 21:877–889. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2004.11.008
Ehrhardt H, Fulda S, Schmid I, Hiscott J, Debatin KM, Jeremias I (2003) TRAIL induced survival and proliferation in cancer cells resistant towards TRAIL-induced apoptosis mediated by NF-kappaB. Oncogene 22:3842–3852. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206520
Ishimura N, Isomoto H, Bronk SF, Gores GJ (2006) Trail induces cell migration and invasion in apoptosis-resistant cholangiocarcinoma cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G129–G136. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00242.2005
Mongkolsapaya J, Grimes JM, Chen N et al (1999) Structure of the TRAIL-DR5 complex reveals mechanisms conferring specificity in apoptotic initiation. Nat Struct Biol 6:1048–1053. doi:10.1038/14935
Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Behrmann I et al (1995) Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J 14:5579–5588
Sprick MR, Weigand MA, Rieser E et al (2000) FADD/MORT1 and caspase-8 are recruited to TRAIL receptors 1 and 2 and are essential for apoptosis mediated by TRAIL receptor 2. Immunity 12:599–609. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80211-3
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A, Schow P, Kim KJ, Ashkenazi A (2000) Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity 12:611–620. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80212-5
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Tinel A et al (2001) Death receptor recruitment of endogenous caspase-10 and apoptosis initiation in the absence of caspase-8. J Biol Chem 276:46639–46646. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105102200
Sprick MR, Rieser E, Stahl H, Grosse-Wilde A, Weigand MA, Walczak H (2002) Caspase-10 is recruited to and activated at the native TRAIL and CD95 death-inducing signalling complexes in a FADD-dependent manner but can not functionally substitute caspase-8. EMBO J 21:4520–4530. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf441
Krueger A, Schmitz I, Baumann S, Krammer PH, Kirchhoff S (2001) Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein splice variants inhibit different steps of caspase-8 activation at the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem 276:20633–20640. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101780200
Golks A, Brenner D, Fritsch C, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN (2005) c-FLIPR, a new regulator of death receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 280:14507–14513. doi:10.1074/jbc.M414425200
Thome M, Schneider P, Hofmann K et al (1997) Viral FLICE-inhibitory proteins (FLIPs) prevent apoptosis induced by death receptors. Nature 386:517–521. doi:10.1038/386517a0
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M et al (1997) Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 388:190–195. doi:10.1038/40657
Micheau O, Thome M, Schneider P et al (2002) The long form of FLIP is an activator of caspase-8 at the Fas death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem 277:45162–45171. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206882200
Varfolomeev EE, Schuchmann M, Luria V et al (1998) Targeted disruption of the mouse Caspase 8 gene ablates cell death induction by the TNF receptors, Fas/Apo1, and DR3 and is lethal prenatally. Immunity 9:267–276. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80609-3
Zhang J, Cado D, Chen A, Kabra NH, Winoto A (1998) Fas-mediated apoptosis and activation-induced T-cell proliferation are defective in mice lacking FADD/Mort1. Nature 392:296–300. doi:10.1038/32681
Stennicke HR, Jurgensmeier JM, Shin H et al (1998) Pro-caspase-3 is a major physiologic target of caspase-8. J Biol Chem 273:27084–27090. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.42.27084
Barnhart BC, Alappat EC, Peter ME (2003) The CD95 type I/type II model. Semin Immunol 15:185–193. doi:10.1016/S1044-5323(03)00031-9
Waterhouse NJ, Ricci JE, Green DR (2002) And all of a sudden it’s over: mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization in apoptosis. Biochimie 84:113–121. doi:10.1016/S0300-9084(02)01379-2
Yin XM (2006) Bid, a BH3-only multi-functional molecule, is at the cross road of life and death. Gene 369:7–19. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2005.10.038
Koschny R, Walczak H, Ganten TM (2007) The promise of TRAIL-potential and risks of a novel anticancer therapy. J Mol Med 85:923–935. doi:10.1007/s00109-007-0194-1
LeBlanc HN, Ashkenazi A (2003) Apo2L/TRAIL and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ 10:66–75. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401187
