Abstract
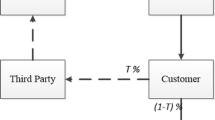
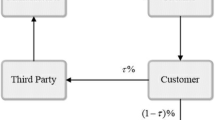
The closed-loop supply chain has been receiving increasing attention in recent years. Supply chain coordination and remanufactured products quality control are two fundamental factors for the closed-loop supply chain to obtain a competitive advantage. Besides, fierce competition brings more uncertainty to the market demand. Supply chain members tend to show the characteristics of loss aversion, which could affect them in making quality decisions. Therefore, this paper attempts to coordinate the closed-loop supply chain under remanufactured products quality control with a loss-averse manufacturer and a loss-averse retailer. Under remanufactured product quality control, expected utility function of manufacturers and retailers are established under centralized decision and decentralized decision respectively. According to the principle of utility maximization, the optimal choices of manufacturers and retailers are obtained. Further, by analyzing and comparing the optimal decisions in decentralized and centralized cases, it is found that the closed-loop supply chain cannot achieve coordination. Therefore, the wholesale price and the quality cost-sharing contract are introduced which is proved to be able to harmonize the supply chain. Finally, the impacts of the parameters change on the optimal quality level and remanufactured product price under two typical decision structures are presented through the sensitivity analysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 March 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04684-6
References
Atabaki, M. S., Mohammadi, M., & Naderi, B. (2020). New robust optimization models for closed-loop supply chain of durable products: Towards a circular economy. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 66, 106520.
Baiman, S., Fischer, P. E., & Rajan, M. V. (2000). Information, contracting, and quality costs. Management Science, 46(6), 776–789.
Banker, R. D., Khosla, I., & Sinha, K. K. (1998). Quality and competition. Management Science, 44(9), 1179–1192.
Chakraborty, T., Chauhan, S. S., & Ouhimmou, M. (2019). Cost-sharing mechanism for product quality improvement in a supply chain under competition. International Journal of Production Economics, 208, 566–587.
Chen, X., Hao, G., & Li, L. (2014). Channel coordination with a loss-averse retailer and option contracts. International Journal of Production Economics, 150, 52–57.
Choi, T.-M. (2018). Impacts of retailer’s risk averse behaviors on quick response fashion supply chain systems. Annals of Operations Research, 268(1–2), 239–257.
De Giovanni, P. (2014). Environmental collaboration in a closed-loop supply chain with a reverse revenue sharing contract. Annals of Operations Research, 220(1), 135–157.
De Giovanni, P. (2016). Coordination in a distribution channel with decisions on the nature of incentives and share-dependency on pricing. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 67(8), 1034–1049.
Dobos, I., & Richter, K. (2006). A production/recycling model with quality consideration. International Journal of Production Economics, 104(2), 571–579.
Dou, G., & Cao, K. (2020). A joint analysis of environmental and economic performances of closed-loop supply chains under carbon tax regulation. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 146, 106624.
El Saadany, A. M., & Jaber, M. Y. (2010). A production/remanufacturing inventory model with price and quality dependant return rate. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 58(3), 352–362.
Felfel, H., Yahia, W. B., Ayadi, O., & Masmoudi, F. (2018). Stochastic multi-site supply chain planning in textile and apparel industry under demand and price uncertainties with risk aversion. Annals of Operations Research, 271(2), 551–574.
Feng, T., Keller, L. R., & Zheng, X. (2011). Decision making in the newsvendor problem: A cross-national laboratory study. Omega, 39(1), 41–50.
Ferrer, G., & Swaminathan, J. M. (2010). Managing new and differentiated remanufactured products. European Journal of Operational Research, 203(2), 370–379.
Fisher, M., & Raman, A. (1996). Reducing the cost of demand uncertainty through accurate response to early sales. Operations Research, 44(1), 87–99.
Gao, J., Han, H., Hou, L., & Wang, H. (2016). Pricing and effort decisions in a closed-loop supply chain under different channel power structures. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112, 2043–2057.
Gaur, J., Amini, M., & Rao, A. (2017). Closed-loop supply chain configuration for new and reconditioned products: An integrated optimization model. Omega, 66, 212–223.
Geissdoerfer, M., Savaget, P., Bocken, N. M., & Hultink, E. J. (2017). The circular economy–A new sustainability paradigm? Journal of Cleaner Production, 143, 757–768.
Ghahremani-Nahr, J., Kian, R., & Sabet, E. (2019). A robust fuzzy mathematical programming model for the closed-loop supply chain network design and a whale optimization solution algorithm. Expert Systems with Applications, 116, 454–471.
Goli, A., & Davoodi, S. M. R. (2018). Coordination policy for production and delivery scheduling in the closed loop supply chain. Production Engineering, 12(5), 621–631.
Govindan, K., Soleimani, H., & Kannan, D. (2015). Reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chain: A comprehensive review to explore the future. European Journal of Operational Research, 240(3), 603–626.
