Abstract
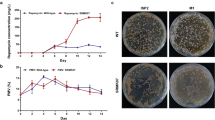
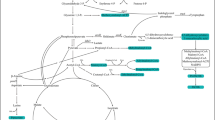
Rapamycin, as a macrocyclic polyketide with immunosuppressive, antifungal, and anti-tumor activity produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus, is receiving considerable attention for its significant contribution in medical field. However, the production capacity of the wild strain is very low. Hereby, a computational guided engineering approach was proposed to improve the capability of rapamycin production. First, a genome-scale metabolic model of Streptomyces hygroscopicus ATCC 29253 was constructed based on its annotated genome and biochemical information. The model consists of 1003 reactions, 711 metabolites after manual refinement. Subsequently, several potential genetic targets that likely guaranteed an improved yield of rapamycin were identified by flux balance analysis and minimization of metabolic adjustment algorithm. Furthermore, according to the results of model prediction, target gene pfk (encoding 6-phosphofructokinase) was knocked out, and target genes dahP (encoding 3-deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase) and rapK (encoding chorismatase) were overexpressed in the parent strain ATCC 29253. The yield of rapamycin increased by 30.8% by knocking out gene pfk and increased by 36.2 and 44.8% by overexpression of rapK and dahP, respectively, compared with parent strain. Finally, the combined effect of the genetic modifications was evaluated. The titer of rapamycin reached 250.8 mg/l by knockout of pfk and co-expression of genes dahP and rapK, corresponding to a 142.3% increase relative to that of the parent strain. The relationship between model prediction and experimental results demonstrates the validity and rationality of this approach for target identification and rapamycin production improvement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alper H, Jin Y-S, Moxley J, Stephanopoulos G (2005) Identifying gene targets for the metabolic engineering of lycopene biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 7:155–164
Andexer JN, Kendrew SG, Nur-e-Alam M, Lazos O, Foster TA, Zimmermann A-S, Warneck TD, Suthar D, Coates NJ, Koehn FE (2011) Biosynthesis of the immunosuppressants FK506, FK520, and rapamycin involves a previously undescribed family of enzymes acting on chorismate. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:4776–4781
Baranasic D, Gacesa R, Starcevic A, Zucko J, Blažič M, Horvat M, Gjuračić K, Fujs Š, Hranueli D, Kosec G (2013) Draft genome sequence of Streptomyces rapamycinicus strain NRRL 5491, the producer of the immunosuppressant rapamycin. Genom Announc 1:e00581–e00613
Becker J, Zelder O, Häfner S, Schröder H, Wittmann C (2011) From zero to hero—Design-based systems metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for l-lysine production. Metab Eng 13:159–168
Boghigian BA, Armando J, Salas D, Pfeifer BA (2012) Computational identification of gene over-expression targets for metabolic engineering of taxadiene production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:2063–2073
Borodina I, Krabben P, Nielsen J (2005) Genome-scale analysis of Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2) metabolism. Genom Res 15:820–829
Borodina I, Siebring J, Zhang J, Smith CP, van Keulen G, Dijkhuizen L, Nielsen J (2008) Antibiotic overproduction in Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2) mediated by phosphofructokinase deletion. J Biol Chem 283:25186–25199
Calne R, Lim S, Samaan A, Collier DSJ, Pollard S, White D, Thiru S (1989) Rapamycin for immunosuppression in organ allografting. Lancet 334:227
Chen X, Li M, Zhou L, Shen W, Algasan G, Fan Y, Wang Z (2014) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for improving shikimate synthesis from glucose. Bioresour Technol 166:64–71
Chen X, Wei P, Fan L, Yang D, Zhu X, Shen W, Xu Z, Cen P (2009) Generation of high-yield rapamycin-producing strains through protoplasts-related techniques. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:507–512
Douros J, Suffness M (1981) New antitumor substances of natural origin. Cancer Treat Rev 8:63–87
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers P, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Fang A, Demain A (1995) Exogenous shikimic acid stimulates rapamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Folia Microbiol 40:607–610
Fowler ZL, Gikandi WW, Koffas MA (2009) Increased malonyl coenzyme A biosynthesis by tuning the Escherichia coli metabolic network and its application to flavanone production. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5831–5839
Gunnarsson N, Eliasson A, Nielsen J (2004) Control of fluxes towards antibiotics and the role of primary metabolism in production of antibiotics. In Molecular biotechnology of fungal beta-lactam antibiotics and related peptide synthetases. Springer, Berlin, pp 137–178
He J, Magarvey N, Piraee M, Vining L (2001) The gene cluster for chloramphenicol biosynthesis in Streptomyces venezuelae ISP5230 includes novel shikimate pathway homologues and a monomodular non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene. Microbiology 147:2817–2829
Helmstaedt K, Strittmatter A, Lipscomb WN, Braus GH (2005) Evolution of 3-deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase-encoding genes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9784–9789
Huang D, Li S, Xia M, Wen J, Jia X (2013) Genome-scale metabolic network guided engineering of Streptomyces tsukubaensis for FK506 production improvement. Microb Cell Fact 12:1
Huang D, Xia M, Li S, Wen J, Jia X (2013) Enhancement of FK506 production by engineering secondary pathways of Streptomyces tsukubaensis and exogenous feeding strategies. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:1023–1037
Jin Y-S, Stephanopoulos G (2007) Multi-dimensional gene target search for improving lycopene biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 9:337–347
Juneja P, Hubrich F, Diederichs K, Welte W, Andexer JN (2014) Mechanistic implications for the chorismatase FkbO based on the crystal structure. J Mol Biol 426:105–115