Kimberley FC, Screaton GR (2004) Following a TRAIL: update on a ligand and its five receptors. Cell Res 14:359–372. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7290236
Sheikh MS, Huang Y, Fernandez-Salas EA et al (1999) The antiapoptotic decoy receptor TRID/TRAIL-R3 is a p53-regulated DNA damage-inducible gene that is overexpressed in primary tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Oncogene 18:4153–4159. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202763
Hornstein M, Hoffmann MJ, Alexa A et al (2008) Protein phosphatase and TRAIL receptor genes as new candidate tumor genes on chromosome 8p in prostate cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 5:123–136
Horak P, Pils D, Haller G et al (2005) Contribution of epigenetic silencing of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand receptor 1 (DR4) to TRAIL resistance and ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res 3:335–343. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-04-0136
Saulle E, Petronelli A, Pasquini L et al (2007) Proteasome inhibitors sensitize ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis. Apoptosis 12:635–655. doi:10.1007/s10495-006-0025-9
Pritzker LB, Scatena M, Giachelli CM (2004) The role of osteoprotegerin and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in human microvascular endothelial cell survival. Mol Biol Cell 15:2834–2841. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-01-0059
De Toni EN, Thieme SE, Herbst A et al (2008) OPG is regulated by beta-catenin and mediates resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:4713–4718. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5019
Horak P, Pils D, Kaider A et al (2005) Perturbation of the tumor necrosis factor—related apoptosis-inducing ligand cascade in ovarian cancer: overexpression of FLIPL and deregulation of the functional receptors DR4 and DR5. Clin Cancer Res 11:8585–8591. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1276
Clarke P, Tyler KL (2007) Down-regulation of cFLIP following reovirus infection sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis 12:211–223. doi:10.1007/s10495-006-0528-4
Geserick P, Drewniok C, Hupe M et al (2008) Suppression of cFLIP is sufficient to sensitize human melanoma cells to TRAIL- and CD95L-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 27:3211–3220. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210985
Siegmund D, Hadwiger P, Pfizenmaier K, Vornlocher HP, Wajant H (2002) Selective inhibition of FLICE-like inhibitory protein expression with small interfering RNA oligonucleotides is sufficient to sensitize tumor cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Mol Med 8:725–732
Ganten TM, Haas TL, Sykora J et al (2004) Enhanced caspase-8 recruitment to and activation at the DISC is critical for sensitisation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by chemotherapeutic drugs. Cell Death Differ 11(Suppl 1):S86–S96. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401437
Hopkins-Donaldson S, Bodmer JL, Bourloud KB, Brognara CB, Tschopp J, Gross N (2000) Loss of caspase-8 expression in highly malignant human neuroblastoma cells correlates with resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 60:4315–4319
Makhov P, Golovine K, Uzzo RG et al (2008) Zinc chelation induces rapid depletion of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 15:1745–1751. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.106
Huang Y, Lu M, Wu H (2004) Antagonizing XIAP-mediated caspase-3 inhibition. Achilles’ heel of cancers? Cancer Cell 5:1–2. doi:10.1016/S1535-6108(03)00340-4
Micheau O, Merino D (2004) Controlling TRAIL-mediated caspase-3 activation. Leukemia 18:1578–1580. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2403497
Shi Y (2004) Caspase activation, inhibition, and reactivation: a mechanistic view. Protein Sci 13:1979–1987. doi:10.1110/ps.04789804
Hinz S, Trauzold A, Boenicke L et al (2000) Bcl-XL protects pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells against CD95- and TRAIL-receptor-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 19:5477–5486. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203936
Fulda S, Meyer E, Debatin KM (2002) Inhibition of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by Bcl-2 overexpression. Oncogene 21:2283–2294. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205258
Adams JM, Cory S (2007) The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 26:1324–1337. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210220
