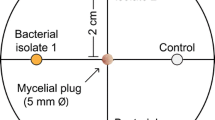
Abstract
Five hundred strains of rhizobacteria were isolated from the rhizosphere of the Central Highlands of Vietnam, where black pepper is cultivated. Of these, seven potent rhizobacteria were evaluated for anti-Phytophthora activity and 16S rRNA gene sequencing and phylogenic analysis classified. Evaluation of their antifungal activity was performed both in vitro and in vivo. The results showed that almost all potent rhizobacteria possessed anti-Phytophthora activity. The rhizobacteria strains displayed over 60% inhibition of Phytophthora during the in vitro test, and six rhizobacteria inhibited Phytophthora by 77.50–98.75% during the in vivo test. Enzymatic activities were measured to determine the antifungal mechanisms; these were identified as protease, chitinase, and β-glucanase. The effects of the rhizobacteria on plant growth and antifungal activity were also investigated. Under greenhouse conditions, black pepper seedlings treated with rhizobacteria were stronger and had lower rates of disease and fatality compared to the control group. The results from the in vitro test also showed that the anti-Phytophthora activity of the rhizobacteria was not dependent on enzyme activity, but rather on their chemical compounds. GC–MS and LC–MS profiles of the culture broth from the promising rhizobacteria strain RBDS.29 revealed seven potent antifungal compounds. The data suggest that Bacillus velezensis RB.DS29 is a promising rhizobacterium that promotes plant growth and the biocontrol of black pepper.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Nakkeeran, K. Kavitha, G. Chandrasekar, P. Renukadevi, W.G.D. Fernando, Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 16, 403 (2006)
F. Ahmad, I. Ahmad, M.S. Khan, Microbiol. Res. 163, 173 (2008)
P.C. Trivedi, in Bacteria in Agrobiology: Disease Management, ed. by D.K. Maheshwari (Springer, Berlin, 2013), p. 349
K.N. Anith, K.M. Faseela, P.A. Archana, K.D. Prathapan, Symbiosis 55, 11 (2011)
B. Lugtenberg, F. Kamilova, Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 63, 541 (2009)
K.N. Anith, N.V. Radhakrishnan, T.P. Manomohandas, Microbiol. Res. 158, 91 (2003)
S. Dastager, D. Kumaran, A. Pandey, Biology 6, 801 (2011)
S.S.K.P. Vurukonda, S. Vardharajula, M. Shrivastava, A. Skz, Microbiol. Res. 184, 13 (2016)
E. Ngumbi, J. Kloepper, Appl. Soil. Ecol. 105, 109 (2016)
F.F. Da Mota, E.A. Gomes, L. Seldin, J. Microbiol. 56, 75 (2008)
L.J. White, V.S. Brözel, S. Subramanian, Bio-Protocol 5, 16 (2015)
M.D. Tran, H. Sugimoto, D.A. Nguyen, T. Watanabe, K. Suzuki, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 82, 1 (2018)
K. Tamura, G. Stecher, D. Peterson, A. Fillipski, S. Kumar, Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 2725 (2013)
M.A. Larkin, G. Blackshields, N.P. Brown, Bioinformatics 23, 2947 (2007)
T. Imoto, K. Yagishita, Agric. Biol. Chem. 35, 1154 (1971)
G.L. Miller, Anal. Chem. 31, 426 (1959)
M.L. Anson, J. Gen. Physiol. 22, 79 (1938)
A. Dinu, A. Kumar, R. Aravind, S.J. Eapen, J. Spices Aromat. Crops 16, 1 (2007)
S.M. Lim, M.Y. Yoon, G.J. Choi, Y.H. Choi, K.S. Jang, T.S. Shin, H.W. Park, N.H. Yu, Y.H. Kim, J.C. Kim, Plant Pathol. J. 33, 488 (2017)
R. Aravind, A. Kumar, S.J. Eapen, K.V. Ramana, Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 48, 58 (2009)
N. Sheoran, A.V. Nadakkakath, V. Munjal, A. Kundu, K. Subaharan, A. Venugopal, S. Rajamma, S.J. Eapen, A. Kumar, Microbiol. Res. 173, 66 (2015)
