Abstract
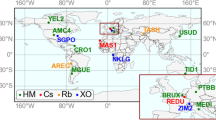
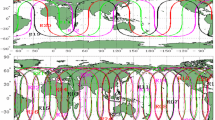
We present the joint estimation model for Global Positioning System/BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (GPS/BDS) real-time clocks and present the initial satellite clock solutions determined from 106 stations of the international GNSS service multi-GNSS experiment and the BeiDou experimental tracking stations networks for 1 month in December, 2012. The model is shown to be efficient enough to have no practical computational limit for producing 1-Hz clock updates for real-time applications. The estimated clocks were assessed through the comparison with final clock products and the analysis of post-fit residuals. Using the estimated clocks and corresponding orbit products (GPS ultra-rapid-predicted and BDS final orbits), the root-mean-square (RMS) values of coordinate differences from ground truth values are around 1 and 2–3 cm for GPS-only and BDS-only daily mean static precise point positioning (PPP) solutions, respectively. Accuracy of GPS/BDS combined static PPP solutions falls in between that of GPS-only and BDS-only PPP results, with RMS values approximately 1–2 cm in all three components. For static sites, processed in the kinematic PPP mode, the daily RMS values are normally within 4 and 6 cm after convergence for GPS-only and BDS-only results, respectively. In contrast, the combined GPS/BDS kinematic PPP solutions show higher accuracy and shorter convergence time. Additionally, the BDS-only kinematic PPP solutions using clock products derived from the proposed joint estimation model were superior compared to those computed using the single-system estimation model.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-Sever Y, Muellerschoen R, Reachert A, Vozoff M, Young L (2001) NASA’s internet-based global differential GPS system. In: Proceedings of NaviTech ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, Netherlands, pp 65–72
Boehm J, Niell A, Tregoning P, Schuh H (2006) Global mapping function (GMF): a new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys Res Lett 33:L07304
Coco DS, Coker C, Dahlke SR, Clynch JR (1991) Variability of GPS satellite differential group delay biases. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 27(6):931–938
Collins P (2008) Isolating and estimating undifferenced GPS integer ambiguities. In: Proceedings of ION-NTM-2008, Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, pp 720–732
Colombo OL (2008) Real-time, wide-area, precise kinematic positioning using data from internet NTRIP streams. In: Proceedings of ION-GNSS-2008, Institute of Navigation, Savannah, Georgia, pp 327–337
Dow JM, Neilan RE, Rizos C (2009) The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J Geod 83(3–4):191–198
Ge M, Gendt G, Rothacher M, Shi C, Liu J (2008) Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in precise point positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J Geod 82(7):389–399
Ge M, Chen JP, Dousa J, Gendt G, Wickert JA (2012a) Computationally efficient approach for estimating high-rate satellite clock corrections in realtime. GPS Solut 16(1):9–17
Ge M, Zhang HP, Jia XL, Song SL, Wickert J (2012b) What is achievable with the current compass constellation? In: Proceedings of ION-GNSS-2012, Institute of Navigation, Nashville, Tennessee
Gendt G, Dick G, Reigber CH, Tomassini M, Liu Y, Ramatschi M (2003) Demonstration of NRT GPS water vapor monitoring for numerical weather prediction in Germany. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 82(1B):360–370
Gong H, Yang W, Wang Y, Zhu X, Wang F (2012) Comparison of short-term stability estimation methods of GNSS on-board clock. In: Sun J, Liu J, Yang Y, Fan S (eds) China satellite navigation conference (CSNC) 2012 proceedings. Lecture notes in electrical engineering, vol 160. Springer, pp 503–513. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-29175-3_46
Han C, Yang Y, Cai Z (2011) BeiDou navigation satellite system and its time scales. Metrologia 48(4):S213–S218. doi:10.1088/0026-1394/48/4/S13