Taniai M, Grambihler A, Higuchi H et al (2004) Mcl-1 mediates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 64:3517–3524. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2770
Ndozangue-Touriguine O, Sebbagh M, Merino D, Micheau O, Bertoglio J, Breard J (2008) A mitochondrial block and expression of XIAP lead to resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis during progression to metastasis of a colon carcinoma. Oncogene 27:6012–6022. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.197
Vogler M, Walczak H, Stadel D et al (2008) Targeting XIAP bypasses Bcl-2-mediated resistance to TRAIL and cooperates with TRAIL to suppress pancreatic cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 68:7956–7965. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1296
Wajant H (2004) TRAIL and NFkappaB signaling—a complex relationship. Vitam Horm 67:101–132. doi:10.1016/S0083-6729(04)67007-5
Li H, Lin X (2008) Positive and negative signaling components involved in TNFalpha-induced NF-kappaB activation. Cytokine 41:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2007.09.016
Harper N, Farrow SN, Kaptein A, Cohen GM, MacFarlane M (2001) Modulation of tumor necrosis factor apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced NF-kappa B activation by inhibition of apical caspases. J Biol Chem 276:34743–34752. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105693200
Varfolomeev E, Maecker H, Sharp D et al (2005) Molecular determinants of kinase pathway activation by Apo2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J Biol Chem 280:40599–40608. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509560200
Secchiero P, Zerbinati C, Rimondi E et al (2004) TRAIL promotes the survival, migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:1965–1974. doi:10.1007/s00018-004-4197-6
Secchiero P, Melloni E, Corallini F et al (2008) TRAIL promotes migration of human bone marrow multipotent stromal cells. Stem Cells 26(11):2955–2963
Vilimanovich U, Bumbasirevic V (2008) TRAIL induces proliferation of human glioma cells by c-FLIPL-mediated activation of ERK1/2. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:814–826. doi:10.1007/s00018-008-7513-8
Belyanskaya LL, Ziogas A, Hopkins-Donaldson S et al (2008) TRAIL-induced survival and proliferation of SCLC cells is mediated by ERK and dependent on TRAIL-R2/DR5 expression in the absence of caspase-8. Lung Cancer 60:355–365. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.11.005
Secchiero P, Gonelli A, Carnevale E et al (2003) TRAIL promotes the survival and proliferation of primary human vascular endothelial cells by activating the Akt and ERK pathways. Circulation 107:2250–2256. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000062702.60708.C4
Joy AM, Beaudry CE, Tran NL et al (2003) Migrating glioma cells activate the PI3-K pathway and display decreased susceptibility to apoptosis. J Cell Sci 116:4409–4417. doi:10.1242/jcs.00712
Trauzold A, Siegmund D, Schniewind B et al (2006) TRAIL promotes metastasis of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 25:7434–7439. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209719
Sanlioglu AD, Korcum AF, Pestereli E et al (2007) TRAIL death receptor-4 expression positively correlates with the tumor grade in breast cancer patients with invasive ductal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69:716–723. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.03.057
Schneider P (2000) Production of recombinant TRAIL and TRAIL receptor: Fc chimeric proteins. Methods Enzymol 322:325–345. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(00)22031-4
Ganten TM, Koschny R, Sykora J et al (2006) Preclinical differentiation between apparently safe and potentially hepatotoxic applications of TRAIL either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs. Clin Cancer Res 12:2640–2646. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2635
Gores GJ, Kaufmann SH (2001) Is TRAIL hepatotoxic? Hepatology 34:3–6. doi:10.1053/jhep.2001.25173a
Lawrence D, Shahrokh Z, Marsters S et al (2001) Differential hepatocyte toxicity of recombinant Apo2L/TRAIL versions. Nat Med 7:383–385. doi:10.1038/86397
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S et al (1999) Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 104:155–162. doi:10.1172/JCI6926
Kelley SK, Ashkenazi A (2004) Targeting death receptors in cancer with Apo2L/TRAIL. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:333–339. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2004.02.006
Buchsbaum DJ, Zhou T, Lobuglio AF (2006) TRAIL receptor-targeted therapy. Future Oncol 2:493–508. doi:10.2217/14796694.2.4.493
