Abstract
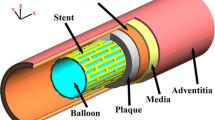
Oversizing of the Nitinol stents in the femoro-popliteal arterial tract is commonly performed by clinicians and further encouraged by stent manufacturers. However, in spite of the procedure’s supposed benefits of strong wall apposition and increased luminal gain, its effects on the mechanical behavior of arteries with peripheral arterial disease are not fully clear. In this study, finite element (FE) analyses of endovascular revascularization of an idealized artery with 70% stenosis and three different plaque types have been performed to examine the influence of Nitinol stent oversizing on the arterial stresses and acute lumen gain. The analyses included the simulation of balloon angioplasty to model plaque failure, followed by stent implantation, in which four different oversizing ratios were investigated. Results showed that balloon angioplasty was crucial in determining the stress levels of the artery prior to stent implantation and heavily affected the outcome of endovascular therapy. For all plaque types, Nitinol stent oversizing was found to produce a marginal lumen gain in contrast to a significant increase in arterial stresses. For the arteries with lightly and moderately calcified plaques, oversizing was found to be non-critical; whereas for the arteries with heavily calcified plaques, the procedure should be avoided due to a risk of tissue failure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfonso, F., R. A. Byrne, F. Rivero, and A. Kastrati. Current treatment of in-stent restenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63:2659–2673, 2014.
Barrett, H. E., E. M. Cunnane, E. G. Kavanagh, and M. T. Walsh. On the effect of calcification volume and configuration on the mechanical behaviour of carotid plaque tissue. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 56:45–56, 2016.
Boland, E. L., J. A. Grogan, C. Conway, and P. E. McHugh. Computer simulation of the mechanical behaviour of implanted biodegradable stents in a remodelling artery. Jom 68:1198–1203, 2016.
Chen, H. Y., B.-K. Koo, D. L. Bhatt, and G. S. Kassab. Impact of stent mis-sizing and mis-positioning on coronary fluid wall shear and intramural stress. J. Appl. Physiol. 115:285–292, 2013.
Chen, H. Y., A. K. Sinha, J. S. Choy, H. Zheng, M. Sturek, B. Bigelow, D. L. Bhatt, and G. S. Kassab. Mis-sizing of stent promotes intimal hyperplasia: impact of endothelial shear and intramural stress. AJP Heart. Circ. Physiol. 301:H2254–H2263, 2011.
Chiastra, C., W. Wu, B. Dickerhoff, A. Aleiou, G. Dubini, H. Otake, F. Migliavacca, and J. F. LaDisa. Computational replication of the patient-specific stenting procedure for coronary artery bifurcations: From OCT and CT imaging to structural and hemodynamics analyses. J. Biomech. 49:2102–2111, 2015.
Cho, H., M. Nango, Y. Sakai, E. Sohgawa, K. Kageyama, S. Hamamoto, T. Kitayama, A. Yamamoto, and Y. Miki. Neointimal hyperplasia after stent placement across size-discrepant vessels in an animal study. Jpn. J. Radiol. 32:340–346, 2014.
Conway, C., J. P. McGarry, and P. E. McHugh. Modelling of atherosclerotic plaque for use in a computational test-bed for stent angioplasty. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 42:2425–2439, 2014.
Conway, C., F. Sharif, J. P. McGarry, and P. E. McHugh. A computational test-bed to assess coronary stent implantation mechanics using a population-specific approach. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 3:374–387, 2012.
Cunnane, E. M., H. E. Barrett, E. G. Kavanagh, R. Mongrain, and M. T. Walsh. The influence of composition and location on the toughness of human atherosclerotic femoral plaque tissue. Acta Biomater. 31:264–275, 2016.
Cunnane, E. M., J. J. Mulvihill, H. E. Barrett, D. A. Healy, E. G. Kavanagh, S. R. Walsh, and M. T. Walsh. Mechanical, biological and structural characterization of human atherosclerotic femoral plaque tissue. Acta Biomater. 11:295–303, 2015.
Cunnane, E. M., J. J. E. Mulvihill, H. E. Barrett, M. M. Hennessy, E. G. Kavanagh, and M. T. Walsh. Mechanical properties and composition of carotid and femoral atherosclerotic plaques: a comparative study. J. Biomech. 49:3697–3704, 2016.
Cunnane, E. M., J. J. E. Mulvihill, H. E. Barrett, and M. T. Walsh. Simulation of human atherosclerotic femoral plaque tissue: the influence of plaque material model on numerical results. Biomed. Eng. Online 14:S7, 2015.
