Abstract
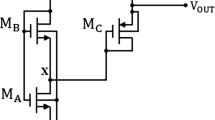
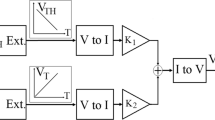
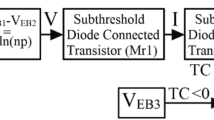
A fully CMOS based voltage reference circuit is presented in this paper. The voltage reference circuit uses the difference between gate-to-source voltages of two MOSFETs operating in the weak-inversion region to generate the voltage with positive temperature coefficient. The reference voltage can be obtained by combining this voltage difference and the extracted threshold voltage of a saturated MOSFET which has a negative temperature coefficient. This circuit, implemented in a standard 0.35-μm CMOS process, provides a nominal reference voltage of 1.361 V at 2-V supply voltage. Experimental results show that the temperature coefficient is 36.7 ppm/°C in the range from −20 to 100°C. It occupies 0.039 mm2 of active area and dissipates 82 μW at room temperature. With a 0.5-μF load capacitor, the measured noise density at 100 Hz and 100 kHz is 3.6 and \( 2 5\,{\text{nV}}/\sqrt {\text{Hz}} , \) respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, P. E., & Holberg, D. R. (2002). CMOS analog circuit design. New York: Oxford.
Blauschild, R. A., Tucci, P. A., Muller, R. S., & Meyer, R. G. (1978). A new NMOS temperature-stable voltage reference. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 13, 767–774.
Giustolisi, G., Palumbo, G., Criscione, M., & Cutri, F. (2003). A low-voltage low-power voltage reference based on subthreshold MOSFETs. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(1), 151–154.
Kuijk, L. E. (1973). A precision reference voltage source. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 8, 222–226.
Lee, I., Kim, G., & Kim, W. (1994). Exponential curvature-compensated BiCMOS bandgap reference. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 29, 1396–1403.
Leung, K. N., & Mok, P. K. T. (2003). A CMOS voltage reference based on weighted △VGS for CMOS low-dropout linear regulators. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(1), 146–150.
Lin, P. H., & Lin, Y. T. (2006). A simple subthreshold CMOS voltage reference circuit with channel—length modulation compensation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems. II, Express Briefs, 53(9), 882–885.
Malcovati, P., Maloberti, F., Fiocchi, C., & Pruzzi, M. (2001). Curvature—compensated BiCMOS bandgap with 1-V supply voltage. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36(7), 1076–1081.
Meijer, G. C. M., Schmall, P. C., & van Zalinge, K. (1982). A new curvature-corrected bandgap reference. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 17, 1139–1143.
Ougey, H. J., & Gerber, B. (1980). MOS voltage reference based on polysilicon gate work function difference. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 15, 264–269.
Stair, R., Connelly, J. A., & Pulkin, M. (2000). A current mode CMOS voltage reference. In Proceeding of Southwest Symposium on Mixed-Signal Design (pp. 23–26).
Harrison, W. T., Connelly, J. A., & Stair, R. (2001). An improved current-mode CMOS voltage reference. In Proceeding of Southwest Symposium on Mixed-Signal Design (pp. 25–27).
Razavi, B. (2001). Design of analog CMOS integrated circuit. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Sanborn, K. E., Ma, D., & Ivanov, V.V. (2006). A sub-1 V low noise bandgap voltage reference. In Proceeding of IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (pp. 607–610).
Tsividis, Y. P. (1987). Operation and modeling of the MOS transistor. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Seo, Y. D., Nam, D., Yoon, B. J., Choi, I. H., & Kim, B. (1997). Low-power CMOS on-chip voltage reference using MOS PTAT: An EP approach. In Proceeding of Tenth Annual IEEE International ASIC Conference and Exhibit (pp. 316–320).
Hoff, M. E. (1978). MOS voltage reference circuit. US Patent, 4(100), 437.
Song, H. J., & Kim, C. K. (1993). A temperature-stabilized SOL voltage reference based on threshold voltage difference between enhancement and depletion NMOSFET’s. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 28, 671–677.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Chip Implementation Center of Taiwan for supporting the chip fabrication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo, TY., Hung, CC. & Ismail, M. CMOS voltage reference based on threshold voltage and thermal voltage. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 62, 9–15 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-009-9321-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-009-9321-y