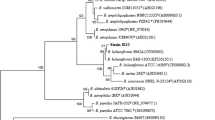
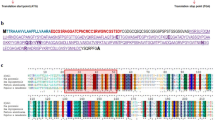
Abstract
Bacillus velezensis RB.IBE29 is a potent biocontrol agent with high chitinase activity isolated from the rhizosphere of black pepper cultivated in the Central Highlands, Vietnam. Genome sequences revealed that this species possesses some GH18 chitinases and AA10 protein(s); however, these enzymes have not been experimentally characterized. In this work, three genes were identified from the genomic DNA of this bacterium and cloned in Escherichia coli. Sequence analysis exhibited that the ORF of chiA consists of 1,203 bp and encodes deduced 45.46 kDa-chitinase A of 400 aa. The domain structure of chitinase A is composed of a CBM 50 domain at the N-terminus and a catalytic domain at the C-terminus. The ORF of chiB includes 1,263 bp and encodes deduced 47.59 kDa-chitinase B of 420 aa. Chitinase B consists of two CBM50 domains at the N-terminus and a catalytic domain at the C-terminus. The ORF of lpmo10 is 621 bp and encodes a deduced 22.44 kDa-AA10 protein, BvLPMO10 of 206 aa. BvLPMO10 contains a signal peptide and an AA10 catalytic domain. Chitinases A and B were grouped into subfamily A of family 18 chitinases. Amino acid sequences in their catalytic domains lack aromatic residues (Trp, Phe, Tyr) probably involved in processivity and substrate binding compared with well-known bacterial GH18 chitinases. chiB was successfully expressed in E. coli. Purified rBvChiB degraded insoluble chitin and was responsible for inhibition of fungal spore-germination and egg hatching of plant-parasitic nematode. This is the first report describing the analysis of the chitinase system from B. velezensis.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Sequences in this study have been deposited in the DNA Data Bank of Japan database under accession numbers LC649802–LC649804.
Abbreviations
- GlcNAc:
-
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine
- GH:
-
Glycoside hydrolases
- AA10:
-
Auxiliary activities family 10
- CBM50:
-
Carbohydrate-binding module family 50
- LB medium:
-
Luria–Bertani medium
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- bp:
-
Base pai
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- SDS–PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- aa:
-
Amino acid
References
Arimori T, Kawamoto N, Shinya S, Okazaki N, Nakazawa M, Miyatake K, Fukamizo T, Ueda M, Tamada T (2013) Crystal structures of the catalytic domain of a novel glycohydrolase family 23 chitinase from Ralstonia sp. A-471 reveals a unique arrangement of the catalytic residues for inverting chitin hydrolysis. J Biol Chem 288:18696–18706
Arkhipova TN, Prinsen E, Veselov SU, Martinenko EV, Melentiev AI, Kudoyarova GR (2007) Cytokinin producing bacteria enhance plant growth in drying soil. Plant Soil 292:305–315
Bateman A, Bycroft M (2000) The structure of a LysM domain from E. coli membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D (MltD). J Mol Biol 299(4):1113–1119
Beier S, Bertilsson S (2013) Bacterial chitin degradation - mechanisms and ecophysiological strategies. Front Microbiol 4:149
Berger LR, Reynolds DM (1958) The chitinase system of a strain of Streptomyces griseus. Biochim Biophys Acta 29(3):522–534
Bhattacharya D, Nagpure A, Gupta RK (2007) Bacterial chitinase: properties and potential. Crit Rev Biotechnol 27:21–28
Bird AF, Mcclure MA (1976) The tylenchid (Nematoda) egg shell: structure, composition and permeability. Parasitology 72:19–28
Blom J, Rueckert C, Niu B, Wang Q, Borriss R (2012) The complete genome of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum CAU B946 contains a gene cluster for nonribosomal synthesis of iturin A. J Bacteriol 194(7):1845–1846
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Buist G, Steen A, Kok J, Kuipers OP (2008) LysM, a widely distributed protein motif for binding to (peptido)glycans. Mol Microbiol 68:838–847
Cai XC, Liu CH, Wang BT, Xue YR (2017) Genomic and metabolic traits endow Bacillus velezensis CC09 with a potential biocontrol agent in control of wheat powdery mildew disease. Microbiol Res 196:89–94