Natoni A, MacFarlane M, Inoue S et al (2007) TRAIL signals to apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells primarily through TRAIL-R1 whereas cross-linked agonistic TRAIL-R2 antibodies facilitate signalling via TRAIL-R2. Br J Haematol 139:568–577. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06852.x
Chuntharapai A, Dodge K, Grimmer K et al (2001) Isotype-dependent inhibition of tumor growth in vivo by monoclonal antibodies to death receptor 4. J Immunol 166:4891–4898
Buchsbaum DJ, Zhou T, Grizzle WE et al (2003) Antitumor efficacy of TRA-8 anti-DR5 monoclonal antibody alone or in combination with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy in a human breast cancer model. Clin Cancer Res 9:3731–3741
Ichikawa K, Liu W, Zhao L et al (2001) Tumoricidal activity of a novel anti-human DR5 monoclonal antibody without hepatocyte cytotoxicity. Nat Med 7:954–960. doi:10.1038/91000
Zeng Y, Wu XX, Fiscella M et al (2006) Monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2 (TRAIL-R2) induces apoptosis in primary renal cell carcinoma cells in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Int J Oncol 28:421–430
MacFarlane M, Inoue S, Kohlhaas SL et al (2005) Chronic lymphocytic leukemic cells exhibit apoptotic signaling via TRAIL-R1. Cell Death Differ 12:773–782. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401649
Takeda K, Yamaguchi N, Akiba H et al (2004) Induction of tumor-specific T cell immunity by anti-DR5 antibody therapy. J Exp Med 199:437–448. doi:10.1084/jem.20031457
Pukac L, Kanakaraj P, Humphreys R et al (2005) HGS-ETR1, a fully human TRAIL-receptor 1 monoclonal antibody, induces cell death in multiple tumour types in vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer 92:1430–1441. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602487
Gazitt Y (1999) TRAIL is a potent inducer of apoptosis in myeloma cells derived from multiple myeloma patients and is not cytotoxic to hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 13:1817–1824. doi:10.1038/sj/leu/2401501
Mitsiades CS, Treon SP, Mitsiades N et al (2001) TRAIL/Apo2L ligand selectively induces apoptosis and overcomes drug resistance in multiple myeloma: therapeutic applications. Blood 98:795–804. doi:10.1182/blood.V98.3.795
Clodi K, Wimmer D, Li Y et al (2000) Expression of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptors and sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in primary B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol 111:580–586. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.02404.x
MacFarlane M, Harper N, Snowden RT et al (2002) Mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in primary B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Oncogene 21:6809–6818. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205853
Snell V, Clodi K, Zhao S et al (1997) Activity of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in haematological malignancies. Br J Haematol 99:618–624. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.1997.4393250.x
Clayer M, Bouralexis S, Evdokiou A, Hay S, Atkins GJ, Findlay DM (2001) Enhanced apoptosis of soft tissue sarcoma cells with chemotherapy: a potential new approach using TRAIL. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 9:19–22
Panner A, James CD, Berger MS, Pieper RO (2005) mTOR controls FLIPS translation and TRAIL sensitivity in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Mol Cell Biol 25:8809–8823. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.20.8809-8823.2005
Todaro M, Lombardo Y, Francipane MG et al (2008) Apoptosis resistance in epithelial tumors is mediated by tumor-cell-derived interleukin-4. Cell Death Differ 15:762–772. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402305
Younes A, Vose JM, Zelenetz AD et al (2005) Results of a phase 2 trial of HGS-ETR1 (agonistic human monoclonal antibody to TRAIL receptor 1) in subjects with relapsed/refractory Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL). Blood 106:489 ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts
Tolcher AW, Mita M, Meropol NJ et al (2007) Phase I pharmacokinetic and biologic correlative study of mapatumumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody with agonist activity to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor-1. J Clin Oncol 25:1390–1395. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.08.8898
Hotte SJ, Hirte HW, Chen EX et al (2008) A phase 1 study of mapatumumab (fully human monoclonal antibody to TRAIL-R1) in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 14:3450–3455. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1416
