Abstract
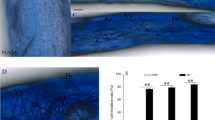
To advance our understanding of the effects of inoculation with ectomycorrhizal fungi (EMF) on seedling colonization in mine wastelands, we conducted a field experiment in a copper tailing. Six-month-old seedlings of Japanese red pine (Pinus densiflora) and oak (Quercus variabilis) separately inoculated with three EMF species (Pisolithus sp., Cenococcum geophilum, Laccaria laccata) were transplanted to the copper tailing. The survival rates of tree seedlings were monitored monthly, and growth (biomass and height), contents of nutrients and heavy metals (K, P, Ca, Mg, Cu, Zn), and mycorrhizal infection rates of seedlings were determined 6 months after planting. Oak seedlings exhibited higher survival rates than pine seedlings after 6 months of growth on the tailing. EMF inoculations of pine seedlings significantly enhanced their survival, growth, and nutrient uptake. In contrast, EMF inoculations of oak seedlings improved growth only in terms of biomass. Additionally, EMF inoculation caused pine seedlings to accumulate more Cu and Zn in roots compared to non-inoculated seedlings, whereas inoculation inhibited the accumulation of heavy metals in shoots. However, similar results were not observed in oak seedlings. Observations of roots indicated that the rates of mycorrhizal infection of both tree species had dramatically declined at harvest time. In conclusion, ectomycorrhizal symbioses can improve the survival and performance of pine seedlings in mine tailings. The present study provided direct evidence of the importance of EMF inoculation of seedlings to the reforestation of mine wastelands.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriaensen K, Vrålstad T, Noben J-P, Vangronsveld J, Colpaert JV (2005) Copper-adapted Suillus luteus, a symbiotic solution for pines colonizing Cu mine spoils. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7279–7284
Adriaensen K, Vangronsveld J, Colpaert Jan V (2006) Zinc-tolerant Suillus bovinus improves growth of Zn-exposed Pinus sylvestris seedlings. Mycorrhiza 16:553–558
Arocena JM, Glowa KR (2000) Mineral weathering in ectomycorrhizosphere of subalpine fir (Abies lasiocarpa (Hook.) Nutt.) as revealed by soil solution composition. For Ecol Manag 133:61–70
Bellion M, Courbot M, Jacob C, Blaudez D, Chalot M (2006) Extracellular and cellular mechanisms sustaining metal tolerance in ectomycorrhizal fungi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 254:173–181
Bellion M, Courbot M, Jacob C, Guinet F, Blaudez D, Chalot M (2007) Metal induction of a Paxillus involutus metallothionein and its heterologous expression in Hebeloma cylindrosporum. New Phytol 174:151–158
Blaudez D, Chalot M (2011) Characterization of the ER-located zinc transporter ZnT1 and identification of a vesicular zinc storage compartment in Hebeloma cylindrosporum. Fungal Genet Biol 48:496–503
Blaudez D, Jacob C, Turnau K, Colpaert JV, Ahonen-jonnarth U, Finlay R, Botton B, Chalot M (2000) Differential responses of ectomycorrhizal fungi to heavy metals in vitro. Mycol Res 104:1366–1371
Burken JG, Schnoor JL (1997) Uptake and metabolism of atrazine by poplar trees. Environ Sci Technol 31:1399–1406
Chappelka A, Kush J, Runion GB, Meier S, Kelley WD (1991) Effects of soil-applied lead on seedling growth and ectomycorrhizal colonization of loblolly pine. Environ Pollut 72:307–316
Chen Y, Nara K, Wen Z, Shi L, Xia Y, Shen Z, Lian C (2015) Growth and photosynthetic responses of ectomycorrhizal pine seedlings exposed to elevated Cu in soils. Mycorrhiza. doi:10.1007/s00572-015-0629-4
Donnelly PK, Fletcher JS (1994) Potential use of mycorrhizal fungi as bioremediation agents. ACS Symp Ser 563:93–99
Gebhardt S, Neubert K, Wöllecke J, Münzenberger B, Hüttl RF (2007) Ectomycorrhiza communities of red oak (Quercus rubra L.) of different age in the Lusatian lignite mining district, East Germany. Mycorrhiza 17:279–290
Gonzalez-Guerrero M, Oger E, Benabdellah K, Azcn-Aguilar C, Lanfranco L, Ferrol N (2010) Characterization of a CuZn superoxide dismutase gene in the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices. Curr Genet 56:265–274
Hartley J, Cairney JWG, Sanders F, Meharg AA (1997) Toxic interactions of metal ions (Cd2+, Pb2+, Zn2+ and Sb3−) on in vitro biomass production of ectomycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 137:551–562
Hrynkiewicz K, Baum C, Niedojadlo J, Dahm H (2008) Promotion of mycorrhiza formation and growth of willows by the bacterial strain Sphingomonas sp. 23L on fly ash. Biol Fertil Soils 45:385–394
Huang J, Nara K, Lian C, Zong K, Peng K, Xue S, Shen G (2012) Ectomycorrhizal fungal communities associated with Masson pine (Pinus massoniana Lamb.) in Pb–Zn mine sites of central south China. Mycorrhiza 22:589–602
Huang J, Nara K, Zong K, Wang J, Xue S, Peng K, Shen G, Lian C (2014) Ectomycorrhizal fungal communities associated with Masson pine (Pinus massoniana) and white oak (Quercus fabri) in a manganese mining region in Hunan Province, China. Fungal Ecol 9:1–10
Jentschke G, Godbold DL (2000) Metal toxicity and ectomycorrhizas. Physiol Plant 109:107–116
Krznaric E, Verbruggen N, Wevers Jan HL, Carleer R, Vangronsveld J, Colpaert Jan V (2009) Cd-tolerant Suillus luteus: a fungal insurance for pines exposed to Cd. Environ Pollut 157:1581–1588
Li MS (2006) Ecological restoration of mineland with particular reference to the metalliferous mine wasteland in China: a review of research and practice. Sci Total Environ 357:38–53
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Nara K (2006) Ectomycorrhizal networks and seedling establishment during early primary succession. New Phytol 169:169–178
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties
Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2000) Removal of toxic metals from solution by leaf, stem and root phytomass of Quercus ilex L. (holly oak). Environ Pollut 110:277–283
Pulford I, Watson C (2003) Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated land by trees: a review. Environ Int 29:529–540
Roy S, Khasa DP, Greer CW (2007) Combining alders, frankiae, and mycorrhizae for the revegetation and remediation of contaminated ecosystems. Botany 85:237–251
Singh OV, Labana S, Pandey G, Budhiraja R, Jain RK (2003) Phytoremediation: an overview of metallic ion decontamination from soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:405–412
Smith SE, Read DJ (2010) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic Press, London
Van Tichelen KK, Vanstraelen T (1999) Nutrient uptake by intact mycorrhizal Pinus sylvestris seedlings: a diagnostic tool to detect copper toxicity. Tree Physiol 19:189–196
Zhou Y, Yue S, Zhou T (2010) Migration of heavy metals in Yangshanchong tailings impoundment in Tongling, Anhui Province. Res Environ Sci 23:497–503
Acknowledgments
This study received grants-in-aid from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Sciences (20380087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zong, K., Huang, J., Nara, K. et al. Inoculation of ectomycorrhizal fungi contributes to the survival of tree seedlings in a copper mine tailing. J For Res 20, 493–500 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-015-0506-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-015-0506-1