Chaplin AK, Wilson MT, Hough MA, Svistunenko DA, Hemsworth GR, Walton PH, Vijgenboom E, Worrall JA (2016) Heterogeneity in the histidine-brace copper coordination sphere in auxiliary activity family 10 (AA10) lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases. J Biol Chem 291:12838–12850
Chen Q, Peng D (2019) Nematode chitin and application. Adv Exp Med Biol 1142:209–219
Chen XH, Koumoutsi A, Scholz R, Eisenreich A, Schneider K, Heinemeyer I, Morgenstern B, Voss B, Hess WR, Reva O et al (2007) Comparative analysis of the complete genome sequence of the plant growth–promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Nat Biotechnol 25:1007–1014
Chen Y, Fukuoka S, Makino S (2000) A novel spore peptidoglycan hydrolase of Bacillus cereus: biochemical characterization and nucleotide sequence of the corresponding gene, sleL. J Bacteriol 182(6):1499–1506
Clarke AJ, Cox PM, Shepherd AM (1967) Chemical composition of egg shells of potato cyst nematode Heterodera rostochiensis Woll. Biochem J 104:1056–1060
Djian-Caporalino C, Fazari A, Arguel MJ, Vernie T, VandeCasteele C, Faure I, Brunoud G, Pijarowski L, Palloix A (2007) Root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.) Me resistance genes in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) are clustered on the P9 chromosome. Theor Appl Genet 114:473–486
Fanelli E, Di Vito M, Jones JT, De Giorgi C (2005) Analysis of chitin synthase function in a plant parasitic nematode, Meloidogyne artiellia, using RNAi. Gene 349:87–95
Forsberg Z, Nelson CE, Dalhus B, Mekasha S, Loose JS, Crouch LI, Røhr ÅK, Gardner JG, Eijsink VG, Vaaje-Kolstad G (2016) Structural and functional analysis of a lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase important for efficient utilization of chitin in Cellvibrio japonicus. J Biol Chem 291:7300–7312
Fujita K, Shimomura K, Yamamoto K, Yamashita T, Suzuki K (2006) A chitinase structurally related to the glycoside hydrolase family 48 is indispensable for the hormonally induced diapause termination in a beetle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345:502–507
Gu Q, Yang Y, Yuan Q, Shi G, Wu L, Lou Z, Huo R, Wu H, Borriss R, Gao X (2017) Bacillomycin D produced by Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens is involved in the antagonistic interaction with the plant-pathogenic fungus Fusarium Graminearum. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e01075-e1117
Gutiérrez-Román MI, Dunn MF, Tinoco-Valencia R, Holguín-Meléndez F, Huerta-Palacios G, Guillén-Navarro K (2014) Potentiation of the synergistic activities of chitinases ChiA, ChiB and ChiC from Serratia marcescens CFFSUR-B2 by chitobiase (Chb) and chitin binding protein (CBP). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:33–42
Hahn M, Hennig M, Schlesier B, Hohne W (2000) Structure of jack bean chitinase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 56:1096–1099
Hart PJ, Pfluger HD, Monzingo AF, Hollis T, Robertus JD (1995) The refined crystal structure of an endochitinase from Hordeum vulgare L. seeds at 1.8 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 248:402–413
Henrissat B (1991) A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 280:309–316
Henrissat B, Bairoch A (1993) New families in the classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 293:781–788
Huang L, Garbulewska E, Sato K, Kato Y, Nogawa M, Taguchi G, Shimosaka M (2012a) Isolation of genes coding for chitin-degrading enzymes in the novel chitinolytic bacterium, Chitiniphilus shinanonensis, and characterization of a gene coding for a family 19 chitinase. J Biosci Bioeng 113:293–299
Huang L, Shizume A, Nogawa M, Taguchi G, Shimosaka M (2012b) Heterologous expression and functional characterization of a novel chitinase from the chitinolytic bacterium Chitiniphilus shinanonensis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:517–522
Hult EL, Katouno F, Uchiyama T, Watanabe T, Sugiyama J (2005) Molecular directionality in crystalline β-chitin: hydrolysis by chitinases A and B from Serratia marcescens 2170. Biochem J 388:851–856
Imoto T, Yagishita K (1971) A simple activity measurement of lysozyme. Agric Biol Chem 35:1154–1156