Derksen, W. J. M., J. P. P. M. De Vries, A. Vink, E. Velema, J. A. Vos, D. De Kleijn, F. L. Moll, and G. Pasterkamp. Histologic atherosclerotic plaque characteristics are associated with restenosis rates after endarterectomy of the common and superficial femoral arteries. J. Vasc. Surg. 52:592–599, 2010.
Dordoni, E., A. Meoli, W. Wu, G. Dubini, F. Migliavacca, G. Pennati, and L. Petrini. Fatigue behaviour of Nitinol peripheral stents: the role of plaque shape studied with computational structural analyses. Med. Eng. Phys. 36:842–849, 2014.
Gasser, T. C., R. W. Ogden, and G. A. Holzapfel. Hyperelastic modelling of arterial layers with distributed collagen fibre orientations. J. R. Soc. Interface 3:15–35, 2006.
Gökgöl, C., N. Diehm, F. R. Nezami, and P. Büchler. Nitinol stent oversizing in patients undergoing popliteal artery revascularization: a finite element study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:2868–2880, 2015.
Gornik, H. L., and J. A. Beckman. Cardiology patient page. Peripheral arterial disease. Circulation 111:e169–e172, 2005.
Herisson, F., M. F. Heymann, M. Chétiveaux, C. Charrier, S. Battaglia, P. Pilet, T. Rouillon, M. Krempf, P. Lemarchand, D. Heymann, and Y. Gouëffic. Carotid and femoral atherosclerotic plaques show different morphology. Atherosclerosis 216:348–354, 2011.
Hoffmann, R., G. S. Mintz, J. J. Popma, L. F. Satler, A. D. Pichard, K. M. Kent, C. Walsh, P. Mackell, and M. B. Leon. Chronic arterial responses to stent implantation: a serial intravascular ultrasound analysis of Palmaz-Schatz stents in native coronary arteries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 28:1134–1139, 1996.
Holzapfel, G. A., J. Casey, and G. Bao. Mechanics of angioplasty: wall, balloon and stent. Mech. Biol. ASME 242:141–156, 2000.
Holzapfel, G. A., G. Sommer, and P. Regitnig. Anisotropic mechanical properties of tissue components in human atherosclerotic plaques. J. Biomech. Eng. 126:657–665, 2004.
Holzapfel, G. A., M. Stadler, and T. C. Gasser. Changes in the mechanical environment of stenotic arteries during interaction with stents: computational assessment of parametric stent designs. J. Biomech. Eng. 127:166–180, 2005.
Holzapfel, G. A., M. Stadler, and C. A. J. Schulze-Bauer. A layer-specific three-dimensional model for the simulation of balloon angioplasty using magnetic resonance imaging and mechanical testing. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 30:753–767, 2002.
Kirsch, E. C., M. S. Khangure, P. Morling, T. J. York, and W. Mcauliffe. Oversizing of self-expanding stents : influence on the development of neointimal hyperplasia of the carotid artery in a canine model. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 23:121–127, 2002.
LaDisa, J. F., L. E. Olson, I. Guler, D. A. Hettrick, J. R. Kersten, D. C. Warltier, and P. S. Pagel. Circumferential vascular deformation after stent implantation alters wall shear stress evaluated with time-dependent 3D computational fluid dynamics models. J. Appl. Physiol. 98:947–957, 2005.
Li, F., M. M. McDermott, D. Li, T. J. Carroll, D. S. Hippe, C. M. Kramer, Z. Fan, X. Zhao, T. S. Hatsukami, B. Chu, J. Wang, and C. Yuan. The association of lesion eccentricity with plaque morphology and components in the superficial femoral artery: a high-spatial-resolution, multi-contrast weighted CMR study. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 12:37, 2010.
Loree, H. M., A. J. Grodzinsky, S. Y. Park, L. J. Gibson, and R. T. Lee. Static circumferential tangential modulus of human atherosclerotic tissue. J. Biomech. 27:195–204, 1994.
Meoli, A., E. Dordoni, L. Petrini, F. Migliavacca, G. Dubini, and G. Pennati. Computational modelling of in vitro set-ups for peripheral self-expanding Nitinol stents: the importance of stent-wall interaction in the assessment of the fatigue resistance. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 4:474–484, 2013.
Migliavacca, F., L. Petrini, P. Massarotti, S. Schievano, F. Auricchio, and G. Dubini. Stainless and shape memory alloy coronary stents: a computational study on the interaction with the vascular wall. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2:205–217, 2004.
Moreno, P. R., K. R. Purushothaman, V. Fuster, and W. N. O’Connor. Intimomedial interface damage and adventitial inflammation is increased beneath disrupted atherosclerosis in the aorta: implications for plaque vulnerability. Circulation 105:2504–2511, 2002.
