Abstract
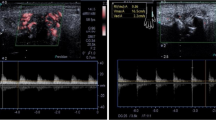
The objective of the study is to examine the relationship between synovial blood flow signals and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) involved in angiogenesis by Doppler ultrasound. Twenty-one patients meeting the diagnostic criteria of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) were enrolled in this study. Doppler ultrasound signals of blood flow in the wrist synovial membrane were measured and classified into three grades: grade 1 = no flow; grade 2 = mild flow; grade 3 = intense flow. A significant correlation was observed between blood flow signals in the wrist synovial membrane and serum VEGF levels (r = 0.5681, P = 0.0072). These results suggest that the measurement of Doppler ultrasound signals of blood flow in the wrist synovial membrane is useful in the evaluation of angiogenesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koch AE. The role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis: recent developments. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(Suppl 1):i65–71.
Klauser A, Frauscher F, Schirmer M, Halpern E, Pallwein L, Herold M, et al. The value of contrast-enhanced color Doppler ultrasound in the detection of vascularization of finger joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:647–53.
Takahashi A, Sato A, Yamadera Y, Takeda I, Kanno T, Ohguchi Y, et al. Doppler sonographic evaluation of effect of treatment with infliximab (Remicade) for rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2005;15:37–40.
Kasukawa R, Yamadera Y, Takahashi A, Takeda I, Kanno T. Power Doppler sonography for detection of intraarticular vascularization in knee joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol.. 2004;14:149–53.
Shio K, Homma F, Kanno Y, Yamadera Y, Ohguchi Y, Nishimaki T, et al. Doppler sonographic comparative study on usefulness of synovial vascularity between knee and metacarpophalangeal joints for evaluation of articular inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated by infliximab. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:220–5.
Qvistgaard E, Røgind H, Torp-Pedersen S, Terslev L, Danneskiold-Samsøe B, Bliddal H. Quantitative ultrasonography in rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of inflammation by Doppler technique. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60:690–3.
Filippucci E, Iagnocco A, Salaffi F, Cerioni A, Valesini G, Grassi W. Power Doppler sonography monitoring of synovial perfusion at the wrist joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:1433–7.
Carotti M, Salaffi F, Manganelli P, Salera D, Simonetti B, Grassi W. Power Doppler sonography in the assessment of synovial tissue of the knee joint in rheumatoid arthritis: a preliminary experience. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61:877–82.
Carvalho JF, Blank M, Shoenfeld Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in autoimmune diseases. J Clin Immunol. 2007;27:246–56.
Ballara S, Taylor PC, Reusch P, Marmé D, Feldmann M, Maini RN, et al. Raised serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels are associated with destructive change in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2055–64.
Clavel G, Bessis N, Lemeiter D, Fardellone P, Mejjad O, Ménard JF, et al. Angiogenesis markers (VEGF, soluble receptor of VEGF and angiopoietin-1) in very early arthritis and their association with inflammation and joint destruction. Clin Immunol. 2007;124:158–64.
Kurosaka D, Yoshida K, Yasuda J, Yasuda C, Noda K, Furuya K, et al. The effect of endostatin evaluated in an experimental animal model of collagen-induced arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2007;36:434–41.
Newman JS, Laing TJ, McCarthy CJ, Adler RS. Power Doppler sonography of synovitis: assessment of therapeutic response—preliminary observations. Radiology. 1996;198:582–4.
Strunk J, Heinemann E, Neeck G, Schmidt KL, Lange U. A new approach to studying angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis by means of power Doppler ultrasonography and measurement of serum vascular endothelial growth factor. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43:1480–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kurosaka, D., Hirai, K., Nishioka, M. et al. Correlation between synovial blood flow signals and serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 19, 187–191 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-008-0146-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-008-0146-9