Inamine S, Onaga S, Ohnuma T, Fukamizo T, Taira T (2015) Purification, cDNA cloning, and characterization of LysM-containing plant chitinase from horsetail (Equisetum arvense). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 79:1296–1304
Itoh T, Sugimoto I, Hibi T, Suzuki F, Matsuo K, Fujii Y, Taketo A, Kimoto H (2014) Overexpression, purification, and characterization of Paenibacillus cell surface-expressed chitinase ChiW with two catalytic domains. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 78:624–634
Jung WJ, Jung SJ, An KN, Jin YL, Park RD, Kim YK, Shon BK, Kim TH (2002) Effect of chitinase-producing Paenibacillus illinoisensis KJA-424 on egg hatching of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita). J Microbiol Biotechnol 12:865–871
Katouno F, Taguchi M, Sakurai K, Uchiyama T, Nikaidou N, Nonaka T, Sugiyama J, Watanabe T (2004) Importance of exposed aromatic residues in Chitinase B from Serratia marcescens 2170 for crystalline chitin hydrolysis. J Biochem 168:163–168
Kawase T, Yokokawa S, Saito A, Fujii T, Nikaidou N, Miyashita K, Watanabe T (2006) Comparison of enzymatic and antifungal properties between family 18 and 19 chitinases from S. coelicolor A3(2). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:988–998
Khan Z, Kim S, Jeon Y, Khan H, Son S, Kim Y (2008) A plant growth promoting rhizobacterium, Paenibacillus polymyxa strain GBR-1, suppresses root-knot nematode. Bioresour Technol 99:3016–3023
Kobayashi DY, Reedy RM, Bick J, Oudemans PV (2002) Characterization of a chitinase gene from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain 34S1 and its involvement in biological control. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1047–1054
Koumoutsi A, Chen X, Henne A, Liesegang H, Hitzeroth G, Franke P, Vater J, Borriss R (2004) Structural and functional characterization of gene clusters directing nonribosomal synthesis of bioactive cyclic lipopeptides in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain FZB42. J Bacteriol 186(4):1084–1096
Krober M, Verwaaijen B, Wibberg D, Winkler A, Pühler A, Schlüter A (2016) Comparative transcriptome analysis of the biocontrol strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 as response to biofilm formation analyzed by RNA sequencing. J Biotechnol 10:212–223
Kurze S, Bahl H, Dahl R, Berg G (2001) Biological control of fungal strawberry diseases by Serratia plymuthica HRO-C48. Plant Dis 85:529–534
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lee YS, Kim KY (2015) Statistical optimization of medium components for chitinase production by Pseudomonas fluorescens strain HN1205: role of chitinase on egg hatching inhibition of root-knot nematode. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 29(3):470–478
Lee YS, Anees M, Park YS, Kim SB, Jung WJ, Kim KY (2014) Purification and properties of a Meloidogyne-antagonistic chitinase from Lysobacter capsici YS1215. Nematology 16:63–72
Lee YS, Nguyen XH, Naing KW, Park YS, Kim KY (2015) Role of lytic enzymes secreted by Lysobacter capsici YS1215 in the control of root-knot nematode of tomato plants. Indian J Microbiol 55(1):74–80
Levasseur A, Drula E, Lombard V, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (2013) Expansion of the enzymatic repertoire of the CAZy database to integrate auxiliary redox enzymes. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:41
Lim SM, Yoon MY, Choi GJ, Choi YH, Jang KS, Shin TS, Park HW, Yu NH, Kim YH, Kim JC (2017) Diffusible and volatile antifungal compounds produced by an antagonistic Bacillus velezensis G341 against various phytopathogenic fungi. Plant Pathol J 33:488–498
Mehmood MA, Xiao X, Hafeez FY, Gai Y, Wang F (2009) Purification and characterization of a chitinase from Serratia proteamaculans. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1955–1961
Nguyen SD, Trinh THT, Tran TD, Nguyen TV, Chuyen HV, Ngo VA, Nguyen AD (2021) Combined application of rhizosphere bacteria with endophytic bacteria suppresses root diseases and increases productivity of black pepper (Piper nigrum L.). Agriculture 11:1–5
Nguyen VB, Wang SL, Nguyen TH, Nguyen TH, Trinh THT, Nong TT, Nguyen TU, Nguyen VN, Nguyen AD (2019) Reclamation of rhizobacteria newly isolated from black pepper plant roots as potential biocontrol agents of root-knot nematodes. Res Chem Intermed 45:5293–5307
