Abstract
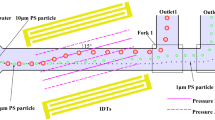
This article presents a novel technique for the continuous sorting and collection of microparticles in a microfluidic chip using a cascaded squeeze effect. In the proposed approach, microparticles of different sizes are separated from the sample stream using sheath flows and are then directed to specific side channels for collection. The sheath flows required to separate the particles are generated using a single high voltage supply integrated with a series of variable resistors designed to create electric fields of different intensities at different points of the microchip. Numerical simulations are performed to analyze the electrical potential contours and flow streamlines within the microchannel. Experimental trials show that the microchip is capable of continuously separating microparticles with diameters of 5, 10 and 20 μm, respectively. To further evaluate the performance of the microchip, a sample composed of yeast cells and polystyrene beads is sorted and collected. The results indicate that the microchip achieves a recovery ratio of 87.7% and a yield ratio of 94.1% for the yeast cells and therefore attains a comparable performance to that of a large-scale commercial flow cytometer. Importantly, the high performance of the microchip is achieved without the need for a complex control system or for sophisticated actuation mechanisms such as embedded microelectrodes, ultrasonic generators, or micropumps, and so forth.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhagat AAS, Kuntaegowdanahalli SS, Papautsky I (2008) Enhanced particle filtration in straight microchannels using shear-modulated inertial migration. Phys Fluids 20:101702
Brown M, Wittwer C (2000) Flow cytometry: principles and clinical applications in hematology. Clin Chem 46:1221–1229
Chen D, Du H (2007) A dielectrophoretic barrier-based microsystem for separation of microparticles. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:603–610
Chen HT, Wang YN (2008) Fluorescence detection in a micro flow cytometer without on-chip fibers. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:689–694
Choi S, Song S, Choi C, Park JK (2007) Continuous blood cell separation by hydrophoretic filtration. Lab Chip 7:1532–1538
Chung TD, Kim HC (2007) Recent advances in miniaturized microfluidic flow cytometry for clinical use. Electrophoresis 28:4511–4520
Di Carlo D, Irimia D, Tompkins RG, Toner M (2007) Continuous inertial focusing, ordering, and separation of particles in microchannels. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:18892–18897
Di Carlo D, Edd JF, Irimia D, Tompkins RG, Toner M (2008) Equilibrium separation and filtration of particles using differential inertial focusing. Anal Chem 80:2204–2211
Durr M, Kentsch J, Muller T, Schnelle T, Stelzle M (2003) Microdevices for manipulation and accumulation of micro- and nanoparticles by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 24:722–731
Ferrari BC, Oregaard G, Sørensen SJ (2004) Recovery of GFP-labeled bacteria for culturing and molecular analysis after cell sorting using a benchtop flow cytometer. Microbial Ecol 48:239–245
Fu LM, Lin CH (2007) A rapid DNA digestion system. Biomed Microdevices 9:277–286
Fu AY, Spence C, Scherer A, Arnold FH, Quake SR (1999) A microfabricated fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Nat Biotechnol 17:1109–1111
Fu LM, Yang RJ, Lee GB, Pan YJ (2003) Multiple injection techniques for microfluidic sample handling. Electrophoresis 24:3026–3032
Fu LM, Lee GB, Lin YH, Yang RJ (2004a) Manipulation of microparticles using new modes of travelling-wave-dielectrophoretic forces: numerical simulation and experiments. IEEE-ASME Trans Mechatron 9:377–383
Fu LM, Yang RJ, Lin CH, Pan YJ, Lee GB (2004b) Electrokinetically-driven micro flow cytometers with integrated optical waveguides for on-line cell/particle detection. Anal Chim Acta 507:163–169
Fu LM, Yang RJ, Lin CH, Chien YS (2005) A novel microfluidic mixer utilizing electrokinetic driving forces under low switching frequency. Electrophoresis 26:1814–1824
Fu LM, Tsai CH, Lin CH (2008) A high-discernment micro-flow cytometer with micro-weir structure. Electrophoresis 29:1874–1878
Gast FU, Dittrich PS, Schwille P, Weigel M, Mertig M, Opitz J, Queitsch U, Diez S, Lincoln B, Wottawah F, Schinkinger S, Guck J, Käs J, SmolinskiJ SalchertK, Werner C, Duschl C, Jäger MS, Uhlig K, Geggier P, Howitz S (2006) The microscopy cell (MicCell), a versatile modular flowthrough system for cell biology, biomaterial research, and nanotechnology. Microfluid Nanofluid 2:21–36
