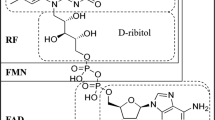
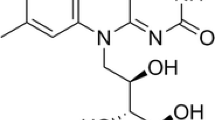
Abstract
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is an essential nutrient for humans and animals that must be obtained from the diet. To ensure an optimal supply, riboflavin is used on a large scale as additive in the food and feed industries. Here, we describe a historical overview of the industrial process of riboflavin production starting from its discovery and the need to produce the vitamin in bulk at prices that would allow for their use in human and animal nutrition. Riboflavin was produced industrially by chemical synthesis for many decades. At present, the development of economical and eco-efficient fermentation processes, which are mainly based on Bacillus subtilis and Ashbya gossypii strains, has replaced the synthetic process at industrial scale. A detailed account is given of the development of the riboflavin overproducer strains as well as future prospects for its improvement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Althöefer H, Revuelta JL, Seulberger H, Zelder O (1999) Genetic method for producing riboflavin. Patent WO1999061623 A2
Bigelis R (1989) Industrial products of biotechnology: application of gene technology. In: Rehm HJ, Reed G (eds) Biotechnology, vol 7b. VCH, Weinheim, p 243
Boeddecker T, Kaesler B, Sahm H, Schmidt G, Seulberger H, Stahmann KP (1997) Riboflavin production process by means of microorganisms with modified isocitrate lyase activity. Patent WO1997003208 A1
Casini A, Storch M, Baldwin GS, Ellis T (2015) Bricks and blueprints: methods and standards for DNA assembly. Nat Rev Cell Mol Biol 16(9):568–576
Demain AL (1972) Riboflavin oversynthesis. Annu Rev Microbiol 26:369–388
Dietrich FS, Voegeli S, Brachat S, Lerch A, Gates K, Steiner S, Mohr C, Pöhlmann R, Luedi P, Choi S, Wing RA, Flavier A, Gaffney TD, Philippsen P (2004) The Ashbya gossypii genome as a tool for mapping the ancient Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Science 304(5668):304–307
Duan YX, Chen T, Chen X, Zhao XM (2010) Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enhances riboflavin production in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(6):1907–1914
Förster C, Santos MA, Ruffert S, Krämer R, Revuelta JL (1999) Physiological consequence of disruption of the VMA1 gene in the riboflavin overproducer Ashbya gossypii. J Biol Chem 274(14):9442–9448
Förster C, Revuelta JL, Krämer R (2001) Carrier-mediated transport of riboflavin in Ashbya gossypii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55(1):85–89
Garcia-Ramirez JJ, Santos MA, Revuelta JL (1995) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RIB4 gene codes for 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine synthase involved in riboflavin biosynthesis. Molecular characterization of the gene and purification of the encoded protein. J Biol Chem 270:23801–23807
Gattiker A, Rischatsch R, Demougin P, Voegeli S, Dietrich FS, Philippsen P, Primig M (2007) Ashbya Genome Database 3.0: a cross-species genome and transcriptome browser for yeast biologists. BMC Genom 8:9
Hahne H, Mäder U, Otto A, Bonn F, Steil L, Bremer E, Hecker M, Becher D (2010) A comprehensive proteomics and transcriptomics analysis of Bacillus subtilis salt stress adaptation. J Bacteriol 192(3):870–882
Jeong BY, Wittmann C, Kato T, Park EY (2015) Comparative metabolic flux analysis of an Ashbya gossypii wild type strain and a high riboflavin-producing mutant strain. J Biosci Bioeng 119(1):101–106
Jimenez A, Santos MA, Pompejus M, Revuelta JL (2005) Metabolic engineering of the purine pathway for riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(10):5743–5751
Jimenez A, Santos MA, Revuelta JL (2008) Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase activity affects growth and riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii. BMC Biotechnol 8:67
Kaplan L, Demain AL (1970) Nutritional studies on riboflavin overproduction by Ashbya gossypii. In: Ahearn DG (ed) Recent trends in yeast research, vol 1. Georgia State University, Atlanta, pp 137–159
