Abstract
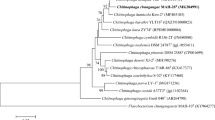
A novel yellow-pigmented bacterial strain (designated BR5-29T), was isolated and its taxonomy was studied. Phylogenetic study based on the 16S rRNA and draft genome sequence placed the strain BR5-29T in a distinct lineage within the family Chitinophagaceae, sharing ≤ 93.4% sequence similarity with members of the closely related genera Ferruginibacter, Flavisolibacter, Flavitalea and Niastella. The novel isolate showed the highest sequence similarity to the genus Ferruginibacter. The draft genome of strain BR5-29T had a total length of 5,505,520 base pairs. A total of 4585 genes were identified, in which 4537 were CDS and 48 RNA genes were assigned a putative function. The genome annotation of BR5-29T showed 225 carbohydrate genes which may be responsible for the conversion of major ginsenosides to minor ginsenosides. Strain BR5-29T contained MK-7 as a predominant quinone, and iso-C15:0, iso-C15:0 G, iso-C17:0 3-OH, and C16:1 ω7c and/or C16:1 ω6c (summed feature 3) as major fatty acids. The polar lipids found in the strain BR5-29T were phosphatidylglycerol (PG), diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), five unidentified polar lipids (L1–L5), two unidentified aminolipid and one unidentified aminophospholipid. Our pilot data demonstrate that the novel isolate shares the similar major polar lipid PE, major quinone MK-7 and major fatty acids with the described members of the family Chitinophagaceae. However, the low 16S rRNA gene sequence (< 93.4%), the little high amount of C12:0, iso-C17:0 2-OH and iso-C15:1 2-OH fatty acids, low DNA G + C content, and the presence of DPG, PG and two unidentified polar lipids (L1 and L3 differentiate the BR5-29T from its closest phylogenetic neighbors. Thus, the isolate represents a novel genus and species in the family Chitinophagaceae for which the name Ginsengibacter hankyongi gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is BR5-29T (= KACC 19446T = LMG 30462T). Thus, we predict that this novel strain may prove useful for the future research analysis (target gene cloning) and mass production of Rg3.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders H, Dunfield PF, Lagutin K, Houghton KM, Power JF, MacKenzie AD, Vyssotski M, Ryan LJR, Hanssen EG, Moreau JW, Stott MBet, (2014) Thermoflavifilum aggregans gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic and slightly halophilic filamentous bacterium from the phylum Bacteroidetes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1264–1270
Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan CS (1999) Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol 58:1685–1693
Baatar D, Siddiqi MZ, Im WT, Khaliq NU, Hwang SG (2018) Anti-inflammatory effect of ginsenoside Rh2-mix on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells. J Med Food 21:1–10
Christensen LP (2009) Ginsenosides chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects. Adv Food Nutr Res 55:1–99
Eder W, Peplies JR, Wanner G, Frühling A, Verbarg S (2015) Hydrobacter penzbergensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from purified water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:920–926
Fautz E, Reichenbach H (1980) A simple test for flexirubin-type pigments. FEMS Microbiol Lett 8:87–89
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limit on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hanada S, Tamaki H, Nakamura K, Kamagata Y (2014) Crenotalea thermophila gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Chitinophagaceae isolated from a hot spring. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1359–1364
Hiraishi A, Ueda Y, Ishihara J, Mori T (1996) Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J Gen Appl Microbiol 42:457–469
Kämpfer P, Young CC, Sridhar KR, Arun AB, Lai WA (2006) Transfer of [Flexibacter] sancti, [Flexibacter] filiformis, [Flexibacter] japonensis, and [Cytophaga] arvensicola to the genus Chitinophaga and description of Chitinophaga skermanii sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2223–2228
Kämpfer P, Lodders N, Falsen E (2011) Hydrotalea flava gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the phylum Bacteroidetes and allocation of the genera Chitinophaga, Sediminibacterium, Lacibacter, Flavihumibacter, Flavisolibacter, Niabella, Niastella, Segetibacter, Parasegetibacter, Terrimonas, Ferruginibacter, Filimonas and Hydrotalea to the family Chitinophagaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:518–523
Kang H, Kim H, Joung Y, Jang TY, Joh K (2015) Ferruginibacter paludis sp. nov., isolated from wetland freshwater, and emended descriptions of Ferruginibacter lapsinanis and Ferruginibacter alkalilentus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:2635–2639
Kang H, Kim H, Joung Y, Joh K (2016) Parasediminibacterium paludis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from wetland in Jeju Island. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:326–331
Kim JK, Kang MS, Park SC, Kim KM, Choi K, Yoon MH, Im WT (2015) Sphingosinicella ginsenosidimutans sp. nov., with ginsenoside converting activity. J Microbiol 53:435–441
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lee JH, Ahn JY, Shin TJ, Choi SH, Lee BH, Hwang SH, Kang J, Kim HJ, Park CW, Nah SY (2011) Effects of minor ginsenosides, ginsenoside metabolites, and ginsenoside epimers on the growth of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Ginseng Res 35:375–383