Le LH, Hirte HW, Hotte SJ et al (2004) Phase I study of a fully human monoclonal antibody to the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand death receptor 4 (TRAIL-R1) in subjects with advanced solid malignancies or non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL). J Clin Oncol 22:2533 Meeting Abstracts
Greco FA, Bonomi P, Crawford J et al (2008) Phase 2 study of mapatumumab, a fully human agonistic monoclonal antibody which targets and activates the TRAIL receptor-1, in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 61:82–90. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.12.011
Plummer R, Attard G, Pacey S et al (2007) Phase 1 and pharmacokinetic study of lexatumumab in patients with advanced cancers. Clin Cancer Res 13:6187–6194. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0950
Patnaik A, Wakelee H, Mita M et al (2006) HGS-ETR2—A fully human monoclonal antibody to TRAIL-R2: results of a phase I trial in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 24:3012 ASCO Meeting Abstracts
Camidge D, Herbst RS, Gordon M et al (2007) A phase I safety and pharmacokinetic study of apomab, a human DR5 agonist antibody, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:3582 ASCO Meeting Abstracts
LoRusso P, Hong D, Heath E et al (2007) First-in-human study of AMG 655, a pro-apoptotic TRAIL receptor-2 agonist, in adult patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 25:3534 ASCO Meeting Abstracts
Herbst RS, Mendolson DS, Ebbinghaus S et al (2006) A phase I safety and pharmacokinetic (PK) study of recombinant Apo2L/TRAIL, an apoptosis-inducing protein in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:3013. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.8678 Meeting Abstracts
Yada A, Yazawa M, Ishida S et al (2008) A novel humanized anti-human death receptor 5 antibody CS-1008 induces apoptosis in tumor cells without toxicity in hepatocytes. Ann Oncol 19:1060–1067. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn015
Jonsson G, Paulie S, Grandien A (2003) High level of cFLIP correlates with resistance to death receptor-induced apoptosis in bladder carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 23:1213–1218
McCarthy MM, Sznol M, DiVito KA, Camp RL, Rimm DL, Kluger HM (2005) Evaluating the expression and prognostic value of TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:5188–5194. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0158
Strater J, Hinz U, Walczak H et al (2002) Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL receptors in colon carcinoma: TRAIL-R1 is an independent prognostic parameter. Clin Cancer Res 8:3734–3740
Pan Y, Xu R, Peach M et al (2007) Application of pharmacodynamic assays in a phase Ia trial of Apo2L/TRAIL in patients with advanced tumors. J Clin Oncol 25:3535 ASCO Meeting Abstracts
Koschny R, Ganten TM, Sykora J et al (2007) TRAIL/bortezomib cotreatment is potentially hepatotoxic but induces cancer-specific apoptosis within a therapeutic window. Hepatology 45:649–658. doi:10.1002/hep.21555
El-Zawahry A, McKillop J, Voelkel-Johnson C (2005) Doxorubicin increases the effectiveness of Apo2L/TRAIL for tumor growth inhibition of prostate cancer xenografts. BMC Cancer 5:2. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-5-2
Shankar S, Singh TR, Srivastava RK (2004) Ionizing radiation enhances the therapeutic potential of TRAIL in prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo: intracellular mechanisms. Prostate 61:35–49. doi:10.1002/pros.20069
Shankar S, Chen X, Srivastava RK (2005) Effects of sequential treatments with chemotherapeutic drugs followed by TRAIL on prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo. Prostate 62:165–186. doi:10.1002/pros.20126
Shamimi-Noori S, Yeow WS, Ziauddin MF et al (2008) Cisplatin enhances the antitumor effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand gene therapy via recruitment of the mitochondria-dependent death signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther 15:356–370. doi:10.1038/sj.cgt.7701120
Ray S, Almasan A (2003) Apoptosis induction in prostate cancer cells and xenografts by combined treatment with Apo2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and CPT-11. Cancer Res 63:4713–4723
Chow LQ, Eckhardt SG, Gustafson DL et al (2006) HGS-ETR1, an antibody targeting TRAIL-R1, in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid malignancies: results of a phase 1 and PK study. J Clin Oncol 24:2515 ASCO Meeting Abstracts
