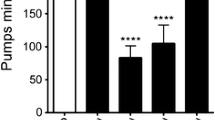
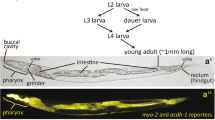
Abstract
This review considers the factors involved in the regulation of feeding and metabolism in response to food deprivation using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model organism. Some of the sensory neurons and interneurons involved in food intake are described, together with an overview of pharyngeal pumping. A number of chemical transmitters control feeding in C. elegans including 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT, serotonin), acetylcholine, glutamate, dopamine, octopamine, and tyramine. The roles of these transmitters are modified by neuropeptides, including FMRFamide-like peptides (FLPs), neuropeptide-like protein (NLPs), and insulin-like peptides. The precise effects of many of these neuropeptides have yet to be elucidated but increasingly they are being shown to play a role in feeding and metabolism in C. elegans. The regulation of fat stores is complex and appears to involve the expression of a large number of genes, many with mammalian homologues, suggesting that fat regulatory signalling is conserved across phyla. Finally, a brief comparison is made between C. elegans and mammals where for both, despite their evolutionary distance, classical transmitters and neuropeptides have anorectic or orexigenic properties. Thus, there is a rationale to support the argument that an understanding of the molecular and genetic basis of feeding and fat regulation in C. elegans may contribute to efforts aimed at the identification of targets for the treatment of conditions associated with abnormal metabolism and obesity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertson DG, Thompson JN (1976) The pharynx of Caenorhabditis elegans. Phil Trans Roy Soc Lond B 275:299–325
Alkema MJ, Hunrer-Ensor M, Ringstad N, Horvitz HR (2005) Tyramine functions independently of Octopamine in the Caenorhabditis elegans nervous system. Neuron 46:247–260
Altun-Gultekin Z, Andachi Y, Tsalik EL, Pilgrim D, Kohara Y, Hobert O (2001) A regulatory cascade of three homeobox genes, ceh-10, ttx-3 and ceh-23 controls cell fate specification of a defined interneuron class in C. elegans. Development 128:1951–1969
Apfeld J, Kenyon C (1999) Regulation of lifespan by sensory perception in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 402:804–809
Arora S, Anubhut C (2006) Role of neuropeptides in appetite regulation and obesity-A review. Neuropeptides 40:375–401
Ashrafi K (2007) Obesity and the regulation of fat metabolism. WormBook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, doi: 10.1895/wormbook. 1.130.1, http://wormbook.org
Ashrafi K, Chang FY, Watts JL, Fraser AG, Kamath RS, Ahringer J, Ruvkun G (2003) Genome-wide RNAi analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans fat regulating genes. Nature 421:268–272
Avery L (1993a) The genetics of feeding in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 133:897–917
Avery L (1993b) Motor-neuron M3 controls pharyngeal muscle-relaxation timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Exp Biol 175:283–297
Avery L (2010) Caenorhabditis elegans behavioural genetics: where are the knobs? BMC Biology 8:69
Avery L, Horvitz HR (1989) Pharyngeal pumping continues after laser killing of the pharyngeal nervous system of C. elegans. Neuron 3:473–485
Avery L, Horvitz HR (1990) Effects of starvation and neuroactive drugs on feeding in C. elegans. J Exp Zool 253:263–270
Avery L, Bargmann CI, Horvitz HR (1993) The Caenorhabditis elegans unc-31 gene affects multiple nervous system-controlled functions. Genetics 134:455–464
Behm CA (1997) The role of trehalose in the physiology of nematodes. Int J Parasitol 27:215–229
Behm CA (2002) Metabolism. In: Lee DL (ed) The biology of nematodes. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 261–290
Bendena WG, Boudreau JR, Papanicolaou T, Maltby M, Tobe SS, Chin-Sang ID (2008) A Caenorhabditis elegans allatostatin/galanin-like receptor NPR-9 inhibits local search behaviour in response to feeding cues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 195:1339–1342
Brock TJ, Browse J, Watts JL (2006) Genetic regulation of unsaturated fatty acid composition in C. elegans. PLoS Genet 2:e108