Jung WS, Yoo YJ, Park JW, Park SR, Han AR, Ban YH, Kim EJ, Kim E, Yoon YJ (2011) A combined approach of classical mutagenesis and rational metabolic engineering improves rapamycin biosynthesis and provides insights into methylmalonyl-CoA precursor supply pathway in Streptomyces hygroscopicus ATCC 29253. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:1389–1397
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kim YH, Park BS, Bhatia SK, Seo H-M, Jeon J-M, Kim H-J, Yi D-H, Lee J-H, Choi K-Y, Park H-Y (2014) Production of rapamycin in Streptomyces hygroscopicus from glycerol-based media optimized by systemic methodology. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1319–1326
Kosec G, Goranovič D, Mrak P, Fujs Š, Kuščer E, Horvat J, Kopitar G, Petković H (2012) Novel chemobiosynthetic approach for exclusive production of FK506. Metab Eng 14:39–46
Kumar VS, Dasika MS, Maranas CD (2007) Optimization based automated curation of metabolic reconstructions. BMC Bioinform 8:1
Kuščer E, Coates N, Challis I, Gregory M, Wilkinson B, Sheridan R, Petković H (2007) Roles of rapH and rapG in positive regulation of rapamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J Bacteriol 189:4756–4763
Lee SJ, Lee D-Y, Kim TY, Kim BH, Lee J, Lee SY (2005) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for enhanced production of succinic acid, based on genome comparison and in silico gene knockout simulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7880–7887
Liu Y-J, Li P-P, Zhao K-X, Wang B-J, Jiang C-Y, Drake HL, Liu S-J (2008) Corynebacterium glutamicum contains 3-deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthases that display novel biochemical features. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:5497–5503
Park JH, Lee KH, Kim TY, Lee SY (2007) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of l-valine based on transcriptome analysis and in silico gene knockout simulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:7797–7802
Park JM, Park HM, Kim WJ, Kim HU, Kim TY, Lee SY (2012) Flux variability scanning based on enforced objective flux for identifying gene amplification targets. BMC Syst Biol 6:106
Patsenker E, Schneider V, Ledermann M, Saegesser H, Dorn C, Hellerbrand C, Stickel F (2011) Potent antifibrotic activity of mTOR inhibitors sirolimus and everolimus but not of cyclosporine A and tacrolimus in experimental liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 55:388–398
Pierson LS, Gaffney T, Lam S, Gong F (1995) Molecular analysis of genes encoding phenazine biosynthesis in the biological control bacterium Pseudomonas aureofaciens 30–84. FEMS Microbiol Lett 134:299–307
Schellenberger J, Que R, Fleming RM, Thiele I, Orth JD, Feist AM, Zielinski DC, Bordbar A, Lewis NE, Rahmanian S (2011) Quantitative prediction of cellular metabolism with constraint-based models: the COBRA Toolbox v2. 0. Nat Protoc 6:1290–1307
Segre D, Vitkup D, Church GM (2002) Analysis of optimality in natural and perturbed metabolic networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:15112–15117
Sehgal S, Baker H, Vézina C (1975) Rapamycin (AY-22,989), a new antifungal antibiotic. II. Fermentation, isolation and characterization. J Antibiot 28:727–732
Sharma B (2011) Modulation of phosphofructokinase (PFK) from Setaria cervi, a bovine filarial parasite, by different effectors and its interaction with some antifilarials. Parasit Vectors 4:1
Sinha R, Singh S, Srivastava P (2014) Studies on process optimization methods for rapamycin production using Streptomyces hygroscopicus ATCC 29253. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37:829–840
Thiele I, Palsson BØ (2010) A protocol for generating a high-quality genome-scale metabolic reconstruction. Nat Protoc 5:93–121
Umbarger HE (1978) Amino acid biosynthesis and its regulation. Annu Rev Biochem 47:533–606
Wilkinson CJ, Hughes-Thomas ZA, Martin CJ, Bohm I, Mironenko T, Deacon M, Wheatcroft M, Wirtz G, Staunton J, Leadlay PF (2002) Increasing the efficiency of heterologous promoters in actinomycetes. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 4:417–426
Wood CE, Giroux D, Gridley K (2003) Fetal brain regional responses to cerebral hypoperfusion: modulation by estrogen. Brain Res 993:84–89
Xu P, Ranganathan S, Fowler ZL, Maranas CD, Koffas MA (2011) Genome-scale metabolic network modeling results in minimal interventions that cooperatively force carbon flux towards malonyl-CoA. Metab Eng 13:578–587
Xu ZN, Shen WH, Chen XY, Lin JP, Cen PL (2005) A high-throughput method for screening of rapamycin-producing strains of Streptomyces hygroscopicus by cultivation in 96-well microtiter plates. Biotechnol Lett 27:1135–1140
Yim H, Haselbeck R, Niu W, Pujol-Baxley C, Burgard A, Boldt J, Khandurina J, Trawick JD, Osterhout RE, Stephen R (2011) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for direct production of 1,4-butanediol. Nat Chem Biol 7:445–452
Yu T-W, Müller R, Müller M, Zhang X, Draeger G, Kim C-G, Leistner E, Floss HG (2001) Mutational analysis and reconstituted expression of the biosynthetic genes involved in the formation of 3-amino-5-hydroxybenzoic acid, the starter unit of rifamycin biosynthesis in Amycolatopsis mediterranei S699. J Biol Chem 276:12546–12555
Zhao S, Huang D, Qi H, Wen J, Jia X (2013) Comparative metabolic profiling-based improvement of rapamycin production by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5329–5341
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National 973 Project of China (No. 2013CB733600), the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21236005), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21376171).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, L., Liu, J., Wang, C. et al. Enhancement of rapamycin production by metabolic engineering in Streptomyces hygroscopicus based on genome-scale metabolic model. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44, 259–270 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1880-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1880-1