Abstract
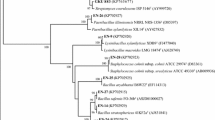
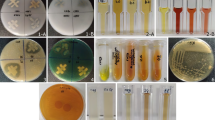
Few studies have evaluated endophytic bacteria in relation to plant growth promotion, nitrogen uptake and biological control. The aim of this study was to molecularly and physiologically characterize thirteen endophytic bacteria strains, evaluate their biological control properties and their ability to promote plant growth and plant N nutrition. All the strains produced indole acetic acid and promoted increase of plant biomass, N accumulative amount and N-use efficiency index. None of the strains carries the nifH gene. Four strains stimulated plant nitrate reductase activity, four solubilized phosphate, nine produced siderophores and none produced HCN. Seven strains inhibited Bipolaris sacchari growth and one was antagonistic to Ceratocystis paradoxa. The pathogens were inhibited by the production of diffusible and volatile metabolites by the bacterial strains. Moreover, this is the first study to demonstrate the effect of Delftia acidovorans on sugarcane plant growth, nitrogen metabolism improvement and antagonism to B. sacchari. The most efficient strains in promoting plant growth and exhibiting antagonistic activities towards fungal pathogens were Herbaspirillum frinsingense (IAC-BECa-152) and three Pantoea dispersa strains (IAC-BECa-128, IAC-BECa-129, and IAC-BECa-132). These bacteria show potential to be used as inoculants for sustainable agricultural management, mainly at the seedling production phase.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adesemoye AO, Yuen G, Watts DB (2017) Microbial inoculants for optimized plant nutrient use in integrated pest and input management systems. In: Kumar V, Kumar M, Sharma S, Prasad R (eds) Probiotics and plant health. Springer, Singapore
Ahmed I, Ehsan M, Sin Y, Paek J, Khalid N, Hayat R, Chang YH (2014) Sphingobacterium pakistanensis sp. nov., a novel plant growth promoting rhizobacteria isolated from rhizosphere of Vigna mungo. A van Leeuw 105:325–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-0077-0
Alves GC, Videira SS, Urquiaga S, Reis VM (2015) Differential plant growth promotion and nitrogen fixation in two genotypes of maize by several Herbaspirillum inoculants. Plant Soil 387:307–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2295
Bach E, Seger GDS, Fernandes GC et al (2016) Evaluation of biological control and rhizosphere competence of plant growth promoting bacteria. Appl Soil Ecol 99:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.11.002
Bailly A, Groenhagen U, Schulz S, Geisler M, Eberl M, Weisskopf L (2014) The inter-kingdom volatile signal indole promotes rootdevelopment by interfering with auxin signaling. Plant J 80:758–771. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12666
Bakker AW, Schippers B (1987) Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas spp.: mediated plant growth-stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:451–457
Barretti PB, Souza RM, Pozza EA (2008) Bactérias endofíticas como agentes promotores do crescimento de plantas de tomateiro e de inibição in vitro de Ralstonia solanacearum. Ciênc Agrotec 32:731–739
Bonaldi M, Chen X, Kumova A, Pizzatti C, Saracchi M, Cortesi P (2015) Colonization of lettuce rhizosphere and roots by tagged Streptomyces. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00025
Bournival BL, Ginoza HS, Schenck S, Moore PH (1994) Characterization of sugarcane response to Bipolaris sacchari: inoculations and host-specific HS-toxin. Phytopathology 84:672–676
Bremner JM (1965) Total nitrogen. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 1149–1178
Cabanás CGL, SchiliròE V-CA, Mercado-Blanco J (2014) The biocontrol endophytic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens PICF7 induces systemic defense responses in aerial tissues upon colonization of olive roots. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00427
Carvalho AV, Alves BJR, Reis VM (2006) Resposta do dendezeiro à adição de nitrogênio e sua influência na população de bactérias diazotróficas. Pesq Agrop Brasileira 41:293–300
Cavalcante VS, Döbereiner J (1988) A new acid tolerant nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with sugarcane. Plant Soil 10:823–831
Cherif-Silini H, Silini A, Yahiaoui H, Ouzari I, Boudabous A (2016) A phylogenetic and plant-growth-promoting characteristics of Bacillus isolated from the wheat rhizosphere. Ann Microbiol 66:1087–1097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-016-1194
Cipriano MAP, Freitas SS (2018) Effect of Pseudomonas putida on chrysanthemum growth under greenhouse and field conditions. Afr J Agric Res 13:302–310
Cipriano MAP, Lupatini M, Lopes-Santos L et al (2016) Lettuce and rhizosphere microbiome responses to growth promoting Pseudomonas species under field conditions. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiw197
Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clement C, Barka EA (2005) Use of plant growth-promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4951–4959
