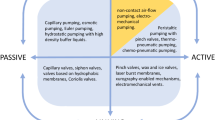
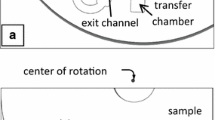
Abstract
The pumping of fluids in microfluidic discs by centrifugal forces has several advantages, however, centrifugal pumping only permits unidirectional fluid flow, restricting the number of processing steps that can be integrated before fluids reach the edge of the disc. As a solution to this critical limitation, we present a novel pumping technique for the centrifugal microfluidic disc platform, termed the thermo-pneumatic pump (TPP), that enables fluids to be transferred the center of a rotating disc by the thermal expansion of air. The TPP is easy to fabricate as it is a structural feature with no moving components and thermal energy is delivered to the pump via peripheral infrared (IR) equipment, enabling pumping while the disc is in rotation. In this report, an analytical model for the operation of the TPP is presented and experimentally validated. We demonstrate that the experimental behavior of the pump agrees well with theory and that flow rates can be controlled by changing how well the pump absorbs IR energy. Overall, the TPP enables for fluids to be stored near the edge of the disc and transferred to the center on demand, offering significant advantages to the microfluidic disc platform in terms of the handling and storage of liquids.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abi-Samra K, Hanson R, Madou M, Gorkin RA III (2011) Infrared controlled waxes for liquid handling and storage on a CD-microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 11(4):723–726. doi:10.1039/c0lc00160k
Cho YK, Lee JG, Park JM, Lee BS, Lee Y, Ko C (2007) One-step pathogen specific DNA extraction from whole blood on a centrifugal microfluidic device. Lab Chip 7(5):565–573. doi:10.1039/B616115D
Ducrée J, Haeberle S, Lutz S, Pausch S, Stetten FV, Zengerle R (2007) The centrifugal microfluidic Bio-Disk platform. J Micromech Microeng 17(7):S103–S115. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/17/7/S07
Garcia-Cordero JL, Barrett LM, Kennedy RO, Ricco AJ (2010a) Microfluidic sedimentation cytometer for milk quality and bovine mastitis monitoring. Biomed Microdevices 12(6):1051–1059. doi:10.1007/s10544-010-9459-5
Garcia-Cordero JL, Basabe-Desmonts L, Ducrée J, Ricco AJ (2010b) Liquid recirculation in microfluidic channels by the interplay of capillary and centrifugal forces. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(4):695–703. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0585-4
Garcia-Cordero JL, Kurzbuch D, Benito-Lopez F, Diamond D, Lee LP, Ricco AJ (2010c) Optically addressable single-use microfluidic valves by laser printer lithography. Lab Chip 10(20):2680–2687. doi:10.1039/c004980h
Gorkin R, Park J, Siegrist J, Amasia M, Lee S, Park JM, Kim J, Kim H, Madou M, Cho YK (2010a) Centrifugal microfluidics for biomedical applications. Lab Chip 10(14):1758–1773. doi:10.1039/b924109d
Gorkin R, Clime L, Madou M, Kido H (2010b) Pneumatic pumping in centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(2):541–549. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0571-x
Ha SM, Cho W, Ahn Y (2009) Disposable thermo-pneumatic micropump for bio lab-on-a-chip application. Microelectron Eng 86(4–6):1337–1339. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2008.12.046
Haeberle S, Brenner T, Zengerle R, Ducrée J (2006) Centrifugal extraction of plasma from whole blood on a rotating disk. Lab Chip 6(6):776–781. doi:10.1039/b604145k
Handique K, Burke DT, Mastrangelo CH, Burns MA (2001) On-chip thermopneumatic pressure for discrete drop pumping. Anal Chem 73(8):1831–1838
Kim J, Kido H, Rangel RH, Madou M (2008) Passive flow switching valves on a centrifugal microfluidic platform. Sens Actuators B 128(2):613–621. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2007.07.079
Kong MCR, Salin ED (2010) Pneumatically pumping fluids radially inward on centrifugal microfluidic platforms in motion. Anal Chem 82(19):8039–8041. doi:10.1021/ac102071b
Lee BS, Lee YU, Kim HS, Kim TH, Park J, Lee JG, Kim J, Kim H, Lee WG, Cho YK (2011) Fully integrated lab-on-a-disc for simultaneous analysis of biochemistry and immunoassay from whole blood. Lab Chip 11(1):70–78. doi:10.1039/c0lc00205d
Madou M, Zoval J, Jia G, Kido H, Kim J, Kim N (2006) Lab on a CD. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8(1):601–628. doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.8.061505.095758
Noroozi Z, Kido H, Micic M, Pan H, Bartolome C, Princevac M, Zoval J, Madou M (2009) Reciprocating flow-based centrifugal microfluidics mixer. Rev Sci Instrum 80(7):075102. doi:10.1063/1.3169508
Siegrist J, Amasia M, Singh N, Banerjee D, Madou M (2010a) Numerical modeling and experimental validation of uniform microchamber filling in centrifugal microfluidics. Lab Chip 10(7):876–886. doi:10.1039/b917880e
Siegrist J, Gorkin R, Clime L, Roy E, Peytavi R, Kido H, Bergeron M, Veres T, Madou M (2010b) Serial siphon valving for centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(1):55–63. doi:10.1007/s10404-009-0523-5
Song WH, Lichtenberg J (2005) Thermo-pneumatic, single-stroke micropump. J Micromech Microeng 15(8):1425–1432. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/8/007
Steigert J, Grumann M, Brenner T, Riegger L, Harter J, Zengerle R, Ducrée J (2006) Fully integrated whole blood testing by real-time absorption measurement on a centrifugal platform. Lab Chip 6(8):1040–1044. doi:10.1039/b607051p
Xi Y, Duford DA, Salin ED (2010) Automated liquid-solid extraction of pyrene from soil on centrifugal microfluidic devices. Talanta 82(3):1072–1076. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2010.06.007
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the WCU (World Class University) program (R32-2008-000-20054-0) and Genome Québec for funding of the presented research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abi-Samra, K., Clime, L., Kong, L. et al. Thermo-pneumatic pumping in centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid Nanofluid 11, 643–652 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0830-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0830-5