Ohno T, Armand S, Hata T, Nikaidou N, Henrissat B, Mitsutomi M, Watanabe T (1996) A modular family 19 chitinase found in the prokaryotic organism Streptomyces griseus HUT 6037. J Bacteriol 178:5065–5070
Onaga S, Tiara T (2008) A new type of plant chitinase containing LysM domains from a fern (Pteris ryukyuensis): roles of LysM domains in chitin binding and antifungal activity. Glycobiology 18:414–423
Pentekhina I, Hattori T, Tran DM, Shima M, Watanabe T, Sugimoto H, Suzuki K (2020) Chitinase system of Aeromonas salmonicida, and characterization of enzymes involved in chitin degradation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 84:1347–6947
Perrakis A, Tews I, Dauter Z, Oppenheim AB, Chet I, Wilson KS, Vorgias CE (1994) Crystal structure of a bacterial chitinase at 2.3 Å resolution. Structure 2:1169–1180
Purushotham P, Arun PV, Prakash JS, Podile AR (2012) Chitin binding proteins act synergistically with chitinases in Serratia proteamaculans 568. PLoS One 7:e36714
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Scholz R, Vater J, Budiharjo A, Wang Z, He Y, Dietel K, Schwecke T, Herfort S, Lasch P, Borriss R (2014) Amylocyclicin, a novel circular bacteriocin produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J Bacteriol 196:1842–1852
Seidl-Seiboth V, Zach S, Frischmann A, Spadiut O, Dietzsch C, Herwig C, Ruth C, Rodler A, Jungbauer A, Kubicek CP (2013) Spore germination of Trichoderma atroviride is inhibited by its LysM protein TAL6. FEBS J 280:1226–1236
Suzuki K, Sugawara N, Suzuki M, Uchiyama T, Katouno F, Nikaidou N, Watanabe T (2002) Chitinases A, B, and C1 of Serratia marcescens 2170 produced by recombinant Escherichia coli: enzymatic properties and synergism on chitin degradation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:1075–1083
Suzuki K, Suzuki M, Taiyoji M, Nikaidou N, Watanabe T (1998) Chitin binding protein (CBP21) in the culture supernatant of Serratia marcescens 2170. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:128–135
Suzuki K, Taiyoji M, Sugawara N, Nikaidou N, Henrissat B, Watanabe T (1999) The third chitinase gene (chiC) of Serratia marcescens 2170 and the relationship of its product to other bacterial chitinases. Biochem J 343:587–596
Synowiecki J, Al-Khateeb NA (2003) Production, properties, and some new applications of chitin and its derivatives. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 43(2):145–1471
Takashima T, Sunagawa R, Uechi K, Taira T (2020) Antifungal activities of LysM-domain multimers and their fusion chitinases. Int J Biol Macromol 154:1295–1302
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tran DM, Sugimoto H, Nguyen DA, Watanabe T, Suzuki K (2018) Identification and characterization of chitinolytic bacteria isolated from a freshwater lake. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82:343–355
Tran TPH, Wang SL, Nguyen VB, Tran DM, Nguyen DS, Nguyen AD (2019) Study of novel endophytic bacteria for biocontrol of black pepper root-knot nematodes in the central highlands of Vietnam. Agronomy 9:714
Trinh THT, Wang SL, Nguyen VB, Tran DM, Doan CT, Vo TPK, Que VH, Nguyen AD (2019) A potent antifungal rhizobacteria Bacillus velezensis isolated from black pepper. Res Chem Intermed 45:5309–5323
Tsujibo H, Okamoto T, Hatano N, Miyamoto K, Watanabe T, Mitsutomi M, Inamori Y (2000) Family 19 chitinases from Streptomyces thermoviolaceus OPC-520: molecular cloning and characterization. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:2445–2453
Uchiyama T, Katouno F, Nikaidou N, Nonaka T, Sugiyama J, Watanabe T (2001) Roles of the exposed aromatic residues in crystalline chitin hydrolysis by chitinase A from Serratia marcescens 2170. J Biol Chem 276:41343–41349
Ueda M, Ohata K, Konishi T, Sutrisno A, Okada H, Nakazawa M, Miyatake K (2009) A novel goose-type lysozyme gene with chitinolytic activity from the moderately thermophilic bacterium Ralstonia sp. A-471: cloning, sequencing, and expression. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:1077–1085
Umarov RK, Solovyev VV (2017) Recognition of prokaryotic and eukaryotic promoters using convolutional deep learning neural networks. PLoS One 12(2):e0171410
