Abstract
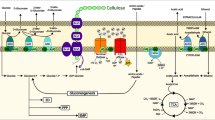
Komagataeibacter hansenii HDM1-3 (K. hansenii HDM1-3) has been widely applied for producing bacterial cellulose (BC). The yield of BC has been frequently limited by the acidification during sugar metabolism, due to the generation of organic acids such as acetic acid. In this study, the acid resistance mechanism of K. hansenii HDM1-3 has been investigated from the aspect of metabolic adaptability of cell membrane fatty acids. Firstly, we observed that the survival rate of K. hansenii HDM1-3 was decreased with lowered pH values (adjusted with acetic acids), accompanied by increased leakage rate. Secondly, the cell membrane adaptability in response to acid stress was evaluated, including the variations of cell membrane fluidity and fatty acid composition. The proportion of unsaturated fatty acids was increased (especially, C18-1w9c and C19-Cyc), unsaturation degree and chain length of fatty acids were also increased. Thirdly, the potential molecular regulation mechanism was further elucidated. Under acid stress, the fatty acid synthesis pathway was involved in the structure and composition variations of fatty acids, which was proved by the activation of both fatty acid dehydrogenase (des) and cyclopropane fatty acid synthase (cfa) genes, as well as the addition of exogenous fatty acids. The fatty acid synthesis of K. hansenii HDM1-3 may be mediated by the activation of two-component sensor signaling pathways in response to the acid stress. The acid resistance mechanism of K. hansenii HDM1-3 adds to our knowledge of the acid stress adaptation, which may facilitate the development of new strategies for improving the industrial performance of this species under acid stress.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar PS, Hernandez-Arriaga AM, Cybulski LE, Erazo AC, de Mendoza D (2001) Molecular basis of thermosensing: a two-component signal transduction thermometer in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J 20:1681–1691. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.7.1681
Aricha B, Fishov I, Cohen Z, Sikron N, Pesakhov S, Khozin-Goldberg I, Dagan R, Porat N (2004) Differences in membrane fluidity and fatty acid composition between phenotypic variants of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 186:4638–4644. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.14.4638-4644.2004
Asakura H, Ekawa T, Sugimoto N, Momose Y, Kawamoto K, Makino S, Igimi S, Yamamoto S (2012) Membrane topology of Salmonella invasion protein SipB confers osmotolerance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 426:654–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.09.012
Badshah M, Ullah H, Khan SA, Park JK, Khan T (2017) Preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation of bacterial cellulose matrices for oral drug delivery. Cellulose 24:5041–5052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1474-8
Bottan S, Robotti F, Jayathissa P, Hegglin A, Bahamonde N, Heredia-Guerrero JA, Bayer IS, Scarpellini A, Merker H, Lindenblatt N, Poulikakos D, Ferrari A (2015) Surface-structured bacterial cellulose with guided assembly-based biolithography (GAB). ACS Nano 9:206–219. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn5036125
Broadbent JR, Oberg TS, Hughes JE, Ward RE, Brighton C, Welker DL, Steele JL (2014) Influence of polysorbate 80 and cyclopropane fatty acid synthase activity on lactic acid production by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 334 at low pH. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:545–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1391-2
Budin-Verneuil A, Maguin E, Auffray Y, Ehrlich SD, Pichereau V (2005) Transcriptional analysis of the cyclopropane fatty acid synthase gene of Lactococcus lactis MG1363 at low pH. FEMS Microbiol Lett 250:189–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2005.07.007
Chang YY, Cronan JE (1999) Membrane cyclopropane fatty acid content is a major factor in acid resistance of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 33:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01456.x
Chen YY, Ganzle MG (2016) Influence of cyclopropane fatty acids on heat, high pressure, acid and oxidative resistance in Escherichia coli. Int J Food Microbiol 222:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.01.017
Choi J, Groisman EA (2016) Acidic pH sensing in the bacterial cytoplasm is required for Salmonella virulence. Mol Microbiol 101:1024–1038. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13439
Choi J, Groisman EA (2017) Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic pH requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL. Sci Signal. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aan6284
Chu-Ky S, Tourdot-Marechal R, Marechal PA, Guzzo J (2005) Combined cold, acid, ethanol shocks in Oenococcus oeni: effects on membrane fluidity and cell viability. Biochim Biophys Acta 1717:118–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2005.09.015
