Abstract
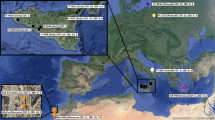
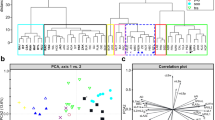
Greater and lesser spotted eagles (Aquila clanga, A. pomarina) are two closely related forest eagles overlapping in breeding range in east-central Europe. In recent years a number of mixed pairs have been observed, some of which fledged hybrid young. Here we use mitochondrial (control region) DNA sequences and AFLP markers to estimate genetic differentiation and possible gene flow between these species. In a sample of 83 individuals (61 pomarina, 20 clanga, 2 F1-hybrids) we found 30 mitochondrial haplotypes which, in a phylogenetic network, formed two distinct clusters differing on average by 3.0% sequence divergence. The two species were significantly differentiated both at the mitochondrial and nuclear (AFLP) genetic level. However, five individuals with pomarina phenotype possessed clanga-type mtDNA, suggesting occasional gene flow. Surprisingly, AFLP markers indicated that these “mismatched” birds (originating from Germany, E Poland and Latvia) were genetically intermediate between the samples of individuals in which mtDNA haplotype and phenotype agreed. This indicates that mismatched birds were either F1 or recent back-cross hybrids. Mitochondrial introgression was asymmetrical (no pomarina haplotype found in clanga so far), which may be due to assortative mating by size. Gene flow of nuclear markers was estimated to be about ten times stronger than for mtDNA, indicating a sex-bias in hybrid fertility in accordance with Haldane’s rule. Hybridization between the two species may be more frequent and may occur much further west than hitherto assumed. This is supported by the recent discovery of a mixed pair producing at least one fledgling in NE Germany.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker AJ, Marshall HD (1996) Mitochondrial control-region sequences as tools for understanding the evolution of avian taxa. In: Mindell DP (ed) Avian molecular systematics and evolution. Academic Press, London, pp 51–82
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16:37–48
Bensch S, Helbig AJ, Salomon M, Seibold I (2002a) AFLP analysis identifies hybrids between two subspecies of warblers. Mol Ecol 11:473–481
Bensch S, Åkesson S, Irwin D (2002b) The use of AFLP to find an informative SNP: genetic differences across a migratory divide in willow warblers. Mol Ecol 11:2359–2366
Bergmanis U (1996) On the taxonomy of the Lesser Spotted Eagle Aquila pomarina and Greater Spotted Eagle A clanga. In: Meyburg BU, Chancellor RD (eds) Eagle Studies. World Working. Group Birds of Prey, Berlin, pp 199–207
Bergmanis U, Petrins A, Strazds M, Krams I (2001) Probable case of hybridization of Greater Aquila clanga and Lesser Spotted Eagle A. pomarina in Eastern Latvia. Acta Ornithoecol 4:297–304
Cramp S (ed) et al (1980) The Birds of the Western Palearctic, vol 2. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 203–216
Dombrovski VC (2002) Hybridization of lesser and greater spotted eagles (Aquila pomarina et A clanga) in Belarus: rule or exception? Subbuteo 5:23–31
Duchesne P, Bernatchez L (2002) AFLPOP: a computer program for simulated and real population allocation, based on AFLP data. Mol Ecol Notes 2:380–383
Fefelov IV (2001) Comparative breeding ecology and hybridization of Eastern and Western Marsh Harriers Circus spilonotus and C aeruginosus in the Baikal region of eastern Siberia. Ibis 143:587–592
Forsman D (1999) The Raptors of Europe and the Middle East: a handbook of field identification. Poyser, London
Grant PR, Grant BR (1992) Hybridization of bird species. Science 256: 193–197
Hagemeijer WJM, Blair MJ (eds) (1997) The EBCC Atlas of European Breeding Birds: their distribution and abundance. Poyser, London
Haldane JBS (1922) Sex ratio and unisexual sterility in hybrid animals. J Genetics 12:101–109
Helbig AJ, Seibold I (1999) Molecular phylogeny of Palearctic-African Acrocephalus and Hippolais warblers (Aves: Sylviidae). Mol Phylogen Evol 11:246–260
Helbig AJ, Salomon M, Bensch S, Seibold I (2001) Male-biased gene flow across an avian hybrid zone: evidence from mitochondrial and microsatellite DNA. J Evol Biol 14:277–287
Helbig AJ, Kocum A, Seibold I, Braun MJ (2005) A multi-gene phylogeny of Aquiline eagles (Aves: Accipitriformes) reveals extensive paraphyly at the genus level. Mol Phylogen Evol 35:147–164
Hewitt GM (2000) The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature 405:907–913
Huntley B (1990) European vegetation history: palaeovegetation maps from pollen data - 13,000 yr BP to present. J Quater Sci 5: 103–122
Lõhmus A, Väli Ü (2001) Interbreeding of the Greater Aquila clanga and Lesser Spotted Eagle A pomarina. Acta Ornithoecol 4: 377–384