Leung KW, Wong AS (2010) Pharmacology of ginsenosides: a literature review. Chin Med 5:20–22
Lim JH, Baek SH, Lee ST (2009) Ferruginibacter alkalilentus gen. nov., sp. nov. and Ferruginibacter lapsinanis sp. nov., novel members of the family 'Chitinophagaceae’ in the phylum Bacteroidetes, isolated from freshwater sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 259:2394–2399
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G + C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Moore DD, Dowhan D (1995) Preparation and analysis of DNA. In: Ausubel FW, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York, pp 2–11
Park MW, Ha J, Chung SH (2008) 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and activates AMPK. Biol Pharm Bull 31:748–751
Qu JH, Yuan HL, Yang JS, Li HF, Chen N (2009) Lacibacter cauensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the phylum Bacteroidetes isolated from sediment of a eutrophic lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1153–1157
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sangkhobol V, Skerman VBD (1981) Chitinophaga, a new genus of Chitinolytic myxobacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 31:285–293
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria through fatty acid analysis. In: Klement Z, Rudolph K, Sands DC (eds) Methods in phytobacteriology. Akademiai Kaido, Budapest, pp 199–204
Siddiqi MZ, Im WT (2016a) Niabella aquatica sp. nov., isolated from lake water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:2774–2779
Siddiqi MZ, Im WT (2016b) Pseudobacter ginsenosidimutans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from ginseng cultivating soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:3449–3455
Siddiqi MH, Siddiqi MZ, Ahn S, Kang S, Kim YJ, Veerappan K, Yang DU, Yang DC (2014) Stimulative effect of ginsenosides Rg5:Rk1 on murine osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cell. Phytother Res 28:1447–1455
Siddiqi MZ, Siddiqi MH, Kim YJ, Jin Y, Huq MA, Yang DC (2015) Effect of fermented red ginseng extract enriched in ginsenoside Rg3 on the differentiation and mineralization of preosteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. J Med Food 18:542–548
Siddiqi MZ, Muhammad Shafi S, Choi KD, Im WT (2016a) Compostibacter hankyongensis gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:3681–3687
Siddiqi MZ, Muhammad Shafi S, Choi KD, Im WT (2016b) Panacibacter ginsenosidivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., with ginsenoside converting activity isolated from soil of a ginseng field. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:4039–4045
Siddiqi MZ, Aslam Z, Im WT (2017a) Arachidicoccus ginsenosidivorans sp. nov., with ginsenoside-converting activity isolated from ginseng cultivating soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1005–1010
Siddiqi MZ, Muhammad Shafi S, Im WT (2017b) Complete genome sequencing of Arachidicoccus ginsenosidimutans sp. nov., and its application for production of minor ginsenosides by finding a novel ginsenoside-transforming β-glucosidase. RSC Adv 7:46745–46759
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1944) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 607–655
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Wang Y, Cai F, Tang Y, Dai J, Qi H, Rahman E, Peng F (2011) Flavitalea populi gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from soil of a euphrates poplar (Populus euphratica) forest. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1554–1560
Weon HY, Kim BY, Yoo SH, Lee SY, Kwon SW, Go SJ, Stackebrandt E (2006) Niastella koreensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Niastella yeongjuensis sp. nov., novel members of the phylum Bacteroidetes, isolated from soil cultivated with Korean ginseng. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1777–1782
Yoon MH, Im WT (2007) Flavisolibacter ginsengiterrae gen. nov., sp. nov. and Flavisolibacter ginsengisoli sp. nov., isolated from ginseng cultivating soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1834–1839
Funding
This work was supported by the project on survey and excavation of Korean indigenous species of the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR) under the Ministry of Environment, by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2019R1I1A1A01061945), and by Korea Research Fellowship (KRF) Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Project No. 2019H1D3A1A02070958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: MZ WTI. Performed the experiments: MZS. Analyzed the data: MZS MAH WTI. Wrote the paper: MZS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This study does not describe any experimental work related to human.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqi, M.Z., Huq, M.A. & Im, WT. Isolation, characterisation and genome analysis of a novel ginsenosides hydrolysing bacterium Ginsengibacter hankyongi gen. nov., sp. nov. isolated from soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 114, 11–22 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01485-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01485-4