de la Haba C, Palacio JR, Martinez P, Morros A (2013) Effect of oxidative stress on plasma membrane fluidity of THP-1 induced macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta 1828:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.08.013
Denich TJ, Beaudette LA, Lee H, Trevors JT (2003) Effect of selected environmental and physico-chemical factors on bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. J Microbiol Methods 52:149–182
Diomande SE, Doublet B, Vasai F, Guinebretiere MH, Broussolle V, Brillard J (2016) Expression of the genes encoding the CasK/R two-component system and the DesA desaturase during Bacillus cereus cold adaptation. FEMS Microbiol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnw174
Diomande SE, Nguyen-the C, Abee T, Tempelaars MH, Broussolle V, Brillard J (2015) Involvement of the CasK/R two-component system in optimal unsaturation of the Bacillus cereus fatty acids during low-temperature growth. Int J Food Microbiol 213:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.04.043
Diomande SE, Nguyen-The C, Guinebretiere MH, Broussolle V, Brillard J (2015) Role of fatty acids in Bacillus environmental adaptation. Front Microbiol 6:813. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00813
Fozo EM, Kajfasz JK, Quivey RG Jr (2004) Low pH-induced membrane fatty acid alterations in oral bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 238:291–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2004.07.047
Fozo EM, Quivey RG Jr (2004) The fabM gene product of Streptococcus mutans is responsible for the synthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids and is necessary for survival at low pH. J Bacteriol 186:4152–4158. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.13.4152-4158.2004
Gautier J, Passot S, Penicaud C, Guillemin H, Cenard S, Lieben P, Fonseca F (2013) A low membrane lipid phase transition temperature is associated with a high cryotolerance of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subspecies bulgaricus CFL1. J Dairy Sci 96:5591–5602. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2013-6802
Guan N, Li J, Shin HD, Du G, Chen J, Liu L (2017) Microbial response to environmental stresses: from fundamental mechanisms to practical applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:3991–4008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8264-y
Guo ZP, Khoomrung S, Nielsen J, Olsson L (2018) Changes in lipid metabolism convey acid tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:297. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1295-5
Kaiser HJ, Surma MA, Mayer F, Levental I, Grzybek M, Klemm RW, Da Cruz S, Meisinger C, Muller V, Simons K, Lingwood D (2011) Molecular convergence of bacterial and eukaryotic surface order. J Biol Chem 286:40631–40637. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.276444
Kenney LJ (2018) The role of acid stress in Salmonella pathogenesis. Curr Opin Microbiol 47:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2018.11.006
Khan S, Ul-Islam M, Ikram M, Ullah MW, Israr M, Subhan F, Kim Y, Jang JH, Yoon S, Park JK (2016) Three-dimensionally microporous and highly biocompatible bacterial cellulose–gelatin composite scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. RSC Adv 6:110840–110849. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra18847h
Kim BH, Kim S, Kim HG, Lee J, Lee IS, Park YK (2005) The formation of cyclopropane fatty acids in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microbiology 151:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.27265-0
Lee YH, Kim JH (2017) Direct interaction between the transcription factors CadC and OmpR involved in the acid stress response of Salmonella enterica. J Microbiol 55:966–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-7410-7
Li L, Jia Y, Hou Q, Charles TC, Nester EW, Pan SQ (2002) A global pH sensor: Agrobacterium sensor protein ChvG regulates acid-inducible genes on its two chromosomes and Ti plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12369–12374. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.192439499
Li Y, Tian C, Tian H, Zhang J, He X, Ping W, Lei H (2012) Improvement of bacterial cellulose production by manipulating the metabolic pathways in which ethanol and sodium citrate involved. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1479–1487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4242-6
Li Y, Tian J, Tian H, Chen X, Ping W, Tian C, Lei H (2016) Mutation-based selection and analysis of Komagataeibacter hansenii HDM1-3 for improvement in bacterial cellulose production. J Appl Microbiol 121:1323–1334. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13244
Li YH, Lau PCY, Tang N, Svensater G, Ellen RP, Cvitkovitch DG (2002) Novel two-component regulatory system involved in biofilm formation and acid resistance in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol 184:6333–6342. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.184.22.6333-6342.2002
Lin Z, Cai X, Chen M, Ye L, Wu Y, Wang X, Lv Z, Shang Y, Qu D (2018) Virulence and stress responses of Shigella flexneri regulated by PhoP/PhoQ. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02689
