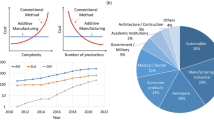
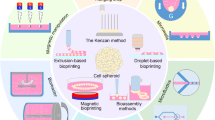
Abstract
Advanced bioinks for 3D printing are rationally designed materials intended to improve the functionality of printed scaffolds outside the traditional paradigm of the “biofabrication window”. While the biofabrication window paradigm necessitates compromise between suitability for fabrication and ability to accommodate encapsulated cells, recent developments in advanced bioinks have resulted in improved designs for a range of biofabrication platforms without this tradeoff. This has resulted in a new generation of bioinks with high print fidelity, shear-thinning characteristics, and crosslinked scaffolds with high mechanical strength, high cytocompatibility, and the ability to modulate cellular functions. In this review, we describe some of the promising strategies being pursued to achieve these goals, including multimaterial, interpenetrating network, nanocomposite, and supramolecular bioinks. We also provide an overview of current and emerging trends in advanced bioink synthesis and biofabrication, and evaluate the potential applications of these novel biomaterials to clinical use.


Adapted and reproduced by permission from American Association for the Advancement of Science29© 2015.

Adapted and reproduced by permission from Wiley31© 2015.

Adapted and reproduced by permission from American Chemical Society66© 2015.

Adapted and reproduced by permission from Wiley28© 2015.

Adapted and reproduced by permission from Wiley37© 2015.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augst, A. D., H. J. Kong, and D. J. Mooney. Alginate hydrogels as biomaterials. Macromol. Biosci. 6:623–633, 2006.
Azagarsamy, M. A., and K. S. Anseth. Bioorthogonal click chemistry: an indispensable tool to create multifaceted cell culture scaffolds. ACS Macro Lett. 2:5–9, 2012.
Bakarich, S. E., R. Gorkin, M. I. H. Panhuis, and G. M. Spinks. 4D printing with mechanically robust, thermally actuating hydrogels. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 36:1211–1217, 2015.
Bertassoni, L. E., J. C. Cardoso, V. Manoharan, A. L. Cristino, N. S. Bhise, W. A. Araujo, P. Zorlutuna, N. E. Vrana, A. M. Ghaemmaghami, and M. R. Dokmeci. Direct-write bioprinting of cell-laden methacrylated gelatin hydrogels. Biofabrication 6:024105, 2014.
Bertassoni, L. E., M. Cecconi, V. Manoharan, M. Nikkhah, J. Hjortnaes, A. L. Cristino, G. Barabaschi, D. Demarchi, M. R. Dokmeci, and Y. Yang. Hydrogel bioprinted microchannel networks for vascularization of tissue engineering constructs. Lab Chip 14:2202–2211, 2014.
Bhattacharjee, T., S. M. Zehnder, K. G. Rowe, S. Jain, R. M. Nixon, W. G. Sawyer, and T. E. Angelini. Writing in the granular gel medium. Sci. Adv. 1:e1500655, 2015.
Billiet, T., M. Vandenhaute, J. Schelfhout, S. Van Vlierberghe, and P. Dubruel. A review of trends and limitations in hydrogel-rapid prototyping for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 33:6020–6041, 2012.
Carrow, J. K., and A. K. Gaharwar. Bioinspired polymeric nanocomposites for regenerative medicine. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 216:248–264, 2015.
Chen, Q., H. Chen, L. Zhu, and J. Zheng. Fundamentals of double network hydrogels. J Mater Chem B 3:3654–3676, 2015.
Chen, Q., L. Zhu, L. Huang, H. Chen, K. Xu, Y. Tan, P. Wang, and J. Zheng. Fracture of the physically cross-linked first network in hybrid double network hydrogels. Macromolecules 47:2140–2148, 2014.
Chimene, D., D. L. Alge, and A. K. Gaharwar. Two-dimensional nanomaterials for biomedical applications: emerging trends and future prospects. Adv. Mater. 27:7261–7284, 2015.