Brockie PJ, Madsen DM, Zheng Y, Mellem J, Maricq AV (2001) Differential expression of glutamate subunits in the nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans and their regulation by the homeodomain protein UNC-42. J Neurosci 21:1510–1522
Brooks KK, Liang B, Watts JL (2009) The influence of bacterial diet on fat storage in C. elegans. PLoS ONE 4:e7545
Carre-Pierrat M, Baillie D, Johnsen R, Hyde R, Hart A, Granger L, Segalat L (2006) Characterization of the Caenorhabditis elegans G protein-coupled serotonin receptors. Invert Neurosci 6:189–205
Chalansani SH, Kato S, Albrecht DR, Nakagawa T, Abbott LF, Bargmann CI (2010) Neuropeptide feedback modifies odor-evoked dynamics in Caenorhabditis elegans olfactory neurons. Nature Neurosci 13:615–621
Chalasani SH, Chronis N, Tsunozaki M, Gray JM, Ramot D, Goodman MB, Bargmann CI (2007) Dissecting a circuit for olfactory behaviour in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 450:63–70
Chao MY, Komatsu H, Fukuto HS, Dionne HM, Hart AC (2004) Feeding status and serotonin rapidly and reversibly modulate a Caenorhabditis elegans chemosensory circuit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15512–15517
Chartrel N, Dujardin C, Anouar Y, Leprince J, Decker A, Clerens S, Do-Rego JC et al (2003) Identification of 26RFa, a hypothalamic neuropeptide of the RFamide peptide family with orexigenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15247–15252
Chiang JTA, Steciuk M, Shtonda B, Avery L (2006) Evolution of pharyngeal behaviour and neuronal function in free-living soil nematodes. J Exp Biol 209:1859–1873
Coates JC, de Bono M (2002) Antagonistic pathways in neurons exposed to body fluid regulate social feeding in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 419:925–929
Cohen M, Reale V, Olofsson B, Knights A, Evans P, de Bono M (2009) Coordinated regulation of foraging and metabolism in C.elegans by RFamide neuropeptide signaling. Cell Metab 9:375–385
Croll NA (1975) Indolealkylamines in the coordination of nematode behavioural activities. Can J Zool 53:894–903
Croll NA, Smith JM (1978) Integrated behaviour in the feeding phase of Caenorhabditis elegans (Nematoda). J Zool (Lond.) 184:507–517
David MW, Fleischhauser R, Dent JA, Joho RH, Avery L (1999) A mutation in the C. elegans EXP-2 Potassium channel that alters feeding behavior. Science 286:2501–2504
de Bono M, Bargmann CI (1998) Natural variation in a Neuropeptide Y Receptor homolog modifies social behaviour and food response in C. elegans. Cell 94:679–689
Dent JA, Davies MW, Avery L (1997) avr-15 encodes a chloride channel subunit that mediates inhibitory glutamatergic neurotransmission and ivermectin sensitivity in Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO J 16:5867–5879
Dufresne M, Seva C, Fourmy D (2006) Cholecystokinin and gastrin receptors. Physiol Rev 86:805–847
Franks CJ, Holden-Dye L, Bull K, Luedtke S, Walker RJ (2006) Anatomy, physiology and pharmacology of Caenorhabditis elegans pharynx: a model to define gene function in a simple neural system. Invert Neurosci 6:105–122
Gao XB, van den Pol AN (2001) Melanin concentrating hormone depresses synaptic activity of Glutamate and GABA neurons from rat lateral hypothalamus. J Physiol 533:237–252
Gray JM, Hill JJ, Bargmann CI (2005) A circuit for navigation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3184–3191
Greer ER, Perez C, Van Gilst MR, Lee BH, Ashrafi K (2008) Neural and molecular dissection of a C.elegans sensory circuit that regulates fat and feeding. Cell Met 8:118–131
Hamdan FF, Ungrin MD, Abramovitz M, Ribeiro P (1999) Characterization of a novel serotonin receptor from Caenorhabditis elegans: cloning and expression of two splice variants. J Neurochem 72:1372–1383
Hart AC, Sims S, Kaplan JM (1995) Synaptic code for sensory modalities revealed by C. elegans GLR-1 glutamate receptor. Nature 378:82–85
Hellerer T, Axang C, Brackmann C, Hillertz P, Pilon M, Enejder A (2007) Monitoring of lipid storage in Caenorhabditis elegans using coherent ant-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14658–14663