Oldenhuis C, Mom C, Sleijfer S et al (2008) A phase I study with the agonistic TRAIL-R1 antibody, mapatumumab, in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin. J Clin Oncol 26:3540 ASCO Meeting Abstracts
Sikic BI, Wakelee HA, von Mehren M et al (2007) A phase Ib study to assess the safety of lexatumumab, a human monoclonal antibody that activates TRAIL-R2, in combination with gemcitabine, pemetrexed, doxorubicin or FOLFIRI. J Clin Oncol 25:14006 ASCO Meeting Abstracts
Held J, Schulze-Osthoff K (2001) Potential and caveats of TRAIL in cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat 4:243–252. doi:10.1054/drup.2001.0208
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V et al (2002) Biologic sequelae of nuclear factor-kappaB blockade in multiple myeloma: therapeutic applications. Blood 99:4079–4086. doi:10.1182/blood.V99.11.4079
Daniel D, Yang B, Lawrence DA et al (2007) Cooperation of the proapoptotic receptor agonist rhApo2L/TRAIL with the CD20 antibody rituximab against non-Hodgkin lymphoma xenografts. Blood 110:4037–4046. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-02-076075
Yee L, Fanale M, Dimick K et al (2007) A phase IB safety and pharmacokinetic (PK) study of recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL in combination with rituximab in patients with low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25:8078 ASCO Meeting Abstracts
Sayers TJ, Brooks AD, Koh CY et al (2003) The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 sensitizes neoplastic cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by reducing levels of c-FLIP. Blood 102:303–310. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-09-2975
Hallett WH, Ames E, Motarjemi M et al (2008) Sensitization of tumor cells to NK cell-mediated killing by proteasome inhibition. J Immunol 180:163–170
Shanker A, Brooks AD, Tristan CA et al (2008) Treating metastatic solid tumors with bortezomib and a tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor agonist antibody. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:649–662. doi:10.1093/jnci/djn113
Guo F, Sigua C, Tao J et al (2004) Cotreatment with histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 enhances Apo-2L/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand-induced death inducing signaling complex activity and apoptosis of human acute leukemia cells. Cancer Res 64:2580–2589. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2629
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Dai Y, Grant S (2003) Simultaneous activation of the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) synergistically induces mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2:1273–1284
Inoue S, MacFarlane M, Harper N, Wheat LM, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM (2004) Histone deacetylase inhibitors potentiate TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in lymphoid malignancies. Cell Death Differ 11(Suppl 2):S193–S206. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401535
Nebbioso A, Clarke N, Voltz E et al (2005) Tumor-selective action of HDAC inhibitors involves TRAIL induction in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Nat Med 11:77–84. doi:10.1038/nm1161
Pathil A, Armeanu S, Venturelli S et al (2006) HDAC inhibitor treatment of hepatoma cells induces both TRAIL-independent apoptosis and restoration of sensitivity to TRAIL. Hepatology 43:425–434. doi:10.1002/hep.21054
Volkmann X, Fischer U, Bahr MJ et al (2007) Increased hepatotoxicity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in diseased human liver. Hepatology 46:1498–1508. doi:10.1002/hep.21846
Frew AJ, Lindemann RK, Martin BP et al (2008) Combination therapy of established cancer using a histone deacetylase inhibitor and a TRAIL receptor agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11317–11322. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801868105
Wu H, Tschopp J, Lin SC (2007) Smac mimetics and TNFalpha: a dangerous liaison? Cell 131:655–658. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.042
Petersen SL, Wang L, Yalcin-Chin A et al (2007) Autocrine TNFalpha signaling renders human cancer cells susceptible to Smac-mimetic-induced apoptosis. Cancer Cell 12:445–456. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2007.08.029
Vince JE, Wong WW, Khan N et al (2007) IAP antagonists target cIAP1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131:682–693. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.037
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM et al (2007) IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131:669–681. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.030