Liebers D, Helbig AJ, de Knijff P (2001) Genetic differentiation and phylogeography of gulls in the Larus fuscus - cachinnans group (Aves: Charadriiformes): inferences from mitochondrial control region sequences. Mol Ecol 10:2447–2462
Meyburg BU, Scheller W, Meyburg C (1995) Zug und Überwinterung des Schreiadlers Aquila pomarina: Satellitentelemetrische Untersuchungen. J Ornithol 136:401–422
Meyburg BU, Haraszthy L, Strazds M, Schäffer N (2001) European species action plan for greater spotted eagle. In: Schäffer N, Gallo-Orsi U (eds) European Union Action Plans for Eight Priority Birds Species. Europ Comm, Luxembourg
Meyburg BU, Meyburg C, Bělka T, Sreibr O, Vrana J (2004) Migration, wintering and breeding of a lesser spotted eagle (Aquila pomarina) from Slovakia tracked by satellite. J Ornithol 145:1–7
Miller SA, Dykes DO, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucl Acid Res 16:1215
Mindell DP, Sorenson MD, Dimcheff DE (1998) Multiple independent origins of mitochondrial gene order in birds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 10693–10697
Paetkau D, Waits LP, Clarkson PL, Craighead L, Strobeck C (1997) An empirical evaluation of genetic distance statistics using microsatellite data from bear (Ursidae) populations. Genetics 147:1943–1957
Porter RF, Willis I, Christensen S, Nielsen BP (1974) Flight identification of European raptors. Poyser, Calton
Röhl A (2004) Network vers 4.1 A program package for calculating phylogenetic networks. Mathematisches Seminar, University of Hamburg. http://www.fluxus-engineering.com
Schmidt HA, Strimmer K, Vingron M, von Haeseler A (2000) TREE-PUZZLE 5.0. http://www.tree-puzzle.de
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L (2000) ARLEQUIN vers. 2.0. A software for population genetic data analysis. University of Geneva, Switzerland. (http://anthro.unige.ch/arlequin)
Short LL (1969) Taxonomic aspects of avian hybridization. Auk 86:84–105
Strimmer K, von Haeseler A (1997) Likelihood mapping: a simple method to visualize phylogenetic content of a sequence alignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6815–6819
Svensson L (1975) Större skrikörn Aquila clanga och mindre skrikörn A pomarina - problemet att artbestämma dem. Var Fagelvarld 34:1–26
Tegelström H, Gelter HP (1990) Haldane’s rule and sex-biased gene flow between two hybridizing flycatcher species (Ficedula albicollis and F hypoleuca, Aves: Muscicapidae). Evolution 44:2012–2021
Väli Ü (2002): Mitochondrial pseudo-control region in old world eagles (genus Aquila). Mol Ecol 11:2189–2194
Väli Ü (2003): The lesser spotted eagle and its conservation in Estonia. Hirundo Suppl 6:1–64
Väli Ü, Lõhmus A (2004) Nestling characteristics and identification of the lesser spotted eagle Aquila pomarina, greater spotted eagle A clanga, and their hybrids. J Ornithol 145:256–263
Väli Ü, Treinys R, Poirazidis K (2004) Genetic structure of Greater Aquila clanga and Lesser Spotted Eagle A pomarina populations: implications for phylogeography and conservation. In: Chancellor RD, Meyburg BU (eds) Raptors Worldwide. World Working Group on Birds of Prey & BirdLife Hungary, Budapest, pp 473–482
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Lee T van der, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP - a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang Z, Baker AJ, Hill GE, Edwards SV (2003) Reconciling actual and inferred population histories in the House Finch (Carpodacus mexicanus) by AFLP analysis. Evolution 57:2852–2864
Waser PM, Strobeck C (1998) Genetic signatures of interpopulation dispersal. Trends Ecol Evol 13:43–44
Wu, CI, Davis AW (1993) Evolution of postmating reproductive isolation— the composite nature of Haldane’s rule and its genetic bases. Am Nat 142:187–212
Zhezherin VD (1969) On taxonomic interrelations of Aquila clanga Pall. and Aquila pomarina Brehm. Zbirn Prats Zool Muz Kiev (Ukrainian with English summary) 33:91–97
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Maciorowski, T. Mizera and H. Shirihai for help with the sampling and J.-P. Schwanbeck for sharing information about a mixed pair he discovered in NE Germany. The study was financially supported by grants of Bundesministerium für Forschung und Technologie (to A.J.H.) and the Swedish Research Council (to S.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Bairlein
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helbig, A.J., Seibold, I., Kocum, A. et al. Genetic differentiation and hybridization between greater and lesser spotted eagles (Accipitriformes:Aquila clanga, A. pomarina). J Ornithol 146, 226–234 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10336-005-0083-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10336-005-0083-8