Chung, J. H., S. Naficy, Z. Yue, R. Kapsa, A. Quigley, S. E. Moulton, and G. G. Wallace. Bio-ink properties and printability for extrusion printing living cells. Biomater. Sci. 1:763–773, 2013.
Discher, D. E., D. J. Mooney, and P. W. Zandstra. Growth factors, matrices, and forces combine and control stem cells. Science 324:1673–1677, 2009.
Duan, B., E. Kapetanovic, L. A. Hockaday, and J. T. Butcher. Three-dimensional printed trileaflet valve conduits using biological hydrogels and human valve interstitial cells. Acta Biomater. 10:1836–1846, 2014.
Durmus, N. G., S. Tasoglu, and U. Demirci. Bioprinting: functional droplet networks. Nat. Mater. 12:478–479, 2013.
Engler, A. J., S. Sen, H. L. Sweeney, and D. E. Discher. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126:677–689, 2006.
Fisher, O. Z., A. Khademhosseini, R. Langer, and N. A. Peppas. Bioinspired materials for controlling stem cell fate. Acc. Chem. Res. 43:419–428, 2010.
Gaharwar, A. K., A. Arpanaei, T. L. Andresen, and A. Dolatshahi-Pirouz. 3D biomaterial microarrays for regenerative medicine: current state-of-the-art, emerging directions and future trends. Adv. Mater. 28:771–781, 2016.
Gaharwar, A. K., R. K. Avery, A. Assmann, A. Paul, G. H. McKinley, A. Khademhosseini, and B. D. Olsen. Shear-thinning nanocomposite hydrogels for the treatment of hemorrhage. ACS Nano 8:9833–9842, 2014.
Gaharwar, A. K., N. A. Peppas, and A. Khademhosseini. Nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 111:441–453, 2014.
Gaharwar, A. K., C. P. Rivera, C.-J. Wu, and G. Schmidt. Transparent, elastomeric and tough hydrogels from poly (ethylene glycol) and silicate nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 7:4139–4148, 2011.
Gao, G., A. F. Schilling, T. Yonezawa, J. Wang, G. Dai, and X. Cui. Bioactive nanoparticles stimulate bone tissue formation in bioprinted three-dimensional scaffold and human mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol. J. 9:1304–1311, 2014.
Gasperini, L., J. F. Mano, and R. L. Reis. Natural polymers for the microencapsulation of cells. J. R. Soc. Interface 11:20140817, 2014.
Goenka, S., V. Sant, and S. Sant. Graphene-based nanomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 173:75–88, 2014.
Guilak, F., D. M. Cohen, B. T. Estes, J. M. Gimble, W. Liedtke, and C. S. Chen. Control of stem cell fate by physical interactions with the extracellular matrix. Cell Stem Cell 5:17–26, 2009.
Haque, M. A., T. Kurokawa, and J. P. Gong. Super tough double network hydrogels and their application as biomaterials. Polymer 53:1805–1822, 2012.
Hart, L. R., J. L. Harries, B. W. Greenland, H. M. Colquhoun, and W. Hayes. Healable supramolecular polymers. Polymer Chemistry 4:4860–4870, 2013.
Highley, C. B., C. B. Rodell, and J. A. Burdick. Direct 3D printing of shear-thinning hydrogels into self-healing hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 27:5075–5079, 2015.
Hinton, T. J., Q. Jallerat, R. N. Palchesko, J. H. Park, M. S. Grodzicki, H.-J. Shue, M. H. Ramadan, A. R. Hudson, and A. W. Feinberg. Three-dimensional printing of complex biological structures by freeform reversible embedding of suspended hydrogels. Sci. Adv. 1:e1500758, 2015.
Hoffman, A. S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 64:18–23, 2012.
Hong, S., D. Sycks, H. F. Chan, S. Lin, G. P. Lopez, F. Guilak, K. W. Leong, and X. Zhao. 3D printing of highly stretchable and tough hydrogels into complex, cellularized structures. Adv. Mater. 27:4035–4040, 2015.
