Abstract
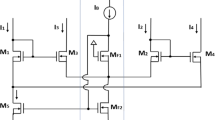
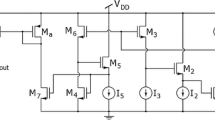
This paper, proposes a low-voltage/power, high-speed configurable analog block (CAB) for current-mode nonlinear computation. A novel MOS translinear cell (MTC), two local switch networks and PMOS-NMOS arrays are the basic building blocks of the proposed CAB. This MTC consists of two overlapped translinear loops using the MOS transistors operating in weak inversion region. The proposed CAB is capable to implement such current-mode analog computational processors as one- and four-quadrant multipliers, one- and two-quadrant dividers, squarer, full-wave rectifier (absolute-value), RMS to DC converter and much other. Post-layout plus Monte Carlo simulations of the proposed design with 0.18 µm (level-49 parameters) TSMC technology is performed that prove its superiority over some other advanced works and robustness against process, voltage and temperature variations. This superb feature plus many others, mostly, are due to the precise multilateral analysis and optimal compensate of mismatches and second order effects of the proposed circuit that led to proper selection of devices sizes and deliberate arrangement of the layout.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vittoz, E. A. (1994). Analog VLSI signal processing: Why, where, and how? Journal of VLSI Signal Processing, 8(1), 27–44.
Chang, C.-C., & Liu, S.-I. (2000). Current-mode full-wave rectifier and vector summation circuit. Electronics Letter, 36(19), 1599–1600.
Tanno, K., Ishizuka, O., & Tang, Z. (2000). Four-quadrant CMOS current-mode multiplier independent of device parameters. IEEE Transactions Circuits and Systems-II, 47(5), 473–477.
Lopez-Martin, A. J., & Carlosena, A. (2001). Current-mode multiplier/divider circuits based on the MOS translinear principle. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 28(3), 265–278.
Gravati, M., Valle, M., Ferri, G., Guerrini, N., & Reyes, L. (2005). A novel current-mode very low power analog CMOS four quadrant multiplier. In Proceedings of ESSCIRC, France (pp. 495–498).
Mahmoudi, A., Khoei, A., & Hadidi, Kh. (2007). A novel current-mode micro power four quadrant CMOS analog multiplier/divider. In IEEE conference on electron devices & solid-state circuits (EDSSC) (pp. 321–324).
Tanno, K., Sugahara, Y., & Tamura, H. (2011). High-linear four-quadrant multiplier based on MOS weak-inversion region translinear principle with adaptive bias technique. In TENCON (pp. 680–684).
Al-Absi, M. A., Hussein, A., & Abuelma’atti, M. T. (2012). A novel current-mode ultra low power analog CMOS four quadrant multiplier. In Proceedings of international conference on computer and communication engineering (pp. 13–17).
Wu, R., & Xing, J. (2012). MOS translinear principle based analog four-quadrant multiplier. In Anti-counterfeiting security and identification (ASID) (pp. 1–4).
Demartinos, Ch., Psychalinosand, C., & Khateb, F. (2014). Ultra-low voltage CMOS current-mode four-quadrant multiplier. International Journal of Electronics Letters, 2(4), 224–233.
Minaei, Sh, & Yuce, E. (2010). New squarer circuits and a current-mode full-wave rectifier topology suitable for integration. Radioengineering, 19(4), 657–661.
Chaisayun, I., Piangprantong, S., & Dejhan, K. (2012). Versatile analog squarer and multiplier free from body effect. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 71(3), 539–547.
Farshidi, E., & Ghanavati Nejad, T. (2012). A new two-quadrant squarer/divider circuit for true RMS-to-DC converters in MOS technology. Measurement, 45(4), 778–784.
Shaterian, M., Twigg, C. M., & Azhari, S. J. (2015). MTL-based implementation of current-mode CMOS RMS-to-DC converters. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 43(6), 793–805.
Al-Absi, M. A., & As-Sabban, I. A. (2014). A CMOS current-mode squaring circuit free of error resulting from carrier mobility reduction. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 81(1), 21–28.
Beyraghi, N., Khoei, A., & Hadidi, Kh. (2014). CMOS design of a four-quadrant multiplier based on a novel squarer circuit. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 80(3), 473–481.
Popa, C. (2014). Improved accuracy current-mode multiplier circuits with applications in analog signal processing. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 22(2), 443–447.
Moradinezhad Maryan, M., Azhari, S. J., & Hajipur, M. R. (2016). A simple low-power high-speed CMOS four-quadrant current multiplier. In Proceedings of 24th Iranian conference on electrical engineering (ICEE) (pp. 1471–1474).
Baturone, I., Huertas, J. L., Barriga, A., & Sanchez-Solano, S. (1995). Extending the functionality of a flexible current-mode CMOS circuit. Electronics Letter, 31(15), 1231–1232.
Abuelma’atti, M. T., & Al-Absi, M. A. (2006). A CMOS analog cell and its applications in analog signal processing. International Journal of Electronics, 93(4), 251–267.
Seon, J.-K. (2008). Design and application of precise analog computational circuits. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 54(1), 55–66.
Sajjadi-Kia, H. (2011). An analog cell and its applications in analog signal processing. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 39(2), 195–201.
Al-Absi, M. A., Hussein, A., & Abuelma’atti, M. T. (2013). A low voltage and low power current-mode analog computational circuit. Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing, 32(1), 321–331.
Srivastava, R., Gupta, M., & Singh, U. (2015). Low-voltage FGMOS squarer/divider-based analog building blocks. International Journal of Electronics, 102(4), 563–581.
Abuelma’atti, M. T., & Al-Yahia, N. M. (2008). An improved universal CMOS current-mode analogue function synthesizer. International Journal of Electronics, 95(11), 1127–1148.
Karimi, Y., & Abrishamifar, A. (2011). A low power configurable analogue block. In Proceedings of 19th Iranian conference on electrical engineering (ICEE) (pp. 1–5).
Fernandez, D., Martinez-Alvarado, L., & Madrenas, J. (2012). A translinear, log-domain FPAA on standard CMOS technology. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 47(2), 490–503.
Schlottmann, C., Abramson, D., & Hasler, P. (2012). A MITE-based translinear FPAA. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 20(1), 1–9.
Shaterian, M., Twigg, C. M., & Azhari, S. J. (2013). An MTL-based configurable block for current-mode nonlinear analog computation. IEEE Transactions Circuits and Systems-II, 60(9), 587–591.
Toumazou, C., Lidgey, F. J., & Haigh, D. G. (1990). Analogue IC design: The current-mode approach. London: IEE Press.
Seevinck, E., Vittoz, E. A., du Plessis, M., Joubert, T.-H., & Beetge, W. (2000). CMOS translinear circuits for minimum supply voltage. IEEE Transactions Circuits and Systems-II, 47(12), 1560–1564.
Seevinck, E., & Wiegerink, R. J. (1991). Generalized translinear circuit principle. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 26(8), 1098–1102.
Andreou, A. G., & Boahen, K. A. (1996). Translinear circuits in subthreshold MOS. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 9(2), 141–166.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maryan, M.M., Azhari, S.J. A MOS translinear cell-based configurable block for current-mode analog signal processing. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 92, 1–13 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-017-0959-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-017-0959-6