Karos M, Vilariño C, Bollschweiler C, Revuelta JL (2004) A genome-wide transcription analysis of a fungal riboflavin overproducer. J Biotechnol 113(1–3):69–76
Karrer P, Schopp K, Benz F (1935) Synthesen von flavinen IV. Helv Chim Acta 18:426–429
Kato T, Park EY (2006) Expression of alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Ashbya gossypii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71(1):46–52
Kuhn R, Reinemund K, Weygand F (1934) Synthesis of lumilactoflavins. Ber 67:1460–1463
Kurth R, Paust W, Haenlein W (1996) Vitamins, Chapter 7. In: Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. VCH, Weinheim, A27: 521–530
Lago BD, Kaplan L (1981) Vitamin fermentations: B2 and B12. Adv Biotechnol 3:241–246
Ledesma-Amaro R, Santos MA, Jimenez A, Revuelta JL (2014) Strain design of Ashbya gossypii for single-cell oil production. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:1237–1244
Ledesma-Amaro R, Kerkhoven EJ, Revuelta JL, Nielsen J (2014) Genome scale metabolic modeling of the riboflavin overproducer Ashbya gossypii. Biotechnol Bioeng 111(6):1191–1199
Ledesma-Amaro R, Serrano-Amatriain C, Jimenez A, Revuelta JL (2015) Metabolic engineering of riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii through pathway optimization. Microb Cell Fact 14(1):163
Ledesma-Amaro R, Buey RM, Revuelta JL (2015) Increased production of inosine and guanosine by means of metabolic engineering of the purine pathway in Ashbya gossypii. Microb Cell Fact 14:58
Ledesma-Amaro R, Lozano-Martinez P, Jimenez A, Revuelta JL (2015) Engineering Ashbya gossypii for efficient biolipid production. Bioengineered 6(2):119–123
Ledesma-Amaro R, Nicaud JM (2016) Metabolic engineering for expanding the substrate range of Yarrowia lipolytica. Trends Biotechnol. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.04.010
Lee JW, Kim TY, Jang YS, Choi S, Lee SY (2011) Systems metabolic engineering for chemicals and materials. Trends Biotechnol 29(8):370–378
Maeting I, Schmidt G, Sahm H, Revuelta JL, Stierhof YD, Stahmann KP (1999) Isocitrate lyase of Ashbya gossypii––transcriptional regulation and peroxisomal localization. FEBS Lett 444:15–21
Mateos L, Jimenez A, Revuelta JL, Santos MA (2006) Purine biosynthesis, riboflavin production, and trophic-phase span are controlled by a Myb-related transcription factor in the fungus Ashbya gossypii. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):5052–5060
Meyer A, Pellaux R, Potot S, Becker K, Hohmann HP, Panke S, Held M (2015) Optimization of a whole-cell biocatalyst by employing genetically encoded product sensors inside nanolitre reactors. Nat Chem 7(8):673–678
Monschau N, Sahm H, Stahmann KP (1998) Threonine aldolase overexpression plus threonine supplementation enhanced riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(11):4283–4290
Park EY, Ito Y, Nariyama M, Sugimoto T, Lies D, Kato T (2011) The improvement of riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii via disparity mutagenesis and DNA microarray analysis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(5):1315–1326
Perkins JB, Sloma A, Hermann T, Theriault K, Zachgo E, Erdenberger T, Hannett N, Chatterjee NP, Williams V, Rufo GA, Hatch R, Pero J (1999) Genetic engineering of Bacillus subtilis for the commercial production of riboflavin. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 22(1):8–18
Perlman D (1979) Microbial process for riboflavin production. In: Pepplev HJ, Pevlman D (eds) Microbial technology, vol I. Academic Press, New York, pp 52–527
Revuelta JL, Buitrago MJ, Santos MA (I995) Riboflavin synthesis in fungi. Patent US 5,821,090
Revuelta JL, Santos MA, Pompejus M, Seulberger H (I999) Promoter from Ashbya gossypii. Patent WO1999033993 A1
Ruhl M, Zamboni N, Sauer U (2010) Dynamic flux responses in riboflavin overproducing Bacillus subtilis to increasing glucose limitation in fed-batch culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 105(4):795–804