Liu LP, Yang XN, Ye L, Xue DD, Liu M, Jia SR, Hou Y, Chu LQ, Zhong C (2017) Preparation and characterization of a photocatalytic antibacterial material: graphene oxide/TiO2/bacterial cellulose nanocomposite. Carbohydr Polym 174:1078–1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.07.042
Liu Y, Betti M, Ganzle MG (2012) High pressure inactivation of Escherichia coli, Campylobacter jejuni, and spoilage microbiota on poultry meat. J Food Prot 75:497–503. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-316
Liu Y, Tang H, Lin Z, Xu P (2015) Mechanisms of acid tolerance in bacteria and prospects in biotechnology and bioremediation. Biotechnol Adv 33:1484–1492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.06.001
Lu P, Ma D, Chen Y, Guo Y, Chen GQ, Deng H, Shi Y (2013) l-glutamine provides acid resistance for Escherichia coli through enzymatic release of ammonia. Cell Res 23:635–644. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2013.13
Lund P, Tramonti A, De Biase D (2014) Coping with low pH: molecular strategies in neutralophilic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38:1091–1125. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6976.12076
Mols M, van Kranenburg R, van Melis CC, Moezelaar R, Abee T (2010) Analysis of acid-stressed Bacillus cereus reveals a major oxidative response and inactivation-associated radical formation. Environ Microbiol 12:873–885. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.02132.x
Mykytczuk NC, Trevors JT, Leduc LG, Ferroni GD (2007) Fluorescence polarization in studies of bacterial cytoplasmic membrane fluidity under environmental stress. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 95:60–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2007.05.001
Nasution O, Lee YM, Kim E, Lee Y, Kim W, Choi W (2017) Overexpression of OLE1 enhances stress tolerance and constitutively activates the MAPK HOG pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 114:620–631. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26093
Oyce LA, Liu P, Stebbins MJ, Hanson BC, Jarboe LR (2013) The damaging effects of short chain fatty acids on Escherichia coli membranes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(18):8317–8327
Parvez S, Malik KA, Ah Kang S, Kim HY (2006) Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J Appl Microbiol 100:1171–1185. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.02963.x
Perez JC, Groisman EA (2007) Acid pH activation of the PmrA/PmrB two-component regulatory system of Salmonella enterica. Mol Microbiol 63:283–293. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05512.x
Porrini L, Cybulski LE, Altabe SG, Mansilla MC, de Mendoza D (2014) Cerulenin inhibits unsaturated fatty acids synthesis in Bacillus subtilis by modifying the input signal of DesK thermosensor. Microbiologyopen 3:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.154
Prost LR, Daley ME, Le Sage V, Bader MW, Le Moual H, Klevit RE, Miller SI (2007) Activation of the bacterial sensor kinase PhoQ by acidic pH. Mol Cell 26:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.03.008
Quivey RG Jr, Faustoferri R, Monahan K, Marquis R (2000) Shifts in membrane fatty acid profiles associated with acid adaptation of Streptococcus mutans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 189:89–92
Rajwade JM, Paknikar KM, Kumbhar JV (2015) Applications of bacterial cellulose and its composites in biomedicine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:2491–2511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6426-3
Rodriguez-Vargas S, Sanchez-Garcia A, Martinez-Rivas JM, Prieto JA, Randez-Gil F (2007) Fluidization of membrane lipids enhances the tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to freezing and salt stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01360-06
Romling U, Galperin MY (2015) Bacterial cellulose biosynthesis: diversity of operons, subunits, products, and functions. Trends Microbiol 23:545–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2015.05.005
Ruan L, Pleitner A, Ganzle MG, McMullen LM (2011) Solute transport proteins and the outer membrane protein NmpC contribute to heat resistance of Escherichia coli AW1.7. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2961–2967. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01930-10
Sandoval NR, Papoutsakis ET (2016) Engineering membrane and cell-wall programs for tolerance to toxic chemicals: beyond solo genes. Curr Opin Microbiol 33:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2016.06.005
Sato M, Tsuchiya H, Tani H, Yamamoto K, Yamaguchi R, Nitta H, Kanematsu N, Namikawa I, Takagi N (1991) Incorporation of fatty acids by Streptococcus mutans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 65:117–121
Sheng L, Zhou X, Liu Z-Y, Wang J-w, Zhou Q, Wang L, Zhang Q, Ji S-j (2016) Changed activities of enzymes crucial to membrane lipid metabolism accompany pericarp browning in ‘Nanguo’ pears during refrigeration and subsequent shelf life at room temperature. Postharvest Biol Technol 117:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.01.015