S.C. Toh, S. Lihan, A.S.A.H. Awang, Int. Food Res. J. 23, 2616 (2016)
Q. Jamal, Y.S. Lee, H.D. Jeon, K.Y. Kim, Plant Protect. Sci. 54, 129 (2018)
M. Krober, B. Verwaaijen, D. Wibberg, A. Winkler, A. Pühler, A. Schlüter, J. Biotechnol. 231, 212 (2016)
B. Fan, J. Blom, H.P. Klenk, R. Borris, Front. Microbiol. 8, 22 (2017)
R. Scholz, J. Vater, A. Budiharjo, Z. Wang, Y. He, K. Dietel, T. Schwecke, S. Herfort, P. Lasch, R. Borriss, J. Bacteriol. 196, 1842 (2014)
L.M. Wu, H.J. Wu, L. Chen, X. Yu, R. Borriss, X. Gao, Sci. Rep. 5, 12975 (2015)
Q. Gu, Y. Yang, Q. Yuan, G. Shi, L. Wu, Z. Lou, R. Huo, H. Wu, R. Borriss, X. Gao, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 83, e01075 (2017)
J.M. Palazzini, C.A. Dunlap, M.J. Bowman, S.N. Chulze, Microbiol. Res. 192, 30 (2016)
X.C. Cai, C.H. Liu, B.T. Wang, Y.R. Xue, Microbiol. Res. 196, 89 (2017)
C. Moon, D.J. Seo, Y.S. Song, S.H. Hong, S.H. Choi, W.J. Jung, Microb. Pathog. 113, 218 (2017)
S.H. Hong, Y.S. Song, D.J. Seo, W.J. Jung, Microb. Pathog. 110, 159 (2017)
C.T. Doan, N.T. Tran, M.T. Nguyen, V.B. Nguyen, A.D. Nguyen, S.L. Wang, Molecules 24, 691 (2017)
C.L. Wang, J.W. Su, T.W. Liang, A.D. Nguyen, S.L. Wang, Res. Chem. Intermed. 40, 2237 (2014)
C.L. Wang, C.J. Chen, A.D. Nguyen, T.W. Liang, Y.K. Twu, S.Y. Huang, S.L. Wang, Res. Chem. Intermed. 40, 2363 (2014)
C.T. Doan, T.N. Tran, V.B. Nguyen, T.P.K. Vo, A.D. Nguyen, S.L. Wang, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 131, 706 (2019)
S.L. Wang, I.L. Shih, T.W. Liang, C.H. Wang, J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 2241 (2002)
T.N. Tran, C.T. Doan, V.B. Nguyen, A.D. Nguyen, S.L. Wang, Res. Chem. Intermed. 45, 727 (2018)
V. Blattel, M. Larisika, P. Pfeiffer, C. Nowak, A. Eich, J. Eckelt, H. König, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 983 (2011)
Y. Chen, H. Xu, M. Zhou, Y. Wang, S. Wang, J. Zhang, PLoS ONE 10, e0134799 (2015)
G.L. Backes, D.M. Neumann, B.S. Jursic, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 22, 4629 (2014)
Ł. Popiołek, A. Biernasiuk, A. Malm, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 53, 1589 (2015)
A.S.O. Mohareb, I.E.A. Kherallah, M.E.I. Badawy, M.Z.M. Salem, H.A. Yousef, J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 3, 331 (2017)
C.S.C. Kumar, L.Y. Then, T.S. Chia, S. Chandraju, Y.F. Win, S.F. Sulaiman, N.S. Hashim, K.L. Ooi, C.K. Quah, H.K. Fun, Molecules 20, 16566 (2015)
T. Mouri, T. Yano, S. Kochi, T. Ando, M. Hori, J. Pestic. Sci. 30, 209 (2005)
Acknowledgements
Authors are expressed to thank Ministry of Education and Training, Vietnam granted the Science and Technology program: Application of Biotechnology for sustainable black pepper production in the Central highland. B 2017–2019. This work was also supported in part by a grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (MOST 106-2320-B-032-001-MY3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ADN conceived the study. ADN, HTT, and VBN designed and performed the study. AND and S-LW contributed the reagents/materials/analysis tools. QVH, CTD, VBN, and PKV analyzed the data. AND and S-LW wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trinh, T.H.T., Wang, SL., Nguyen, V.B. et al. A potent antifungal rhizobacteria Bacillus velezensis RB.DS29 isolated from black pepper (Piper nigrum L.). Res Chem Intermed 45, 5309–5323 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03971-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03971-5