Mulvihill, J. J., E. M. Cunnane, S. M. McHugh, E. G. Kavanagh, S. R. Walsh, and M. T. Walsh. Mechanical, biological and structural characterization of in vitro ruptured human carotid plaque tissue. Acta Biomater. 9:9027–9035, 2013.
Norgren, L., W. R. Hiatt, J. A. Dormandy, M. R. Nehler, K. A. Harris, and F. G. R. Fowkes. Inter-society consensus for the management of peripheral arterial disease (TASC II). J. Vasc. Surg. 45:S5–S67, 2007.
Petrini, L., A. Trotta, E. Dordoni, F. Migliavacca, G. Dubini, P. V. Lawford, J. N. Gosai, D. M. Ryan, D. Testi, and G. Pennati. A computational approach for the prediction of fatigue behaviour in peripheral stents: application to a clinical case. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015. doi:10.1007/s10439-015-1472-7.
Petrini, L., W. Wu, E. Dordoni, A. Meoli, F. Migliavacca, and G. Pennati. Fatigue behavior characterization of Nitinol for peripheral stents. Funct. Mater. Lett. 05:1250012, 2012.
Piamsomboon, C., G. S. Roubin, M. W. Liu, S. S. Iyer, A. Mathur, L. S. Dean, C. R. Gomez, J. J. Vitek, N. Chattipakorn, and G. Yates. Relationship between oversizing of self-expanding stents and late loss index in carotid stenting. Cathet. Cardiovasc. Diagn. 143:139–143, 1998.
Rebelo, N., R. Fu, and M. Lawrenchuk. Study of a Nitinol stent deployed into anatomically accurate artery geometry and subjected to realistic service loading. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 18:655–663, 2009.
Saguner, A. M., T. Traupe, L. Räber, N. Hess, Y. Banz, A. R. Saguner, N. Diehm, and O. M. Hess. Oversizing and restenosis with self-expanding stents in iliofemoral arteries. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 35:906–913, 2012.
Schulze-bauer, C. A. J., P. Regitnig, and G. A. Holzapfel. Mechanics of the human femoral adventitia including the high-pressure response. Am. J. Physiol. Hear. Circ. Physiol. 282:2427–2440, 2002.
Smilde, T. J., F. W. van den Berkmortel, G. H. Boers, H. Wollersheim, T. de Boo, H. van Langen, and f Stalenhoef. Carotid and femoral artery wall thickness and stiffness in patients at risk for cardiovascular disease, with special emphasis on hyperhomocysteinemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 18:1958–1963, 1998.
Stary, H. C., D. Blankenhorn, A. B. Chandler, S. Glagov, W. Insull, M. E. Rosenfeld, S. Schaffer, C. J. Schwartz, and W. D. Wagner. A definition of the intima of human arteries and of its atherosclerosis-prone regions. Circulation 85:391–405, 1992.
Stiegler, H., and R. Brandl. Importance of ultrasound for diagnosing periphereal arterial disease. Ultraschall Med. 30:334–374, 2009.
Stoeckel, D., A. Pelton, and T. Duerig. Self-expanding Nitinol stents: material and design considerations. Eur. Radiol. 14:292–301, 2004.
Tai, N. R., A. Giudiceandrea, H. J. Salacinski, A. M. Seifalian, and G. Hamilton. In vivo femoropopliteal arterial wall compliance in subjects with and without lower limb vascular disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 30:936–945, 1999.
Timmins, L. H., M. W. Miller, F. J. Clubb, and J. E. Moore. Increased artery wall stress post-stenting leads to greater intimal thickening. Lab. Invest. 91:955–967, 2011.
Zeller, T. Current state of endovascular treatment of femoro-popliteal artery disease. Vasc. Med. 12:223–234, 2007.
Zhao, H. Q., A. Nikanorov, R. Virmani, R. Jones, E. Pacheco, and L. B. Schwartz. Late stent expansion and neointimal proliferation of oversized Nitinol stents in peripheral arteries. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 32:720–726, 2009.
Acknowledgments
This investigation was supported by the Research Council of the Kantonsspital Aarau, the Swiss Heart Foundation and the Gotthard Schettler Foundation. The authors have no commercial, proprietary, or financial interest in any products or companies described in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Peter E. McHugh oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gökgöl, C., Diehm, N. & Büchler, P. Numerical Modeling of Nitinol Stent Oversizing in Arteries with Clinically Relevant Levels of Peripheral Arterial Disease: The Influence of Plaque Type on the Outcomes of Endovascular Therapy. Ann Biomed Eng 45, 1420–1433 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1803-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1803-y