Abstract
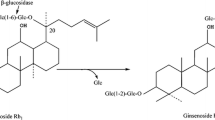
Rb1 and Rg1 are the major ginsenosides in protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol. Their content in ginsenosides was 23.8 and 17.6%, respectively. A total of 22 isolates of β-glucosidase producing microorganisms were isolated from the soil of a ginseng field using Esculin-R2A agar. Among these isolates, the strain GH21 showed the strongest activities to convert ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1 to minor ginsenosides compound-K and F1, respectively. Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 bioconversion rates were 74.2 and 89.3%, respectively. Meanwhile, the results demonstrated that the ginsenoside Rg1 could change the biotransformation pathway of ginsenoside Rb1 by inhibiting the formation of the intermediate metabolite gypenoside-XVII. GH21 was identified as a Cladosporium cladosporioides species based on the internal transcribed spacers (ITS) ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 rRNA gene sequences constructed phylogenetic trees.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen GT, Yang M, Song Y, Lu ZQ, Zhang JQ, Huang HL, Wu LJ, Guo DA (2008) Microbial transformation of ginsenoside Rb1 by Acremonium strictum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:1345–1350
Cheng LQ, Kim MK, Lee JW, Lee YJ, Yang DC (2006) Conversion of major ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside F2 by Caulobacter leidyia. Biotechnol Lett 28:1121–1127
Cheng LQ, Na JR, Kim MK, Bang MH, Yang DC (2007) Microbial conversion of minor ginsenoside F2 and gypenoside XVII by intrasporangium sp.GS603 isolated from soil. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:1937–1943
Chi H, Kim DH, Ji GE (2005) Transformation of ginsenosides Rb2 and Rc from Panax ginseng by food microorganisms. Biol Pharm Bull 28:2102–2105
Chi H, Ji GE (2005) Transformation of ginsenosides Rb1 and Re from Panax ginseng by food microorganisms. Biotechnol Lett 27:765–771
Choi K, Kim M, Ryu J, Choi C (2007) Ginsenosides compound K and Rh2 inhibit tumor necrosis factor-α-induced activation of the NF-kB and JNK pathways in human astroglial cells. Neurosci Lett 421:37–41
Dong A, Ye M, Guo H, Zheng J, Guo D (2003) Microtransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 by Rhizopus stolon and Curvularia lunata. Biotechnol Lett 25:339–344
Dong AL, Cui YJ, Guo H, Zheng JH, Guo D (2001) Microbiological transformation of ginsenoside Rg1. J Chin Pharm Sci 10:115–118
Han Y, Sun BS, Hu XM, Zhang H, Jiang BH, Spranger MI, Zhao YQ (2007) Transformation of bioactive compounds by Fusariun sacchari fungus isolated from the soil-cultivated Ginseng. J Agric Food Chem 55:9373–9379
Hasegawa H (2004) Proof of the mysterious efficacy of ginseng: Basic and clinical trials: metabolic activation of ginsenoside: deglycosylation by intestinal bacteria and esterification with fatty acid. J Pharmacol Sci 95:153–157
Kim MK, Lee JW, Lee KY, Yang DC (2005) Microbial conversion of major ginsenoside Rb1 to pharmaceutically active minor ginsenoside Rd. J Microbiol 43:456–462
Lee BH, You HJ, Park MS, Kwin B, Ji GE (2006) Transformation of the glycosides from food materials by probiotics and food microorganisms. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:497–504
Lee EH, Cho SY, Kim SJ, Shin ES, Chang HK et al (2003) Ginsenoside F1 protects human HaCaT keratinocytes from ultraviolet-B-induced apoptosis by maintaining constant levels of Bcl-2. J Invest Dermatol 121:607–613
Lee HU, Bae EA, Han MJ, Kim NJ, Kim DH (2005) Hepatoprotective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 and compound K on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced liver injury. Liver Int 25:1069–1073
Lee SJ, Sung JH, Lee BH (1999) Antitumor activity of a novel ginseng saponin metabolite in human pulmonary adenocarcinoma cells resistant to cisplatin. Cancer Lett 144:39–43
Lim JH, Wen TC, Matsuda S, Tanaka J, Maeda N, Peng H, Aburaya J, Ishihara K, Sakanaka M (1997) Protection of ischemic hippocampal neurons by ginsenoside Rb1, a main ingredient of ginseng root. Neurosci Res 28:191–200
Odani T, Tanizawa H, Takino Y (1983) Studies on the absorption, distribution, excretion and metabolism of ginseng saponins, the absorption, distribution and excretion of ginsenoside Rg1 in the rat. Chem Pharm Bull 31:1059–1066
Park JH (2004) Sun a new processed ginseng with fortified activity. Food Ind Nutr 9:23–27
Son JW, Kim HJ, Oh DK (2008) Ginsenoside Rd production from the major ginsenoside Rb1 by beta-glucosidase from Thermus caldophilus. Biotechnol Lett 30:713–716
Wang XY, Zhang JT (2003) Effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of anaesthetized rats. J Asian Nat Prod Res 5:1–4
Yoo DS, Rho HS, Lee YG, Yeom MH et al (2011) Ginsenoside F1 modulates cellular responses of skin melanoma cells. J Ginseng Res 35:86–91
Zhang JT, Liu Y, Qu ZW (1988) Influence of ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1 on some central neurotransmitter receptors and protein biosynthesis in the mouse brain. Acta Pharm Sin 23:12–16
Zhang DS, Zhang JT (2000) Effects of total ginsenoside on learning and memory impairment induced by transient betaamyloid peptide. Chin Pharm Bull 16:422–425
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.20862017) and National Ginseng Products Quality Supervision Inspection Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Jin, Y., Yin, C. et al. Co-transformation of Panax major ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 to minor ginsenosides C–K and F1 by Cladosporium cladosporioides . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 521–527 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-011-1058-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-011-1058-9