Huang, T., H. G. Xu, K. X. Jiao, L. P. Zhu, H. R. Brown, and H. L. Wang. A novel hydrogel with high mechanical strength: a macromolecular microsphere composite hydrogel. Adv. Mater. 19:1622–1626, 2007.
Jaiswal, M. K., J. R. Xavier, J. K. Carrow, P. Desai, D. Alge, and A. K. Gaharwar. Mechanically stiff nanocomposite hydrogels at ultralow nanoparticle content. ACS Nano 10:246–256, 2016.
Jakab, K., C. Norotte, F. Marga, K. Murphy, G. Vunjak-Novakovic, and G. Forgacs. Tissue engineering by self-assembly and bio-printing of living cells. Biofabrication 2:022001, 2010.
Kang, H.-W., S. J. Lee, I. K. Ko, C. Kengla, J. J. Yoo, and A. Atala. A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity. Nat. Biotechnol. 34:312–319, 2016.
Kerativitayanan, P., J. K. Carrow, and A. K. Gaharwar. Nanomaterials for engineering stem cell responses. Adv. Healthc Mater. 4:1600–1627, 2015.
Kesti, M., M. Müller, J. Becher, M. Schnabelrauch, M. D’Este, D. Eglin, and M. Zenobi-Wong. A versatile bioink for three-dimensional printing of cellular scaffolds based on thermally and photo-triggered tandem gelation. Acta Biomater. 11:162–172, 2015.
Kirchmajer, D. M., R. Gorkin, III, and M. I. H. Panhuis. An overview of the suitability of hydrogel-forming polymers for extrusion-based 3D-printing. J. Mater. Chem. B 3:4105–4117, 2015.
Kirchmajer, D. M., and M. I. H. Panhuis. Robust biopolymer based ionic-covalent entanglement hydrogels with reversible mechanical behaviour. J. Mater. Chem. B 2:4694–4702, 2014.
Kloxin, A. M., C. J. Kloxin, C. N. Bowman, and K. S. Anseth. Mechanical properties of cellularly responsive hydrogels and their experimental determination. Adv. Mater. 22:3484–3494, 2010.
Lee, V. K., D. Y. Kim, H. Ngo, Y. Lee, L. Seo, S.-S. Yoo, P. A. Vincent, and G. Dai. Creating perfused functional vascular channels using 3D bio-printing technology. Biomaterials 35:8092–8102, 2014.
Lee, V., G. Singh, J. P. Trasatti, C. Bjornsson, X. Xu, T. N. Tran, S.-S. Yoo, G. Dai, and P. Karande. Design and fabrication of human skin by three-dimensional bioprinting. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 20:473–484, 2013.
Malda, J., and J. Groll. A step towards clinical translation of biofabrication. Trends Biotechnol. 34:356, 2016.
Malda, J., J. Visser, F. P. Melchels, T. Jüngst, W. E. Hennink, W. J. Dhert, J. Groll, and D. W. Hutmacher. 25th anniversary article: engineering hydrogels for biofabrication. Adv. Mater. 25:5011–5028, 2013.
Markstedt, K., A. Mantas, I. Tournier, H. C. Martínez Ávila, D. Hägg, and P. Gatenholm. 3D Bioprinting human chondrocytes with nanocellulose-alginate bioink for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Biomacromolecules 16:1489–1496, 2015.
Melchels, F. P., M. A. Domingos, T. J. Klein, J. Malda, P. J. Bartolo, and D. W. Hutmacher. Additive manufacturing of tissues and organs. Prog. Polym. Sci. 37:1079–1104, 2012.
Mironov, V., N. Reis, and B. Derby. Review: bioprinting: a beginning. Tissue Eng. 12:631–634, 2006.
Mironov, V., R. P. Visconti, V. Kasyanov, G. Forgacs, C. J. Drake, and R. R. Markwald. Organ printing: tissue spheroids as building blocks. Biomaterials 30:2164–2174, 2009.
Murphy, S. V., and A. Atala. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 32:773–785, 2014.
Murphy, S. V., A. Skardal, and A. Atala. Evaluation of hydrogels for bio-printing applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 101A:272–284, 2013.