Hills T, Brockie PJ, Maricq AV (2004) Dopamine and glutamate control area-restricted search behaviour in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 24:1217–1225
Hobson RJ, Geng J, Gray AD, Komuniecki RW (2003) SER-7b, a constitutively active Gα-coupled 5-HT7-like receptor expressed in the Caenorhabditis elegans M4 pharyngeal motoneuron. J Neurochem 87:22–29
Hobson RJ, Hapiak VM, Xiao H, Buehrer KL, Kommuniecki PR (2006) SER-7 a Caenorhabditis elegans 5HT7-like receptor is essential for the 5-HT stimulation of pharyngeal pumping and egg-laying. Genetics 172:159–169
Horvitz HR, Chalfie M, Trent C, Sulston JE, Evans PD (1982) Serotonin and octopamine in the nematode C. elegans. Science 216:1012–1014
Husson SJ, Clynen E, Baggerman G, Janssen T, Schoofs L (2006) Defective processing of neuropeptide precursors in Caenorhabditis elegans lacking proprotein convertase 2 (KPC-2/EGL-3): mutant analysis by mass spectrometry. J Neurochem 98:1999–2012
Husson SJ, Janssen T, Baggerman G, Bogert B, Kahn-Kirby AH, Ashrafi K, Schoofs L (2007) Impaired processing of FLP and NLP peptides in carboxypeptidase E (EGL-21)-deficient Caenorhabditis elegans as analyzed by mass spectrometry. J Neurochem 102:246–260
Janssen T, Meelkop E, Lindemans M, Verstraelen K, Husson SJ, Temmerman L, Nachman RJ, Schoofs L (2008) Discovery of a Cholecystokinin-Gastrin-like signaling system in Nematodes. Endocrinology 149:2826–2839
Kageyama H, Takenoya F, Shiba K, Shioda S (2010) Neuronal circuits involving ghrelin in the hypothalamus-mediated regulation of feeding. Neuropeptides 44:133–138
Kang C, Avery L (2009) Systemic regulation of starvation response in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Develop 23:12–17
Kim K, Li C (2004) Expression and regulation of an FMRFamide-related Neuropeptide gene family in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Comp Neurol 475:540–550
Kimura KD, Tissenbaum HA, Liu Y, Ruvkun G (1997) daf-2, an insulin receptor-like gene that regulates longevity and diapause in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 277:942–946
Konturek PC, Konturek JW, Czesnikiewcz-Guzik M, Brzozowski T, Sito E, Konturek SJ (2005) Neuro-hormonal control of food intake; Basic mechanisms and clinical implications. J Physiol Pharmacol 56(Supp 6):5–25
Lee BH, Ashrafi K (2008) A TRPV channel modulates C. elegans neurosecretion, larval starvation survival, and adult lifespan. PLoS Genetics 4:e1000213
Lee RN, Lobel L, Hengartner M, Horvitz HR, Avery L (1999) Eat-4, a homolog of a mammalian sodium-dependent inorganic phosphate co-transporter, is necessary for glutamatergic neurotransmission in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 19:159–167
Leibowitz S, Alexander J (1998) Hypothalamic serotonin in control of eating behaviour, meal size and body weight. Biol Psychiatry 44:851–864
Lewis GF, Carpentier A, Adell K, Giacca A (2002) Disordered fat storage and mobilization in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. Endocrin Rev 23:201–229
Li C (2005) The ever-expanding neuropeptide gene families in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Parasitology 131 (Suppl): S109–S127
Li C, Kim K (2008) Neuropeptides.WormBook, ed. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook, doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.142.1, http://www.wormbook.org
Li H, Avery L, Denk W, Hess GP (1997) Identification of chemical synapses in the pharynx of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5912–5916
Li W, Kennedy SG, Ruvkun G (2003) daf-28 encodes a C. elegans insulin superfamily member that is regulated by environmental cues and acts in the DAF-2 signaling pathway. Genes Develop 17:844–858
Li W, Feng Z, Sternberg PW, Shawn Xu XZ (2006) A C. elegans stretch receptor neuron revealed by a mechanosensitive TRP channel homologue. Nature 440:684–687
Liu LX, Spoerke JM, Mulligan EL, Chen J, Reardon B, Westlund B, Abel K, Armstrong B, Hardiman G, King J et al (1999) High-throughput isolation of Caenorhabditis elegans deletion mutants. Genome Res 9:859–867
Mak HY, Nelson LS, Basson M, Johnson CD, Ruvkun G (2006) Polygenic control of Caenorhabditis elegans fat storage. Nat Genet 38:363–368
Maricq AV, Peckol E, Driscoll M, Bargmann C (1995) glr-1, a C.elegans glutamate receptor that mediates mechanosensory signaling. Nature 378:78–81