Li L, Thomas RM, Suzuki H, De Brabander JK, Wang X, Harran PG (2004) A small molecule Smac mimic potentiates TRAIL- and TNFalpha-mediated cell death. Science 305:1471–1474. doi:10.1126/science.1098231
Petrucci E, Pasquini L, Petronelli A et al (2007) A small molecule Smac mimic potentiates TRAIL-mediated cell death of ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol 105:481–492. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.01.011
Shrader M, Pino MS, Lashinger L et al (2007) Gefitinib reverses TRAIL resistance in human bladder cancer cell lines via inhibition of AKT-mediated X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein expression. Cancer Res 67:1430–1435. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1224
Garcia-Echeverria C, Sellers WR (2008) Drug discovery approaches targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway in cancer. Oncogene 27:5511–5526. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.246
Bremer E, Kuijlen J, Samplonius D, Walczak H, de Leij L, Helfrich W (2004) Target cell-restricted and -enhanced apoptosis induction by a scFv:sTRAIL fusion protein with specificity for the pancarcinoma-associated antigen EGP2. Int J Cancer 109:281–290. doi:10.1002/ijc.11702
Bremer E, Samplonius D, Kroesen BJ, van Genne L, de Leij L, Helfrich W (2004) Exceptionally potent anti-tumor bystander activity of an scFv:sTRAIL fusion protein with specificity for EGP2 toward target antigen-negative tumor cells. Neoplasia 6:636–645. doi:10.1593/neo.04229
Bremer E, Samplonius DF, Peipp M et al (2005) Target cell-restricted apoptosis induction of acute leukemic T cells by a recombinant tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand fusion protein with specificity for human CD7. Cancer Res 65:3380–3388
Stieglmaier J, Bremer E, Kellner C et al (2008) Selective induction of apoptosis in leukemic B-lymphoid cells by a CD19-specific TRAIL fusion protein. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:233–246. doi:10.1007/s00262-007-0370-8
Bremer E, Samplonius DF, van Genne L et al (2005) Simultaneous inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and enhanced activation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor-mediated apoptosis induction by an scFv:sTRAIL fusion protein with specificity for human EGFR. J Biol Chem 280:10025–10033. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413673200
Griffith TS, Broghammer EL (2001) Suppression of tumor growth following intralesional therapy with TRAIL recombinant adenovirus. Mol Ther 4:257–266. doi:10.1006/mthe.2001.0439
Herman JR, Adler HL, Aguilar-Cordova E et al (1999) In situ gene therapy for adenocarcinoma of the prostate: a phase I clinical trial. Hum Gene Ther 10:1239–1249. doi:10.1089/10430349950018229
Ravi R, Bedi GC, Engstrom LW et al (2001) Regulation of death receptor expression and TRAIL/Apo2L-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Nat Cell Biol 3:409–416. doi:10.1038/35070096
Romagnoli M, Desplanques G, Maiga S et al (2007) Canonical nuclear factor kappaB pathway inhibition blocks myeloma cell growth and induces apoptosis in strong synergy with TRAIL. Clin Cancer Res 13:6010–6018. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0140
Roue G, Perez-Galan P, Lopez-Guerra M, Villamor N, Campo E, Colomer D (2007) Selective inhibition of IkappaB kinase sensitizes mantle cell lymphoma B cells to TRAIL by decreasing cellular FLIP level. J Immunol 178:1923–1930
Kim KM, Song JJ, An JY, Kwon YT, Lee YJ (2005) Pretreatment of acetylsalicylic acid promotes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by down-regulating BCL-2 gene expression. J Biol Chem 280:41047–41056. doi:10.1074/jbc.M503713200
Uno T, Takeda K, Kojima Y et al (2006) Eradication of established tumors in mice by a combination antibody-based therapy. Nat Med 12:693–698. doi:10.1038/nm1405
Takeda K, Kojima Y, Ikejima K et al (2008) Death receptor 5 mediated-apoptosis contributes to cholestatic liver disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10895–10900. doi:10.1073/pnas.0802702105
Suntharalingam G, Perry MR, Ward S et al (2006) Cytokine storm in a phase 1 trial of the anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody TGN1412. N Engl J Med 355:1018–1028. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa063842
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Newsom-Davis and S. Prieske contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newsom-Davis, T., Prieske, S. & Walczak, H. Is TRAIL the holy grail of cancer therapy?. Apoptosis 14, 607–623 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0321-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0321-2