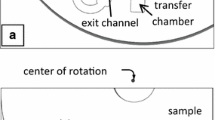
Abstract
Recently, several biological assays have become available on the centrifugal microfluidic platform. Despite many innovative solutions developed for on-disc fluid handling for these assays, certain challenges, including liquid incubation and simplification of a multi-step assay on a plastic device, still need to be further addressed. Incubating fluids that require downstream processing, which we call “midstream incubation”, can often be difficult on the microfluidic disc platform due to surface tension changes induced by varying temperatures, thus causing operating instability. We describe here strategies for liquid reagent storage, release, incubation, and transfer, all of which utilize a single combination of actuation methods—wax valving and heat actuation by halogen lamp—on a centrifugal microfluidic device made using pristine materials. The strategies that we use to perform these steps, termed multifunctional wax valves, enable manipulation of a microlitre range fluid volume without the need for complex fabrication steps or hardware. This technology’s reliability and ease of use will hopefully allow for more powerful fluidics-based diagnostic tools to be created.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abi-Samra K, Clime L, Kong L et al (2011a) Thermo-pneumatic pumping in centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid Nanofluidics 11:643–652. doi:10.1007/s10404-011-0830-5
Abi-Samra K, Hanson R, Madou M, Gorkin RA (2011b) Infrared controlled waxes for liquid handling and storage on a CD-microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 11:723–726. doi:10.1039/c0lc00160k
Amasia M, Cozzens M, Madou MJ (2012) Centrifugal microfluidic platform for rapid PCR amplification using integrated thermoelectric heating and ice-valving. Sens Actuators B Chem 161:1191–1197. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2011.11.080
Cho Y-K, Lee J-G, Park J-M et al (2007) One-step pathogen specific DNA extraction from whole blood on a centrifugal microfluidic device. Lab Chip 7:565–573. doi:10.1039/b616115d
Ducrée J, Haeberle S, Lutz S et al (2007) The centrifugal microfluidic bio-disk platform. J Micromech Microeng 17:S103–S115. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/17/7/S07
Focke M, Stumpf F, Roth G et al (2010) Centrifugal microfluidic system for primary amplification and secondary real-time PCR. Lab Chip 10:3210–3212. doi:10.1039/c0lc00161a
Garcia-Cordero J, Benito-Lopez F, Diamond D, Ducree J, Ricco AJ (2009) Low-cost microfluidic single-use valves and on-board reagent storage using laser-printer technology. In: IEEE 22nd international conference on micro electro mechanical systems, pp 439–442. doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.2009.480541
Gorkin R, Clime L, Madou M, Kido H (2010a) Pneumatic pumping in centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid Nanofluidics 9:541–549. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0571-x
Gorkin R, Park J, Siegrist J et al (2010b) Centrifugal microfluidics for biomedical applications. Lab Chip 10:1758–1773. doi:10.1039/b924109d
Gorkin R, Soroori S, Southard W et al (2011) Suction-enhanced siphon valves for centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid Nanofluidics 12:345–354. doi:10.1007/s10404-011-0878-2
Gorkin R, Nwankire CE, Gaughran J et al (2012) Centrifugo-pneumatic valving utilizing dissolvable films. Lab Chip 12:2894–2902. doi:10.1039/c2lc20973j
Hébert B, Bergeron J, Potworowski EF, Tijssen P (1993) Increased PCR sensitivity by using paraffin wax as a reaction mix overlay. Mol Cell Probes 7:249–252. doi:10.1006/mcpr.1993.1036
Hoffmann J, Mark D, Lutz S et al (2010) Pre-storage of liquid reagents in glass ampoules for DNA extraction on a fully integrated lab-on-a-chip cartridge. Lab Chip 10:1480–1484. doi:10.1039/b926139g
Hou H-H, Wang Y-N, Chang C-L et al (2011) Rapid glucose concentration detection utilizing disposable integrated microfluidic chip. Microfluid Nanofluidics 11:479–487. doi:10.1007/s10404-011-0813-6
Kido H, Micic M, Smith D et al (2007) A novel, compact disk-like centrifugal microfluidics system for cell lysis and sample homogenization. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 58:44–51. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.03.015
Kong L, Rodriguez JM, Perebikovsky A et al (2013) Novel heating and cooling techniques on a centrifugal fluidic platform for polymerase chain reaction. Microtechnol Med Biol
Lutz S, Weber P, Focke M et al (2010) Microfluidic lab-on-a-foil for nucleic acid analysis based on isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA). Lab Chip 10:887–893. doi:10.1039/b921140c
Madou MJ (2002) Fundamentals of microfabrication: the science of miniaturization, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 493
Madou M, Zoval J, Jia G et al (2006) Lab on a CD. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:601–628. doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.8.061505.095758
Malmstadt N, Hoffman AS, Stayton PS (2004) “Smart” mobile affinity matrix for microfluidic immunoassays. Lab Chip 4:412–415. doi:10.1039/b315394k
Miralles V, Huerre A, Malloggi F, Jullien M-C (2013) A review of heating and temperature control in microfluidic systems: techniques and applications. Diagnostics 3:33–67. doi:10.3390/diagnostics3010033
Noroozi Z, Kido H, Madou MJ (2011a) Electrolysis-induced pneumatic pressure for control of liquids in a centrifugal system. J Electrochem Soc 158:P130. doi:10.1149/2.028111jes
Noroozi Z, Kido H, Peytavi R et al (2011b) A multiplexed immunoassay system based upon reciprocating centrifugal microfluidics. Rev Sci Instrum 82:064303. doi:10.1063/1.3597578
Nwankire CE, Chan D-SS, Gaughran J et al (2013) Fluidic automation of nitrate and nitrite bioassays in whole blood by dissolvable-film based centrifugo-pneumatic actuation. Sensors (Basel) 13:11336–11349. doi:10.3390/s130911336
Sagar DM, Aoudjane S, Gaudet M et al (2013) Optically induced thermal gradients for protein characterization in nanolitre-scale samples in microfluidic devices. Sci Rep 3:1–6. doi:10.1038/srep02130
Siegrist J, Gorkin R, Clime L et al (2010) Serial siphon valving for centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid Nanofluidics 9:55–63. doi:10.1007/s10404-009-0523-5
Soroori S, Kulinsky L, Madou M (2013) Centrifugal microfluidics: characteristics & possibilities. In: Chakraborty S (ed) Microfluidics and microscale transport processes, pp 149–186. CRC Press, USA
Sundberg SO, Wittwer CT, Gao C, Gale BK (2010) Spinning disk platform for microfluidic digital polymerase chain reaction. Anal Chem 82:1546–1550. doi:10.1021/ac902398c
Van Oordt T, Barb Y, Zengerle R, Von Stetten F (2011) Miniature stick-packaging—an industrial technology for pre-storage and release of reagents in lab-on-a-chip systems. MicroTAS, pp 437–439
Wainwright LA, Seifert HS (1993) Paraffin beads can replace mineral oil as an evaporation barrier in PCR. Biotechniques 14:34–36
Zhang C, Xing D (2007) Miniaturized PCR chips for nucleic acid amplification and analysis: latest advances and future trends. Nucleic Acids Res 35:4223–4237. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm389
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Genome Quebec and the National Institute of Health (Grant 1 R01 AI089541-01). The authors would also like to acknowledge Bryce Kubo and Jigar Shah for their contribution to the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MPG 44202 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, L.X., Parate, K., Abi-Samra, K. et al. Multifunctional wax valves for liquid handling and incubation on a microfluidic CD. Microfluid Nanofluid 18, 1031–1037 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1492-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1492-x