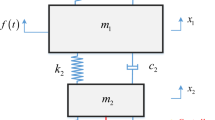
Abstract
The traditional passive absorber is fully effective within a narrow and certain frequency band. To solve this problem, a time-delayed acceleration feedback is introduced to convert a passive absorber into an active one. Both the inherent and the intentional time delays are included. The former mainly comes from signal acquiring and processing, computing, and applying the actuation force, and its value is fixed. The latter is introduced in the controller, and its value is actively adjustable. Firstly, the mechanical model is established and the frequency response equations are obtained. The regions of stability are delineated in the plane of control parameters. Secondly, the design scheme of control para- meters is performed to help select the values of the feedback gain and time delay. Thirdly, the experimental studies are conducted. Effects of both negative and positive feedback control are investigated. Experimental results show that the proper choices of control parameters may broaden the effective frequency band of vibration absorption. Moreover, the time-delayed absorber greatly suppresses the resonant response of the primary system when the passive absorber totally fails. The experimental results are in good agreement with the theoretical predictions and numerical simulations.
Graphical Abstract
A time-delayed acceleration feedback is introduced to convert a passive absorber into an active one. The design scheme of control parameters is performed for selection guidance of the values of feedback gain and time delay. Experimental results show the effectiveness of the time-delayed absorber on suppressing the vibration of the primary system.

































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Den Hartog, J.P.: Mechanical Vibrations. Dover Publications Inc., New York (1985)
Fang, J., Wang, S.M., Wang, Q.: Optimal design of vibration absorber using minimax criterion with simplified constraints. Acta Mech. Sin. 28, 848–853 (2012)
Jovanovic, M.M., Simonovic, A.M., Zoric, N.D., et al.: Experimental studies on active vibration control of a smart composite beam using a PID controller. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 115038 (2013)
Guo, S.X., Li, Y.: Non-probabilistic reliability method and reliability-based optimal LQR design for vibration control of structures with uncertain-but-bounded parameters. Acta Mech. Sin. 29, 864–874 (2013)
Shan, J.J., Liu, H.T., Sun, D.: Slewing and vibration control of a single-link flexible manipulator by positive position feedback (PPF). Mechatronics 15, 487–503 (2005)
Lin, J., Liu, W.Z.: Experimental evaluation of a piezoelectric vibration absorber using a simplified fuzzy controller in a cantilever beam. J. Sound Vib. 296, 567–582 (2006)
Megahed, S.M., El-Razik, A.K.A.: Vibration control of two degrees of freedom system using variable inertia vibration absorbers: modeling and simulation. J. Sound Vib. 329, 4841–4865 (2010)
Ghorbani-Tanha, A.K., Rahimian, M., Noorzad, A.: A Novel semiactive variable stiffness device and its application in a new semiactive tuned vibration absorber. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 137, 390–399 (2011)
Hidaka, S., Ahn, Y.K., Morishita, S.: Adaptive vibration control by a variable-damping dynamic absorber using ER fluid. J. Vib. Acoust. 121, 373–378 (1999)
Udwadia, F.E., Phohomsiri, P.: Active control of structures using time delayed positive feedback proportional control designs. Struct. Control Health Monit. 13, 536–552 (2006)
Wang, Z.H., Hu, H.Y.: A modified averaging scheme with application to the secondary Hopf bifurcation of a delayed van der Pol oscillator. Acta Mech. Sin. 24, 449–454 (2008)
Zhang, S., Xu, J.: Bursting-like motion induced by time-varying delay in an internet congestion control model. Acta Mech. Sin. 28, 1169–1179 (2012)
Zhen, B., Xu, J.: Influence of the time delay of signal transmission on synchronization conditions in drive-response systems. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 3, 25–28 (2013)
Jiang, S.Y., Xu, J., Yan, Y.: Stability and oscillations in a slow-fast flexible joint system with transformation delay. Acta Mech. Sin. 30, 727–738 (2014)
Nakamura, Y., Goto, S., Wakui, S.: Tuning methods of a Smith predictor for pneumatic active anti-vibration apparatuses. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 7, 666–676 (2013)
Chung, L.L., Reinhorn, A.M., Soong, T.T.: Experiments on active control of seismic structures. J. Eng. Mech. 114, 241–256 (1988)
Agrawa, A.K., Yang, J.N.: Compensation of time-delay for control of civil engineering structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 29, 37–62 (2000)
Liu, K., Chen, L.X., Cai, G.P.: An experimental study of delayed positive feedback control for a flexible plate. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 17, 171–180 (2012)
Li, X.P., Wei, D.M., Zhu, W.Q.: Time-delayed feedback control optimization for quasi linear systems under random excitations. Acta Mech. Sin. 25, 395–402 (2009)
Xu, J., Chung, K.W.: Effects of time delayed position feedback on a van der Pol-Duffing oscillator. Phys. D 180, 17–39 (2003)
Li, Z.C., Wang, Q., Gao, H.P.: Control of friction oscillator by Lyapunov redesign based on delayed state feedback. Acta Mech. Sin. 25, 257–264 (2009)
Olgac, N., Holm-Hansen, B.T.: A novel active vibration absorption technique–delayed resonator. J. Sound Vib. 176, 93–104 (1994)
Olgac, N., Elmali, H., Hosek, M., et al.: Active vibration control of distributed systems using delayed resonator with acceleration feedback. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 119, 380–389 (1997)
Sipahi, R., Olgac, N.: Active vibration suppression with time delayed feedback. J. Vib. Acoust. 125, 384–388 (2003)
Wang, Z.H., Xu, Q.: Vibration control via positive delayed feedback. In: 10th Biennial International Conference on Vibration Problems (ICOVP), Prague, Czech Republic, SEP 05–08 (2011)
Tootoonchi, A.A., Gholami, M.S.: Application of time delay resonator to machine tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 56, 879–891 (2011)
Liu, J., Liu, K.: Application of an active electromagnetic vibration absorber in vibration suppression. Struct. Control Health Monit. 17, 278–300 (2010)
Zhao, Y.Y., Xu, J.: Effects of delayed feedback control on nonlinear vibration absorber system. J. Sound Vib. 308, 212–230 (2007)
Chatterjee, S., Mahata, P.: Time-delayed absorber for controlling friction-driven vibration. J. Sound Vib. 322, 39–59 (2009)
El-Sayed, A.T., Bauomy, H.S.: Vibration control of helicopter blade flapping via time-delay absorber. Meccanica 49, 587–600 (2014)
El-Gohary, H.A., El-Ganaini, W.A.A.: Vibration suppression of a dynamical system to multi-parametric excitations via time-delay absorber. Appl. Math. Model. 36, 35–45 (2012)
Elmali, H., Renzulli, M., Olgac, N.: Experimental comparison of delayed resonator and PD controlled vibration absorbers using electromagnetic actuators. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 122, 514–520 (2000)
Hosek, M., Olgac, N.: A single-step automatic tuning algorithm for the delayed resonator vibration absorber. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 7, 245–255 (2002)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 11032009) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 11272236).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Sun, Y. Experimental studies on active control of a dynamic system via a time-delayed absorber. Acta Mech Sin 31, 229–247 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-015-0411-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-015-0411-z