Parani, M., G. Lokhande, A. Singh, and A. K. Gaharwar. Engineered nanomaterials for infection control and healing acute and chronic wounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8:10049–10069, 2016.
Pati, F., J. Gantelius, and H. A. Svahn. 3D bioprinting of tissue/organ models. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55:4650–4665, 2016.
Pati, F., J. Jang, D.-H. Ha, S. Won Kim, J.-W. Rhie, J.-H. Shim, D.-H. Kim, and D.-W. Cho. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nat. Commun. 5:3935, 2014.
Paul, A. Nanocomposite hydrogels: an emerging biomimetic platform for myocardial therapy and tissue engineering. Nanomedicine 10:1371–1374, 2015.
Peak, C. W., J. K. Carrow, A. Thakur, A. Singh, and A. K. Gaharwar. Elastomeric cell-laden nanocomposite microfibers for engineering complex tissues. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 8:404–415, 2015.
Pereira, R. F., H. A. Almeida, and P. J. Bártolo. Drug delivery systems: advanced technologies potentially applicable in personalised treatmentBiofabrication Hydrogel Constr., Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 225–254, 2013.
Rowley, J. A., G. Madlambayan, and D. J. Mooney. Alginate hydrogels as synthetic extracellular matrix materials. Biomaterials 20:45–53, 1999.
Rutz, A. L., K. E. Hyland, A. E. Jakus, W. R. Burghardt, and R. N. Shah. A multimaterial bioink method for 3D printing tunable, Cell-compatible hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 27:1607–1614, 2015.
Skardal, A., and A. Atala. Biomaterials for Integration with 3-D Bioprinting. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:730–746, 2015.
Slaughter, B. V., S. S. Khurshid, O. Z. Fisher, A. Khademhosseini, and N. A. Peppas. Hydrogels in regenerative medicine. Adv. Mater. 21:3307–3329, 2009.
Stanton, M., J. Samitier, and S. Sánchez. Bioprinting of 3D hydrogels. Lab Chip 15:3111–3115, 2015.
Suekama, T. C., J. Hu, T. Kurokawa, J. P. Gong, and S. H. Gehrke. Double-network strategy improves fracture properties of chondroitin sulfate networks. ACS Macro Lett. 2:137–140, 2013.
Thakur, T., J. R. Xavier, L. Cross, M. K. Jaiswal, E. Mondragon, R. Kaunas, and A. K. Gaharwar. Photocrosslinkable and elastomeric hydrogels for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A 104:879–888, 2016.
Thiele, J., Y. Ma, S. Bruekers, S. Ma, and W. T. Huck. 25th Anniversary article: designer hydrogels for cell cultures: a materials selection guide. Adv. Mater. 26:125–148, 2014.
Tibbitt, M. W., and K. S. Anseth. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 103:655–663, 2009.
Xavier, J. R., T. Thakur, P. Desai, M. K. Jaiswal, N. Sears, E. Cosgriff-Hernandez, R. Kaunas, and A. K. Gaharwar. Bioactive nanoengineered hydrogels for bone tissue engineering: a growth-factor-free approach. ACS Nano 9:3109–3118, 2015.
Xu, Y., and X. Wang. Application of 3D biomimetic models in drug delivery and regenerative medicine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 21:1618–1626, 2015.
Yang, L., X. Tan, Z. Wang, and X. Zhang. Supramolecular polymers: historical development, preparation, characterization, and functions. Chem. Rev. 115:7196–7239, 2015.
Zhu, W., X. Ma, M. Gou, D. Mei, K. Zhang, and S. Chen. 3D printing of functional biomaterials for tissue engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 40:103–112, 2016.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation Award No. HRD-1406755 and CBET-1264848 and NIH R01 AR066033-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Michael S. Detamore oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chimene, D., Lennox, K.K., Kaunas, R.R. et al. Advanced Bioinks for 3D Printing: A Materials Science Perspective. Ann Biomed Eng 44, 2090–2102 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-016-1638-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-016-1638-y