Conrath U, Beckers GJ, Flors V, García-Agustín P, Jakab G, Mauch F, Newman MA, Pieterse CM, Poinssot B, Pozo MJ et al (2006) Priming: getting ready for battle. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:1062–1071
Dhole A, Shelat H, Vyas R, Jhala Y, Bhange M (2016) Endophytic occupation of legume root nodules by nifH-positive non-rhizobial bacteria, and their efficacy in the groundnut (Arachshypogaea). Ann Microbiol 66:1397
Dick CM, Hutchinson SA (1966) Biological activity of volatile fungal metabolites. Nature 211:868
Ding T, Melcher U (2016) Influences of plant species, season and location on leaf endophytic bacterial communities of non-cultivated plants. PLoS ONE 11(3):0150895. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150895
Döbereiner J, Baldani VLD, Baldani JI (1995) Como isolar e identificar bactérias diazotróficas de plantas não-leguminosas. Embrapa-SPI, Brasília, p p60
Donato VMTS, Andrade AG, Douza ES, França JGE, Maciel GA (2004) Atividade enzimática em variedades de cana-de-açúcar cultivadas in vitro sob diferentes níveis de nitrogênio. PesqAgrop Bras 39:1087–1093
Dong Z, Heydrich M, Bernard K, McCully ME (1995) Further evidence that the N2-fixing endophytic bacterium from theintercellular spaces of sugarcane stems is Acetobacter diazotrophicus. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(5):1843–1846
Duca D, Lorv J, Patten C, Rose D, Glick B (2014) Microbial indole-3-acetic acid and plant growth. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek 106:85–125
Eljounaidi K, Lee SY, Bae H (2016) Bacterial endophytes as potential biocontrol agents of vascular wilt diseases: review and future prospects. Biol Control 103:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.07.013
Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl MC, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using Phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genom Res 8:175–185
Fávaro LCL, Sebastianes FLDS, Araújo WL (2012) Epicoccum nigrum P16, a sugarcane endophyte, produces antifungal compounds and induces root growth. PLoS ONE 7(6):e36826. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036826
Finkel OM, Castrillo G, Paredes SH, Gonzaléz IS, Dangl JL (2018) Understanding and exploiting plant beneficial microbes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 38:155–163
Freitas RP (2011) Bactérias diazotróficas endofíticas associadas à cana-de-açúcar. Dissertation, Instituto Agronômico de Campinas
Gibbs JN (1967) A study of the epiphytic growth habit of Fomes annosus. Ann Bot 32:755–774
Girard JC, Rott P (2000) Pineaple disease. In: Rott P, Bailey RA, Comstock JC, Croft BJ, Saumtally AS (eds) A guide to sugarcane diseases. CIRAD-ISSCT, Montpellier, pp 131–135
Glick BR (2014) Bacteria with ACC deaminase can promote plant growth and help to feed the world. Microbiol Res 169:30–39
Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P (1998) Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genom Res 8:195–202
Hardoim PR, van Overbeek LS, Berg G, Pirttilä CS, Campisano A, Dörin M, Sessitch A (2015) The gidden world within plants: ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 79:293–320
Hernández-León R, Rojas-Solís D, Contreras-Pérez M, Orozco-Mosqueda MC, Macías-Rodríguez LI, Cruz HR, Valencia-Cantero E, Santoyo G (2015) Characterization of the antifungal and plant growth-promoting effects of diffusible and volatile organic compounds produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens strains. Biol Control 81:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2014.11.011
James Ek, Olivares FL, de Oliveira AL, dos Reis FB Jr., da Silva LG, Reis VM (2001) Further observations on the interaction between sugar cane and Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus under laboratory and greenhouse conditions. J Exp Bot 52:747–760
Katznelson H, Bose B (1959) Metabolic activity and phosphate dissolving capability of bacterial isolates from wheat roots, rhizosphere, and non rhizosphere soil. Can J Microb 5:79–85
Khalaf EM, Raizada MN (2018) Bacterial seed endophytes of domesticated cucurbits antagonize fungal and oomycete pathogens including powdery mildew. Front Microbiol 9:42
Kielak AM, Cipriano MAP, Kuramae EE (2016) Acidobacteria strains from subdivision 1 act as plant growth-promoting bacteria. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1260-2
Kirhhof G, Eckert B, Stoffels M, Baldani JI, Veronica MR, Hartmann A (2001) Herbaspirillum frisingense sp. nov., a new nitrogen-fixing bacterial species that occurs in C4-fibre plants. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:157–168
Kojima K (1996) Changes of absicic acid, indole-3-acetic acid and gibberellin-like substances in flowers and developing fruits of citrus cultivar Hyaganatsu. Sci Hortic 65:901–902