McKay RM, McKay JP, Avery L, Graff JM (2003) c. elegans: A model for exploring the genetics of fat storage. Devel Cell 4:131–142
McKay JP, Raizen DM, Gottschalk A, Schafer WR, Avery L (2004) eat-2 and eat-18 are required for nicotinic transmission in the Caenorhabditis elegans pharynx. Genetics 166:161–169
McKay RM, McKay JP, Suh JM, Avery L, Graff JM (2007) Tripeptidyl peptidase II promotes fat formation in a conserved fashion. EMBO Reports 8:1183–1189
Mellem JE, Brockie PJ, Zheng Y, Madsen DM, Maricq AV (2002) Decoding of polymodel sensory stimuli by postsynaptic glutamate receptors in C. elegans. Neuron 36:933–944
Mukhopadhyay A, Deplancke B, Walhout AJM, Tissenbaum HA (2005) C. elegans tubby regulates life span and fat metabolism by two independent mechanisms. Cell Metabol 2:35–42
Mullaney BC, Ashrafi K (2009) C. elegans fat storage and metabolic regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791:474–478
Nakazato M, Murakami N, Date Y, Kojima M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K, Matsukura S (2001) A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 409:194–198
Nass R, Merchant KM, Ryan T (2008) Caenorhabditis elegans in Parkinson’s disease drug discovery: addressing an unmet clinical need. Mol Interv 8:284–293
Nathoo AN, Moeller RA, Westlund BA, Hart AC (2001) Identification of neuro-peptide-like gene families in Caenorhabditis elegans and other species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14000–14005
Niacaris T, Avery L (2003) Serotonin regulates repolarization of the C. elegans pharyngeal muscle. J Exp Biol 206:223–231
Noben-Trauth K, Naggert JK, North MA, Nishina PM (1996) A candidate gene for the mouse mutation tubby. Nature 380:534–538
O’Rahilly S, Farooqi IS (2008) Human obesity: a heritable neurobehavioural disorder that is highly sensitive to environmental conditions. Diabetes 57:2905–2910
Packham R, Walker RJ, Holden-Dye L (2010) The effect of a selective octopamine antagonist, epinastine, on pharyngeal pumping in Caenorhabditis elegans. Invert Neurosci 10:47–52
Panula P, Aarnisalo AA, Wasowicz K (1996) Neuropeptide FF, a mammalian neuropeptide with multiple functions. Prog Neurobiol 48:461–487
Papaioannou S, Marsden D, Franks CJ, Walker RJ, Holden-Dye L (2005) Role of a FMRFamide-like family of neuropeptides in the pharyngeal nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurobiol 65:304–319
Papaiouannou S, Holden-Dye L, Walker RJ (2008) The actions of Caenorhabditis elegans neuropeptde-like peptides (NLPs) on body wall muscle of Ascaris suum and pharyngeal muscle of C. elegans. Acta Biol Hung 59(Suppl):189–197
Pellerone FI, Archer CA, Behm CA, Grant WN, Lacey MJ, Somerville AC (2003) Trehalose metabolism genes in Caenorhabditis elegans and filarial nematodes. Int J Parasitol 33:1195–1206
Pierce SB, Costa M, Wisotzkey R, Devadhar S, Homburger SA, Ferguson KC, Heller J, Platt DM, Pasquinelli AA, Liu LX, Doberstein SK, Ruvkun G (2001) Regulation of DAF-2 receptor signaling by human insulin and ins-1, a member of the unusually large and diverse C. elegans insulin gene family. Genes Dev 15:672–686
Rand JB, Duerr JS, Frisby DL (2000) Neurogenetics of vesicular transporters in C. elegans. FASEB J 14:2414–2422
Ranganathan R, Cannon SC, Horvitz HR (2000) MOD-1 is a serotonin-gated chloride channel that modulates locomotory behaviour in C. elegans. Nature 408:470–475
Ren P, Lim CS, Johnsen R, Albert PS, Pilgrim D, Riddle DL (1996) Control of C. elegans larval development by neuronal expression of a TGF-β homolog. Science 274:1389–1391
Rogers CM, Franks CJ, Walker RJ, Burke JF, Holden-Dye L (2001) Regulation of the pharynx of Caenorhabditis elegans by 5-HT, octopamine and FMRFamide-like neuropeptides. J Neurobiol 49:235–244
Rogers C, Reale V, Kim K, Chatwin H, Li C, Evans P, de Bono M (2003) Inhibition of Caenorhabditis elegans social feeding by FMRFamide-related peptide activation of NPR-1. Nat Neurosci 6:1178–1185
Rosen E, Walkey C, Pulgserver P, Splegelman B (2000) Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes Dev 14:1293–1307