Tabanelli G, Patrignani F, Gardini F, Vinderola G, Reinheimer J, Grazia L, Lanciotti R (2014) Effect of a sublethal high-pressure homogenization treatment on the fatty acid membrane composition of probiotic lactobacilli. Lett Appl Microbiol 58:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12164
Ter Beek A, Keijser BJ, Boorsma A, Zakrzewska A, Orij R, Smits GJ, Brul S (2008) Transcriptome analysis of sorbic acid-stressed Bacillus subtilis reveals a nutrient limitation response and indicates plasma membrane remodeling. J Bacteriol 190:1751–1761. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01516-07
Ul-Islam M, Khan S, Ullah MW, Park JK (2015) Bacterial cellulose composites: synthetic strategies and multiple applications in bio-medical and electro-conductive fields. Biotechnol J 10:1847–1861. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201500106
Ullah A, Orij R, Brul S, Smits GJ (2012) Quantitative analysis of the modes of growth inhibition by weak organic acids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:8377–8387. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02126-12
Umemura T, Matsumoto Y, Ohnishi K, Homma M, Kawagishi I (2002) Sensing of cytoplasmic pH by bacterial chemoreceptors involves the linker region that connects the membrane-spanning and the signal-modulating helices. J Biol Chem 277:1593–1598. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109930200
Velly H, Bouix M, Passot S, Penicaud C, Beinsteiner H, Ghorbal S, Lieben P, Fonseca F (2015) Cyclopropanation of unsaturated fatty acids and membrane rigidification improve the freeze-drying resistance of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis TOMSC161. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:907–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6152-2
Viarengo G, Sciara MI, Salazar MO, Kieffer PM, Furlan RL, Garcia Vescovi E (2013) Unsaturated long chain free fatty acids are input signals of the Salmonella enterica PhoP/PhoQ regulatory system. J Biol Chem 288:22346–22358. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.472829
Weber MH, Klein W, Muller L, Niess UM, Marahiel MA (2001) Role of the Bacillus subtilis fatty acid desaturase in membrane adaptation during cold shock. Mol Microbiol 39:1321–1329
Wu C, Huang J, Zhou R (2014) Progress in engineering acid stress resistance of lactic acid bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:1055–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5435-3
Wu C, Zhang J, Wang M, Du G, Chen J (2012) Lactobacillus casei combats acid stress by maintaining cell membrane functionality. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:1031–1039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1104-2
Yang XN, Xue DD, Li JY, Liu M, Jia SR, Chu LQ, Wahid F, Zhang YM, Zhong C (2016) Improvement of antimicrobial activity of graphene oxide/bacterial cellulose nanocomposites through the electrostatic modification. Carbohydr Polym 136:1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.020
Zhang YM, Rock CO (2008) Membrane lipid homeostasis in bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:222–233. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1839
Zhao Y, Hindorff LA, Chuang A, Monroe-Augustus M, Lyristis M, Harrison ML, Rudolph FB, Bennett GN (2003) Expression of a cloned cyclopropane fatty acid synthase gene reduces solvent formation in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2831–2841. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.69.5.2831-2841.2003
Zheng DQ, Liu TZ, Chen J, Zhang K, Li O, Zhu L, Zhao YH, Wu XC, Wang PM (2013) Comparative functional genomics to reveal the molecular basis of phenotypic diversities and guide the genetic breeding of industrial yeast strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:2067–2076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4698-z
Zschiedrich CP, Keidel V, Szurmant H (2016) Molecular mechanisms of two-component signal Transduction. J Mol Biol 428:3752–3775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.08.003
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (C2015023), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province Department of Education (12541625), Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Plant Genetic Engineering and Biological Fermentation Engineering for Cold Region, Shenzhen science and technology application demonstration project (KJYY20180201180253571) and Shenzhen science and technology key project (JSGG20171013091238230). We thank Dr. Jiliang Zhang and Dr. Senanayake Indunil Chinthani for the correction of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Yan, P., Lei, Q. et al. Metabolic adaptability shifts of cell membrane fatty acids of Komagataeibacter hansenii HDM1-3 improve acid stress resistance and survival in acidic environments. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46, 1491–1503 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02225-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02225-y