Hauschild A, Montenbruck O (2009) Kalman-filter-based GPS clock estimation for near realtime positioning. GPS Solut 13(3):173–182. doi:10.1007/s10291-008-0110-3
Kouba J (2009) A simplified yaw-attitude model for eclipsing GPS satellites. GPS Solut 13(1):1–12. doi:10.1007/s10291-008-0092-1
Li Z, Yuan Y, Li H, Ou J, Huo X (2012) Two-step method for the determination of the differential code biases of COMPASS satellites. J Geod 86(11):1059–1076
Lou Y, Liu Y, Shi C, Yao X, Zheng F (2014a) Precise orbit determination of BeiDou constellation based on BETS and MGEX network. Sci Rep 4:4692. doi:10.1038/srep04692
Lou Y, Zhang W, Wang C, Yao X, Shi C, Liu J (2014b) The impact of orbital errors on the estimation of satellite clock errors and PPP. Adv Space Res 54(8):1571–1580
McCarthy DD, Petit G (2004) IERS 2003 conventions. Verlag des Bundes fur Kartographie und Geodasie, Frankfurt am Main, p 127
Montenbruck O, Hauschild A, Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Teunissen P, Nakamura S (2013) Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut 17(2):211–222. doi:10.1007/s10291-012-0272-x
Montenbruck O, Hauschild A, Steigenberger P (2014a) Differential code bias estimation using multi-GNSS observations and global ionosphere map. In: Proceedings of ION-ITM-2014, Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, pp 26–28
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Khachikyan R, Weber G, Langley RB, Mervart L, Hugentobler U (2014b) IGS-MGEX: preparing the ground for multi-constellation GNSS science. Inside GNSS 9(1):42–49
Schaer S, Steigenberger S (2006) Determination and use of GPS differential code bias values. IGS Workshop 2006, May 8–11, Darmstadt, Germany
Schmid R, Steigenberger P, Gendt G, Ge M, Rothacher M (2007) Generation of a consistent absolute phase-center correction model for GPS receiver and satellite antennas. J Geod 81(12):781–798
Schönemann E, Becker M, Springer T (2011) A new approach for GNSS analysis in a multi-GNSS and multi-signal environment. J Geod Sci 1(3):201–214
Shi C, Zhao Q, Geng J, Lou Y, Ge M, Liu J (2008) Recent development of PANDA software in GNSS data processing. In: In: Proceedings of SPIE, international conference on earth observation data processing and analysis (ICEODPA), p 72851S. doi:10.1117/12.816261
Shi C, Zhao Q, Li M, Tang W, Hu Z, Lou Y, Zhang H, Niu X, Liu J (2012) Precise orbit determination of Beidou Satellites with precise positioning. Sci China Earth Sci 55(7):1079–1086
Shi C, Zhao Q, Hu Z, Liu J (2013) Precise relative positioning using real tracking data from COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. GPS Solut 17(1):103–119. doi:10.1007/s10291-012-0264-x
Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Hauschild A, Montenbruck O (2013) Orbit and clock analysis of Compass GEO and IGSO satellites. J Geod 87(6):515–525. doi:10.1007/s00190-013-0625-4
Weber G, Mervart L, Lukes Z, Rocken C, Dousa J (2007) Real-time clock and orbit corrections for improved point positioning via NTRIP. In: Proceedings of ION-GNSS-2007, Fort Worth, TX, 1992–1998
Wu J, Wu S, Hajj G, Bertiger W, Lichten S (1993) Effect of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr Geod 18:91–98
Zhao Q, Guo J, Li M, Qu L, Hu Z, Shi C, Liu J (2013) Initial results of precise orbit and clock determination for COMPASS navigation satellite system. J Geod 87(5):475–486. doi:10.1007/s00190-013-0622-7
Zumberge J, Heflin M, Jefferson D, Watkins M, Webb F (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102(B3):5005–5017
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No.: 41374034), the National “863 Program” of China (Grant No. 2012AA12A202), the Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities (2042014kf0081) and the China Scholarship Council (No.: 201406270066). We would like to thank two anonymous reviewers and Jeffrey Sussman from UC San Diego for their valuable suggestions and comments. The MGEX data were provided by the IGS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Lou, Y., Gu, S. et al. Joint estimation of GPS/BDS real-time clocks and initial results. GPS Solut 20, 665–676 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-015-0476-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-015-0476-y