Sawin ER, Ranganathan R, Horvitz HR (2000) C. elegans locomotion rate is modulated by the environment through a dopaminergic pathway and by experience through a serotonergic pathway. Neuron 26:619–631
Seymour MK, Wright KA, Doncaster CC (1983) The action of the anterior feeding apparatus of Caenorhabditis elegans (Nematoda: Rhabditida). J Zool 201:527–539
Shtonda BB, Avery L (2006) Dietary choice behaviour in C. elegans. J Exp Biol 209:89–102
Speese S, Petri M, Schuske K, Ailon M, Ann K, Iwasaki K, Jorgensen EM, Martin TFJ (2007) UNC-31 (CAPS) is required for dense-core vesicle but not synaptic vesicle exocytosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 27:6150–6162
Srinivasan S (2008) Serotonin regulates C. elegans fat and feeding through independent molecular mechanisms. Cell Metabol 7:533–544
Steger KA, Avery L (2004) The GAR-3 muscarinic receptor cooperates with calcium signals to regulate muscle contraction in the Caenorhabditis elegans pharynx. Genetics 167:633–643
Suo S, Kimura Y, Van Tol HHM (2006) Starvation induces cAMP response element-binding protein-dependent gene expression through Octopamine-Gq signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 26:10082–10090
Suo S, Culotti JG, Van Tol HHM (2009a) Dopamine counteracts octopamine signalling in a neural circuit mediating food response in C. elegans. EMBO J 28:2437–2448
Suo S, Culotti JG, Van Tol HHM (2009b) Dopamine suppresses octopamine signalling in C. elegans: possible involvement of dopamine in the regulation of lifespan. Aging 1:870–874
Sze JY, Victor M, Loer C, Shi Y, Ruvkun G (2000) Food and metabolic signaling defects in a Caenorhabditis elegans serotonin-synthesis mutant. Nature 403:560–564
Tsalik EL, Hobert O (2003) Functional mapping of neurons that control locomotory behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurobiol 56:178–197
Tsalik EL, Niacaria T, Wenick AS, Pau K, Avery L, Hobert O (2003) LIM homeobox gene-dependent expression of biogenic amine receptors in restricted regions of the C. elegans nervous system. Develop Biol 263:81–102
van Gilst MR, Hadjivassiliou H, Jolly A, Yamamoto KR (2005) Nuclear hormone receptor NHR-49 controls fat consumption and fatty acid composition in C. elegans. PLos Biol 3:e53
Walker DS, Gower NJD, Ly S, Bradley GL, Baylis HA (2002) Regulated disruption of Inositol 1, 4, 5-Triphosphate signalling in Caenorhabditis elegans reveals new functions in feeding and embryogenesis. Mol Biol Cell 13:1329–1337
Watts JL (2008) Fattening up without overeating. Cell Metabolism 8:95–96
Watts JL (2009) Fat synthesis and adiposity regulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Trends Endocrin Metabol 20:58–65
Wenick AS, Hobert O (2004) Genomic cis-regulatory architecture and trans-acting regulators of a single interneuron-specific gene battery in C. elegans. Develop Cell 6:757–770
White J, Southgate E, Thomson JN, Brenner S (1986) The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Phil Trans Roy Soc Lond B 314:1–340
Wicks SR, Roehrig CJ, Rankin CH (1996) A dynamic network simulation of the nematode tap withdrawal circuit: predictions concerning synaptic function using behavioural criteria. J Neurosci 16:4017–4031
Wolkow CA, Kimura KD, Lee MS, Ruvkun G (2000) Regulation of C. elegans lifespan by insulin-like signaling in the nervous system. Science 290:147–150
Xiao H, Hapiak VM, Smith KA, Lin L, Hobson RJ, Plenefisch J, Komuniecki R (2006) SER-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans 5-HT2-like receptor, and a multi-PDZ domain containing protein (MPZ-1) interact in vulval muscle to facilitate serotonin-stimulated egg-laying. Develop Biol 298:379–391
You Y-J, Kim J, Cobb M, Avery L (2006) Starvation activates MAP kinase through the muscarinic acetylcholine pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans pharynx. Cell Metabol 3:237–245
Acknowledgments
Sarah Luedtke was supported by a studentship from the Gerald Kerkut Charitable Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luedtke, S., O’Connor, V., Holden-Dye, L. et al. The regulation of feeding and metabolism in response to food deprivation in Caenorhabditis elegans . Invert Neurosci 10, 63–76 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-010-0112-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-010-0112-z