Abstract
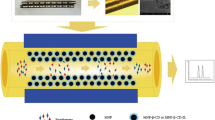
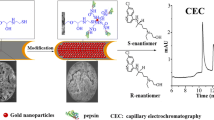
A newly-developed method of complete separation and sensitive determination of o-, m-, and p-aminobenzoic acid isomers was achieved by combining open-tubular columns for capillary electrochromatography (OT-CEC) and online sample stacking. In this study, spherical gold nanoparticles were modified by a covalent attachment of mono-6-thio-β-cyclodextrin, and OT-CEC was formed by immobilizing cyclodextrin-modified gold nanoparticles (CD-AuNP) on prederivatized 3-mercaptopropyl-trimethoxysilane fused-silica capillaries. Based on the theory of moving chemical reaction boundary, effects of several important factors such as the pH and concentration of running buffer and the conditions of stacking analytes were optimized. The optimized separations were carried out in 58 mmol/L HAc buffer at pH 3.0 using a capillary coated with CD-AuNP, while the optimized concentration was carried out in 50 mmol/L disodium hydrogen phosphate (pH 9.5). The linear ranges for m-, p-, and o-aminobenzoic acid were from 5.0 × 10−4–0.1, 5.0 × 10−4–0.1 and 1.0 × 10−4–0.1 mmol/L, respectively. And the detection limits (S/N = 3) were as low as 8.22 × 10−5, 8.21 × 10−5, and 3.76 × 10−5 mmol/L for m-, p-, and o-aminobenzoic acid, respectively. The run-to-run, day-to-day, and column-to-column reproducibilities of migration time were satisfactory with relative standard deviation values of less than 4.5 % in all cases. This method was successfully used in determining procaine hydrochloride injection sample with recoveries in the range of 96.1–106.6 % and relative standard deviations less than 5.0 %.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boughtflower RJ, Underwood T, Paterson CJ (1995) Chromatographia 40:329–335
Gübitz G, Schmid MG (2008) J Chromatogr A 1204:140–156
Guihen E, Glennon JD (2004) J Chromatogr A 1044:67–81
Wang YC, Zeng ZR, Xie CH, Guan N, Fu EQ, Cheng JK (2001) Chromatographia 54:475–479
Nilsson C, Birnbaum S, Nilsson S (2007) J Chromatogr A 1168:212–224
Yu CJ, Su CL, Tseng WL (2006) Anal Chem 78:8004–8010
Li M, Liu X, Jiang F, Guo L, Yang L (2011) J Chromatogr A 1218:3725–3729
Hongjun E, Yang Y, Su P, Zhang W (2009) J Anal Chem 64:393–397
Dai R, Tang L, Li H, Deng Y, Fu R, Parveen Z (2007) J Appl Polym Sci 106:2041–2046
Wang Y, Zeng Z, Guan N, Cheng J (2001) Electrophoresis 22:2167–2172
Frost NW, Jing M, Bowser MT (2010) Anal Chem 82:4682–4698
Zhu Z, Zhou X, Yan N, Zhou L, Chen X (2010) J Chromatogr A 217:1856–1861
Cao CX, He YZ, Li M, Qian YT, Yang L, Qu QS, Zhou SL, Chen WK (2002) J Chromatogr A 952:39–46
Cao CX, He YZ, Li M, Qian YT, Gao MF, Ge LH, Zhou SL, Yang L, Qu QS (2002) Anal Chem 74:4167–4174
Burgi DS (1993) Anal Chem 65:3726–3729
Chien RL, Burgi DS (1992) Anal Chem 64:489A–496A
Quirino JP, Iwai Y, Otsuka K, Terabe S (2000) Electrophoresis 21:2899–2903
Quirino JP, Terabe S (1999) Anal Chem 71:1638–1644
Quirino JP, Terabe S (2000) Anal Chem 72:1023–1030
Kim B, Chung DS (2002) Electrophoresis 23:49–55
Weiss DJ, Saunders K, Lunte CE (2001) Electrophoresis 22:59–65