Hashimoto M, Garstecki P, Whitesides GM (2007) Synthesis of composite emulsions and complex foams with the use of microfluidic flow-focusing devices. Small 3:1792–1802
Holmes D, Green NG, Morgan H (2003) Microdevices for dielectrophoretic flow-through cell separation. IEEE Eng Med Biol 22:85–90
Huang LR, Cox EC, Austin RH, Sturm JC (2004) Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 304:987–990
Hunt HC, Wilkinson JS (2008) Optofluidic integration for microanalysis. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:53–79
Kang JH, Park JK (2007) Magnetophoretic continuous purification of single-walled carbon nanotubes from catalytic impurities in a microfluidic device. Small 3:1784–1791
Lee GB, Lin CH, Lee GH, Lin YF (2005) On the surface modification of microchannels for micro capillary electrophoresis chips. Electrophoresis 26:4616–4624
Lim CT, Zhang Y (2007) Novel dome-shaped structures for high-efficiency patterning of individual microbeads in a microfluidic device. Small 3:573–579
Lin CH, Lee GB (2003) Micromachined flow cytometers with embedded etched optic fibers for optical detection. J Micromech Microeng 13:447–453
Lin CH, Lee GB, Lin YH, Chang GL (2001) A fast prototyping process for fabrication of microfluidic systems on soda-lime glass. J Micromech Microeng 11:726–732
Lin CH, Lee GB, Fu LM, Hwey BH (2004) Vertical focusing device utilizing dielectrophoretic force and its application on microflow cytometer. J Microelectromech Syst 13:923–932
Lin CC, Chen A, Lin CH (2008a) Microfluidic cell counter/sorter utilizing multiple particle tracing technique and optically switching approach. Biomed Microdevices 10:55–63
Lin CH, Wang JH, Fu LM (2008b) Improving the separation efficiency of DNA biosamples in capillary electrophoresis microchips using high-voltage pulsed DC electric fields. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:403–410
McCloskey KE, Chalmers JJ, Zborowski M (2003) Magnetic cell separation: characterization of magnetophoretic mobility. Anal Chem 75:6868–6874
Moon J, Kim SH, Cho J (2006) Characterizations of natural organic matter as nano particle using flow field-flow fractionation. Colloid Surface A 287:232–236
Prikulis J, Svedberg F, Käll M, Enger J, Ramser K, Goksor M, Hanstorp D (2004) Optical spectroscopy of single trapped metal nanoparticles in solution. Nano Lett 4:115–118
Rodriguez-Trujillo R, Mills CA, Samitier J, Gomila G (2007) Low cost micro-Coulter counter with hydrodynamic focusing. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:171–176
Schrum DP, Culbertson CT, Jacobson SC, Ramsey JM (1999) Microchip flow cytometry using electrokinetic focusing. Anal Chem 71:4173–4177
Seo D, Agca Y, Feng ZC, Critser JK (2007) Development of sorting, aligning, and orienting motile sperm using microfluidic device operated by hydrostatic pressure. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:561–570
Suzuki H, Ho CM, Kasagi N (2004) A chaotic mixer for magnetic bead-based micro cell sorter. J Microelectromech Syst 13:779–790
Takagi J, Yamada M, Yasuda M, Seki M (2005) Continuous particle separation in a microchannel having asymmetrically arranged multiple branches. Lab Chip 5:778–784
Tsai CH, Chen HT, Wang YN, Lin CH, Fu LM (2007) Capabilities and limitations of 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional numerical methods in modeling the fluid flow in sudden expansion microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:13–18
Tsai CH, Hou HH, Fu LM (2008) An optimal three-dimensional focusing technique for micro-flow cytometers. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:827–836
Wang MM, Tu E, Raymond DE, Yang JM, Zhang HC, Hagen N, Dees B, Mercer EM, Forster AH, Kariv I, Marchand PJ, Butler WF (2005) Microfluidic sorting of mammalian cells by optical force switching. Nat Biotechnol 23:83–87
Yamada M, Seki M (2006) Microfluidic particle sorter employing flow splitting and recombinig. Anal Chem 78:1357–1362
Yamada M, Nakashima M, Seki M (2004) Pinched flow fractionation: continuous size separation of particles utilizing a laminar flow profile in a pinched microchannel. Anal Chem 76:5465–5471
Yang AS, Hsieh WH (2007) Hydrodynamic focusing investigation in a micro-flow cytometer. Biomed Microdevices 9:113–122
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial support provided by the National Science Council in Taiwan (NSC97-2221-E-110-018-MY3 and NSC97-2320-B-020 -001-MY3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CH., Lee, CY., Tsai, CH. et al. Novel continuous particle sorting in microfluidic chip utilizing cascaded squeeze effect. Microfluid Nanofluid 7, 499 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0403-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0403-z