Kröber M, Wibberg D, Grosch R (2014) Effect of the strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciensFZB42 on the microbial community in the rhizosphere of lettuce under field conditions analyzed by whole metagenome sequencing. Front Microbiol 5:252. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00252
Kruasuwan W, Thamchaipenet A (2016) Diversity of culturable plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes associated with sugarcane roots and their effect of growth by co-inoculation of diazotrophs and actinomycetes. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9604-3
Kumar M, Grader G, Sessitsch A, Mäki A, van Elsas JD, Nissien R (2017) Plants assemble species specific bacterial communities from common core taxa in three arcto-alpine climate zones. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00012
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randal RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mantelin S, Touraine B (2004) Plant growth-promoting bacteria and nitrate availability: impacts on root development and nitrate uptake. J Exp Bot 55:27–34
Marcos FCC, Iório RPF, Silveira APD, Ribeiro RV, Machado EC, Lagôa AMA (2016) Endophytic bacteria affect sugarcane physiology without changing plant growth. Bragantia 75:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4499.256
Marques JRRBM, Canellas LP, Silva LGO (2008) Promoção de enraizamento de microtoletes de cana-de-açúcar pelo uso conjunto de substâncias húmicas e de bactérias diazotróficas endofíticas. Rev Bras Ciência Solo 32:1121–1128
Meena VS, Meena SK, Verma JP, Kumar A, Aeron A, Mishra PK, Bisht JK, Pattanayak A, Naveed M, Dotaniya ML (2017) Plant beneficial rhizospheric microorganism (PBRM) strategies to improve nutrients use efficiency: a review. Ecol Eng 107:8–32
Mehnaz S, Baig DN, Lazarovits G (2010) Genetic and phenotypic diversity of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria isolated from sugarcane plants growing in Pakistan. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:1614–1623
Mendes R, Pizzinari-Kleiner AA, Araujo WL, Raaijmakers JM (2007) Diversity of cultivated endophytic bacteria from sugarcane: genetic and biochemical characterization of Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01222-07
Murashige T, Skogg FA (1962) Revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:397–473
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chem Acta 27:31–36
Nautiyal CS (1999) An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 170:265–270
Olanrewaju O, Glick BR, Babalola OO (2017) Mechanisms of action of plant growth promoting bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2364-9
Oliveira AL, Canuto EL, Urquiaga AL, Reis AL, Baldani JI (2006) Yield of micropropagated sugarcane varieties in different soil types following inoculation with diazotrophic bacteria. Plant Soil 284:23–32
Pandey PK, Mayanglambam CS, Sungh S, Sing AK, Kumar M, Pathak M, Shakywar BC, Pandey AK (2017) Inside the plants: endophytic bacteria and their functional attributes for plant growth promotion. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 6:11–21
Patel DH, Naik JH, Amaresan N (2017) Synergistic effect of root-associated bacteria on plant growth and certain physiological parameters of banana plant (Musa acuminate). Arch Agron Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1410703
Patten CL, Glick BR (2002) Role of Pseudomonas putida indoleacetic acid in development of the host plant root system. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3795–3801. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.68.8.3795-3801
Pittol M, Durso L, Valiati VH, Fiuza LM (2016) Agronomic and environmental aspects of diazotrophic bacteria in rice fields. Ann Microbiol 66:511–527
Prasannakumar SP, Gowtham HG, Hariprasad P (2015) Delftia tsuruhatensis WGR-UOM-BT1, a novel rhizobacterium woth PGPR properties from Rauwolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. Ex Kurz supressess fungal phytopathogens by producing a new antibiotic-AMTM. Lett Appl Microbiol 61:460–468
Quecine MC, Araújo WL, Rossetto PB, Ferreira A, Tsui S, Lacava PT, Mondin M, Azevedo JL, Pizzirani-Kleinera AA (2012) Sugarcane growth promotion by the endophytic bacterium Pantoea agglomerans 33.1. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:7511–7518
Rafikova GF, Korshunova TY, Minnebaev LF, Chetverikov SP, Loginov ON (2016) A new bacterial strain, Pseudomonas koreensis IB-4, as a promising agent for plant pathogen biological control. Microbiology 85:333–341
Rampazzo PE, Marcos FCC, Cipriano MAP, Marchiori PER, Freitas SS, Machado EC, Nascimento LC, Brocchi M, Ribeiro RV (2018) Rhizobacteria improve sugarcane growth and photosynthesis under well-watered conditions. Ann Appl Biol 172:309
Rashid S, Charles TC, Glick BR (2012) Isolation and characterization of new plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Appl Soil Ecol 61:217–224
Reed AJ, Below FE, Hageman RH (1980) Grain protein accumulation and the relationship between leaf nitrate reductase and proteases activities during grain development in maize. Plant Physiol 66:1179–1183