He, Y., Xu, Q., Xu, B., & Wu, P. (2016). Supply chain coordination in quality improvement with reference effects. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 67(9), 1158–1168.
Heydari, J., Govindan, K., & Jafari, A. (2017). Reverse and closed loop supply chain coordination by considering government role. Transportation Research Part d: Transport and Environment, 52, 379–398.
Huynh, C. H., & Pan, W. (2015). Operational strategies for supplier and retailer with risk preference under VMI contract. International Journal of Production Economics, 169, 413–421.
Jeihoonian, M., Zanjani, M. K., & Gendreau, M. (2017). Closed-loop supply chain network design under uncertain quality status: Case of durable products. International Journal of Production Economics, 183, 470–486.
Jensen, J. P., Prendeville, S. M., Bocken, N. M., & Peck, D. (2019). Creating sustainable value through remanufacturing: Three industry cases. Journal of Cleaner Production, 218, 304–314.
Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (2013). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. In Handbook of the fundamentals of financial decision making: Part I (pp. 99–127). World Scientific.
Kunter, M. (2012). Coordination via cost and revenue sharing in manufacturer–retailer channels. European Journal of Operational Research, 216(2), 477–486.
Li, J., & Gong, S. (2020). Coordination of closed-loop supply chain with dual-source supply and low-carbon concern. Complexity, 6(66), 2020.
Lin, C., Chow, W. S., Madu, C. N., Kuei, C.-H., & Yu, P. P. (2005). A structural equation model of supply chain quality management and organizational performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 96(3), 355–365.
Liu, B., & De Giovanni, P. (2019). Green process innovation through Industry 4.0 technologies and supply chain coordination. Annals of Operations Research, 66, 1–36.
Liu, M., Cao, E., & Salifou, C. K. (2016). Pricing strategies of a dual-channel supply chain with risk aversion. Transportation Research Part e: Logistics and Transportation Review, 90, 108–120.
Liu, Y. Z., & Fan, Z. P. (2017). Supply chain coordination contract model considering loss aversion and quality level. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 25(1), 65–77.
Maiti, T., & Giri, B. (2015). A closed loop supply chain under retail price and product quality dependent demand. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 37, 624–637.
Maiti, T., & Giri, B. (2017). Two-way product recovery in a closed-loop supply chain with variable markup under price and quality dependent demand. International Journal of Production Economics, 183, 259–272.
Masoudipour, E., Amirian, H., & Sahraeian, R. (2017). A novel closed-loop supply chain based on the quality of returned products. Journal of Cleaner Production, 151, 344–355.
Miao, Z., Fu, K., Xia, Z., & Wang, Y. (2017). Models for closed-loop supply chain with trade-ins. Omega, 66, 308–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2015.11.001
Modak, N. M., Modak, N., Panda, S., & Sana, S. S. (2018). Analyzing structure of two-echelon closed-loop supply chain for pricing, quality and recycling management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171, 512–528.
Modak, N. M., Panda, S., & Sana, S. S. (2016). Three-echelon supply chain coordination considering duopolistic retailers with perfect quality products. International Journal of Production Economics, 182, 564–578.
Parker, D., & Butler, P. (2007). An introduction to remanufacturing. Aylesbury. Center for Remanufacturing and Reuse. Retrieved from www.remanufacturing.org.uk/pdf/reman_primer.pdf
Savaskan, R. C., Bhattacharya, S., & Van Wassenhove, L. N. (2004). Closed-loop supply chain models with product remanufacturing. Management Science, 50(2), 239–252.
Savaskan, R. C., & Van Wassenhove, L. N. (2006). Reverse channel design: The case of competing retailers. Management Science, 52(1), 1–14.
Schweitzer, M. E., & Cachon, G. P. (2000). Decision bias in the newsvendor problem with a known demand distribution: Experimental evidence. Management Science, 46(3), 404–420.
Seitz, M. A., & Peattie, K. (2004). Meeting the closed-loop challenge: The case of remanufacturing. California Management Review, 46(2), 74–89.
Vahdani, B., Zandieh, M., & Roshanaei, V. (2011). A hybrid multi-stage predictive model for supply chain network collapse recovery analysis: A practical framework for effective supply chain network continuity management. International Journal of Production Research, 49(7), 2035–2060.
Zhang, C., & Ren, M. (2016). Coordination strategy of closed-loop supply chain for remanufacture of patented products under competitive demands. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 40(13–14), 6243–6255.
Zhao, S., & Zhu, Q. (2017). Remanufacturing supply chain coordination under the stochastic remanufacturability rate and the random demand. Annals of Operations Research, 257(1–2), 661–695.
Zhao, S., & Zhu, Q. (2018). A risk-averse marketing strategy and its effect on coordination activities in a remanufacturing supply chain under market fluctuation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171, 1290–1299.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China under Grant NSFC71871017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Wang, D., Younas, A. et al. Coordination of closed-loop supply chain considering loss-aversion and remanufactured products quality control. Ann Oper Res (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04619-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04619-1