Abstract
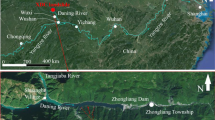
At 4:40p.m. on November 23, 2008, the Gongjiafang slope collapsed on the north bank of Yangtze River in Wu Gorge of Three Gorges Reservoir. The 380,000-m3 sliding mass consisted mainly of cataclastic rock. A video record of the major sliding incident was analyzed using the general laws of physical motion. The analysis indicated that the maximum speed and maximum acceleration of the sliding mass were 11.65 m/s and 2.23 m/s2, respectively, and that the maximum amplitude and the propagation velocity of the water wave near the landslide were 31.8 m and 18.36 m/s, respectively. Wave run-up investigation indicated that the maximum run-up on shore was 13.1 m, which declined to 1.1 m at Wushan dock 4 km away. The incident causes no casualties, but did result in economic losses of RMB five million. The numerical simulation model GEOWAVE was used to simulate and reproduced the impulse wave generated by the landslide; the results were in good agreement with the observed incident. The numerical simulation data were then applied to analyze the decay and amplification effects of the landslide wave in the river course. The field investigations and witness information provide valuable materials for the studies of landslide kinematics and impulse waves generated by landslides. In addition, the research results provide a useful reference for future similar waves generated by landslides in reservoirs.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Applied Fluids Engineering Inc., Center for Applied Coastal Research (2008) Geowave 11 tutorial. University of Delaware, Newark
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Malek-Mohammadi S (2007) Near field amplitude of sub-aerial landslide generated waves in dam reservoirs. Dam Eng XVII 4:197–222
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Yavari-Ramshe S (2011) Numerical simulation of wave generated by landslide incidents in dam reservoirs. Landslides. doi:10.1007/S10346-011-0258-8
Bolin H, Lide C, Xuanming P, Guanning L, Xiaoting C, Haogang D, Tianci L (2010) Assessment of the risk of rockfalls in Wu Gorge, Three Gorges, China. Landslides 7(1):1–11
Fritz HM, Hager WH, Minor HE (2004) Near field characteristics of landslide generated impulse waves. ASCE J Waterway, Port, Coastal and Ocean Eng 130:287–302
Fuchs H, Heller V, Hager W (2010) Impulse wave run-over: experimental benchmark study for numerical modeling. Exp Fluids 49:985–1004
Yusheng L (2010) Some importance potential geohazard in Three Gorges Reservoir of Chongqing City. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control 21(1):133–135
Rahiman T, Pettinga J, Watts P (2007) The source mechanism and numerical modeling of the 1953 Suva tsunami, Fiji. Mar Geol 237:55–70
Tappin DR, Watts P, Grilli ST (2008) The Papua New Guinea tsunami of 17 July 1998: anatomy of a catastrophic event. Nat Haz Earth Syst Sci NHESS 8:243–266
Tinti S, Bortolucci E (2000) Energy of water waves induced by submarine landslides. Pure Appl Geophys 157:281–318
Walder JS, Watts P, Sorensen OE, Janssen K (2003) Tsunamis generated by subaerial mass flows. J Geophys Res 108(B5):2236–2255
Watts P, Grilli ST, Kirby JT, Fryer GJ, Tappin DR (2003) Landslide tsunami case studies using a Boussinesq model and a fully nonlinear tsunami generation model. Nat Haz Earth Syst Sci, EGU 3(5):391–402
Yichang Institute of Geology & Mineral Resource (2001) Geological map of Wushan Town in China
Zhang Z, Wang S, Wang L (1997) Principle of engineering geology analysis. Chinese Geology, Beijing, pp 338–340
107 Team of Chongqing Municipal Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development (2009) Gongjiafang–Dulong slope stability investigation report of Wushan County, Chongqing City
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the China Geological Survey (project ID 1212011014027). We would like to express our gratitude to our friends: Prof. Guangze Peng, Prof. Fei Ma, Prof. Zhongfu Chen, and Engr. Huang Zhou from Chongqing Three Gorges Reservoir Geological Hazards Prevention and Control Office for supplying us with necessary data. We also want to thank Prof. Changsheng Huang and Prof. Lide Chen from Wuhan Center of China Geological Survey for providing us with a relaxed working environment and favorable writing atmosphere. Finally, we want to thank Dr. Philip Watts who helped us register for GEOWAVE and helped us much in using GEOWAVE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, B., Yin, Y., Liu, G. et al. Analysis of waves generated by Gongjiafang landslide in Wu Gorge, three Gorges reservoir, on November 23, 2008. Landslides 9, 395–405 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-012-0331-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-012-0331-y