Rodrigues EP (2004) Caraterização fisiológica de estirpes de Azospirillum amazonense e a avaliação dos efeitos da inoculação em plantas de arroz inundado. Federal Rural of Rio de Janeiro, Seropédica, Rio de Janeiro
Rybakova D, Cernava T, Köberl M, Liebminger S, Etemadi M, Berg G (2016) Endophytes-assisted biocontrol: novel insights in ecology and the mode of action of Paenibacillus. Plant Soil 405:125–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2526-1
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Schlemper TR, Dimitrov MR, Silva FAO, van Veen JA, Silveira APD, Kuramae EE (2018) Effect of Burkholderia tropica and Herbaspirillum frisingense strains on sorgun growth isplant genotype dependent. Peer J 6:e5346. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5346
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Ann Biochem 160:47–56
Sevilla M, Burris RH, Gunapala N, Kennedy C (2001) Comparison of benefit to sugarcane plant growth and 15N2 incorporation following inoculation of sterile plants with Acetobacter diazotrophicus wild type and Nif− mutant strains. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:358–366
Shahid I, Rzwan M, Baig DN, Saleem RS, Malik KA, Mehnaz S (2017) Secondary metabolites production and plant growth promotion by Pseudomonas chlororaphis and P. aurantiaca strains isolated from cactus, cotton, and para grass. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:480–491
Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM (1981) Utilization index: a modified approach to the estimation and comparison of nutrient efficiency in plants. J Plant Nutr 4:289–302
Silveira APD, Sala VMR, Cardoso EJBN, Labanca EG, Cipriano MAP (2016) Nitrogen metabolism and growth of wheat plant under diazotrophic endophytic bacteria inoculation. Appl Soil Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.07.005
Souza RSC et al (2016) Unlocking the bacterial and fungal communities assemblages of sugarcane microbiome. Sci Rep 6:28774. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28774
Sreenivasan J, Sreenivasan TV (1984) In vitro propagation of Sccharum officinarum L. x Sclerostachya fusca (Roxb) a cane hybrid. Theor Appl Genet 67:171–174
Ueda T, Suga Y, Yahiro N, Matsuguchi T (1995) Remarkable N2-fixing bacterial diversity detected in Rice roots by molecular evolutionary analysis of nifH gene sequences. J Bacteriol 177:1414–1417
Upreti R, Thomas P (2015) Root-associated bacterial endophytes from Ralstonia solanacearum resistant and susceptible tomato cultivars and their pathogen antagonistic effects. Front Microbiol 6:255. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00255
Vacheron J, Desbrosses G, Bouffaud M-L, Touraine B, Moënne-Loccoz Y, Muller D, Legendre L, Wisniewski-Dyé F, Prigent-Combaret C (2013) Plant growth- promoting rhizobacteria and root system functioning. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00356
Verma SK, Kingsley K, Bergen M, English C, Elmore M, Kharwar RN, White JF (2018) Bacterial endophytes from rice cut grass (Leersiaoryzoides L.) increase growth, promot root gravitropic response, stimulate root hair formation, and protect rice seedlings from disease. Plant Soil 422:223–238
Vurukonda SSKP, Giovanardi D, Stefani E (2018) Plant growth promoting and biocontrol activity of Streptomyces spp. as endophytes. Int J Mol Sci 19:952
Xing YX, Wei CY, Mo Y, Yang LT, Huang SL, Li YR (2016) Nitrogen-fixing and plant growth-promoting ability of two endophytic bacterial strains isolated from sugarcane stalks. Sugar Tech 18:373–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-015-0397-7
Zhang L, Birch RG (1997) Mechanisms of biocontrol by Pantoea dispersa of sugar cane leaf scald disease caused by Xanthomonas albilineans. J Appl Microbiol 82:448–454. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.1997.00135.x
Zhang XH, Zhao GH, Li DW, Li SP, Hong Q (2014) Identification and evaluation of strain B37 of Bacillus subtilis antagonistic to Sapstain fungi on poplar wood. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/149342
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge FAPESP financial support and CAPES for Master and Post-doctoral fellowships. This research was supported by BIOEN/FAPESP (2008/56147-1), The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO-729.004.013), and the CNPq/NWO Program (Project Number 456420/2013-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
APDS conceived the study. APDS, RPFI, FCCM, AOF, SCS and MAPC performed the experiments. APDS, RPFI, EEK and MAPC wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silveira, A.P.D., Iório, R.P.F., Marcos, F.C.C. et al. Exploitation of new endophytic bacteria and their ability to promote sugarcane growth and nitrogen nutrition. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 283–295 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1157-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1157-y