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Horn SJ, van Aalten DM, Synstad B, Eijsink VG (2010) An oxidative enzyme boosting the enzymatic conversion of recalcitrant polysaccharides. Science 330:219–222
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Horn SJ, van Aalten DM, Synstad B, Eijsink VG (2005a) The non-catalytic chitin-binding protein CBP21 from Serratia marcescens is essential for chitin degradation. J Biol Chem 280:28492–28497
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Houston DR, Riemen AH, Eijsink VG, van Aalten DM (2005b) Crystal structure and binding properties of the Serratia marcescens chitin-binding protein CBP21. J Biol Chem 280:11313–11319
van Aalten DM, Synstad B, Brurberg MB, Hough E, Riise BW, Eijsink VG, Wierenga RK (2000) Structure of a two-domain chitotriosidase from Serratia marcescens at 1.9-Å resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5842–5847
Watanabe T, Ariga Y, Sato U, Toratani T, Hashimoto M, Nikaidou N, Kezuka Y, Nonaka T, Sugiyama J (2003) Aromatic residues within the substrate-binding cleft of Bacillus circulans chitinase A1 are essential for hydrolysis of crystalline chitin. Biochem J 376:237–244
Watanabe T, Kanai R, Kawase T, Tanabe T, Mitsutomi M, Sakuda S, Miyashita K (1999) Family 19 chitinases of Streptomyces species: characterization and distribution. Microbiology 145:3353–3363
Watanabe T, Kimura K, Sumiya T, Nikaidou N, Suzuki K, Suzuki M, Taiyoji M, Ferrer S, Regue M (1997) Genetic analysis of the chitinase system of Serratia marcescens 2170. J Bacteriol 179:7111–7117
Watanabe T, Kobori K, Miyashita K, Fujii T, Sakai H, Uchida M, Tanaka H (1993) Identification of glutamic acid 204 and aspartic acid 200 in chitinase A1 of Bacillus circulans WL-12 as essential residues for chitinase activity. J Biol Chem 268:18567–18572
Watanabe T, Oyanagi W, Suzuki K, Tanaka H (1990) Chitinase system of Bacillus circulans WL-12 and importance of chitinase A1 in chitin degradation. J Bacteriol 172:4017–4022
Wu L, Wu H, Chen L, Xie S, Zang H, Borriss R, Gao X (2014) Bacilysin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 has specific bactericidal activity against harmful algal bloom species. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:7512–7520
Wu L, Wu H, Chen L, Yu X, Borriss R, Gao X (2015) Difficidin and bacilysin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 have antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae rice pathogens. Sci Rep 5:12975
Yu C, Bassler BL, Roseman S (1993) Chemotaxis of the marine bacterium Vibrio furnissii to sugars. a potential mechanism for initiating the chitin catabolic cascade. J Biol Chem 268:9405–9409
Zhang Y, Foster JM, Nelson LS, Ma D, Carlow CK (2005) The chitin synthase genes chs-1 and chs-2 are essential for C. elegans development and responsible for chitin deposition in the eggshell and pharynx, respectively. Dev Biol 285(2):330–339
Zuckerkandl E, Pauling L (1965) Evolutionary divergence and convergence in proteins. Edited in Evolving Genes and Proteins by Bryson V and Vogel HJ, Academic Press, New York, pp 97–166
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Ministry of Education and Training under grant number B2020-TTN-04. The authors wish to thank Dr. Ngoc Luong Nguyen (School of Science, Hue University) for his generous sharing of the pColdII vector (Takara, Japan) and E. coli BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-RIPL cells (Agilent, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DMT conceived the study, designed the experiments, analyzed, and wrote the manuscript. DMT, TUH, THN, TOD, QVN, and ADN performed experiments. ADN involved in the interpretation of the data and critical reading of the draft. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors reported no potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, D.M., Huynh, T.U., Nguyen, T.H. et al. Molecular analysis of genes involved in chitin degradation from the chitinolytic bacterium Bacillus velezensis. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 115, 215–231 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01697-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01697-2