Santos MA, Jimenez A, Revuelta JL (2000) Molecular characterization of FMN1, the structural gene for the monofunctional flavokinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 275:28618–28624
Santos MA, Mateos L, Stahmann KP, Revuelta JL (2005) Insertional mutagenesis in the vitamin B2 producer fungus Ashbya gossypii. In: Barredo JL (ed) Methods in biotechnology, vol 18., Microbial processes and productsHumana Press Inc, Totowa, pp 283–290
Sasajima K, Yoneda M (1971) Carbohydrate metabolism-mutants of a Bacillus species, Part II: d-ribose accumulation by pentose phosphate pathway mutants. Agric Biol Chem 35:509–517
Schmidt G, Stahmann KP, Sahm H (1996) Isolation and characterization of isocitrate lyase from the riboflavin-producing fungus Ashbya gossypii. Microbiology 142:411–417
Schlüpen C, Santos MA, Weber U, de Graaf A, Revuelta JL, Stahmann KP (2003) Disruption of the SHM2 gene, encoding one of two serine hydroxymethyltransferase isoenzymes, reduces the flux from glycine to serine in Ashbya gossypii. Biochem J 369:263–273
Schwechheimer SK, Park EY, Revuelta JL, Becker J, Wittmann C (2016) Biotechnology of riboflavin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(5):2107–2119
Shi SB, Chen T, Zhang ZG, Chen X, Zhao XM (2009) Transcriptome analysis guided metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis for riboflavin production. Metab Eng 11(4–5):243–252
Shi SB, Shen Z, Chen X, Chen T, Zhao XM (2009) Increased production of riboflavin by metabolic engineering of the purine pathway in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Eng J 46(1):28–33
Shi T, Wang YC, Wang ZW, Wang GL, Liu DY, Fu J, Chen T, Zhao XM (2014) Deregulation of purine pathway in Bacillus subtilis and its use in riboflavin biosynthesis. Microb Cell Fact 13:101
Simeonidis E, Price ND (2015) Genome-scale modeling for metabolic engineering. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42(3):327–338
Stahmann KP, Revuelta JL, Seulberger H (2000) Three biotechnical processes using Ashbya gossypii, Candida famata, or Bacillus subtilis compete with chemical ribofl̄avin production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:509–516
Sugimoto T, Kanamasa S, Kato T, Park EY (2009) Importance of malate synthase in the glyoxylate cycle of Ashbya gossypii for the efficient production of riboflavin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83(3):529–539
Tischler M, Wellman JW, Ladenburg K (1945) The preparation of riboflavin; the synthesis of alloxazines and isoalloxazines. J Am Chem Soc 67:2165–2168
Tischler M, Pfisterrd K, Babson RD, Ladenburg K, Fleming AJ (1947) The reaction between o-aminoazo compounds and barbituric acid. A new synthesis of riboflavin. J Am Chem Soc 69:1487–1492
Wagner AF, Folkers K (1962) Vitamins and coenzymes. Wiley (Interscience), New York
Wickerham LJ, Flickinger MH, Johnsten RM (1946) The production of riboflavin by Ashbya gossypii. Arch Biochem 9:95–98
Zhu Y, Chen X, Chen T, Shi S, Zhao X (2006) Over-expression of glucose dehydrogenase improves cell growth and riboflavin production in Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Lett 28(20):1667–1672
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by BASF SE and grant BIO2014-23901 from the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad. Rubén M Buey was supported by a “Ramón y Cajal” contract from the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad. P. L.-M. was recipient of an FPI fellowship from the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad. R. L.-A. was recipient of FPI predoctoral fellowship from the Spanish Ministerio de Educación, Cultura y Deporte. D. F.-D. was recipient of a predoctoral fellowship from the Universidad de Salamanca, Spain. We thank M. D. Sánchez and S. Domínguez for excellent technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Revuelta, J.L., Ledesma-Amaro, R., Lozano-Martinez, P. et al. Bioproduction of riboflavin: a bright yellow history. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44, 659–665 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1842-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1842-7