He JF, Yang WY, Yao FJ, Zhao H, Li XJ, Yuan ZB (2011) J Chromatogr A 1218:3816–3821
Frost NW, Jing M, Bowser MT (2010) Anal Chem 82:4682-4698
Zhu W, Zhang W, Fan LY, Shao J, Li S, Chen JL, Cao CX (2009) Talanta 78:1194–1200
Jiang S, ter Horst JH, Jansens PJ (2007) Cryst Growth Des 8:37–43
Svärd M, Nordström FL, Jasnobulka T, Rasmuson ÅC (2009) Cryst Growth Des 10:195–204
He Y, Wu C, Kong W (2005) J Phys Chem 109:748–753
Terekhova IV (2009) Mendeleev Commun 19:110–112
Tatsuya Kitade KK (1998) Yutaka Wada. Anal Chim Acta 367:33–39
Panadero S, Gómez-Hens A, Pérez-Bendito D (1998) Talanta 45:829–834
Chen Y, Han FM, Yuan ZB (1996) Chin J Anal Lab 15:55–57
Turkevich J (1985) Gold Bull 18:86–91
Jiang Y, Zhao H, Zhu NN, Lin YQ, Yu P, Mao LQ (2008) Angew. Chem Int Ed 47:8601–8604
Liang X, Wei H, Cui Z, Deng J, Zhang Z, You X, Zhang XE (2011) Analyst 136:179–183
Řezanka P, Navrátilová K, Žvátora P, Sýkora D, Matějka P, Mikšík I, Kašička V, Král V (2011) J Nanopart Res 13:5947–5957
Shuang SM, Yang Y, Pan JH (2002) Anal Chim Acta 458:305–310
Bartle KD, Myers P (2001) J Chromatogr A 916:3–23
Yang Y, Shuang SM, Chao JB (2004) Acta Chim Sin 62:176–182
Cao CX, Zhang W, Qin WH, Li S, Zhu W, Liu W (2005) Anal Chem 77:955–963
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21145006) and the Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig S1 UV–Vis spectroscopy of CD-AuNP dispersed in water.
Fig S2 Influence of pH on migration time. HAc buffer with concentration of 60 mmol/L and pH of 2.5, 2.75, 3.0, 3.25, 3.5, and 4.0 were used as the running buffer.
Fig S3 Effect of concentration on migration time. HAc buffer with pH of 3.0 and concentrations of HAcbuffer from 10 to 80 mM were used as the running buffer.
Fig S4 The comparisons of six different buffer salts on stacking results in the MCRB system. Concentration of buffer salt, 50 mmol/L, modulated with H2SO4 or NaOH to pH 9.0.
Fig S5 Influence of disodium hydrogen phosphate pH on stacking result in MCRB. Concentration of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 50 mmol/L, modulated with H2SO4 or NaOH to desired pH.
Fig S6 Influence of disodium hydrogen phosphate concentration on stacking result in MCRB. Concentrations of 58 mmol/L HAc buffer at pH 3.0 and 50 mmol/L at pH 9.5 hydrogen phosphate as stacking buffer.
Fig S7 The electrophoregrams of aminobenzoic acid isomers with normal CZE modeand with the online MCRB stacking mode under the optimized conditions,respectively. Peak identification: 1 m-aminobenzoic acid, 2 p-aminobenzoic acid, 3 o-aminobenzoic acid. Separation conditions: 58 mmol/L HAc buffer at pH 3.0, 50 mmol/L hydrogen phosphate (pH 9.5) as stacking buffer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Dong, Y., Cui, H. et al. Cyclodextrin-Modified Gold Nanoparticle Capillary Electrochromatography with Online Sample Stacking for Simultaneous and Sensitive Determination of Aminobenzoic Acid Isomers. Chromatographia 77, 821–828 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-014-2686-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-014-2686-9