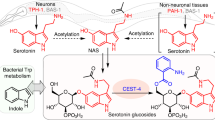
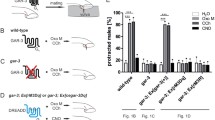
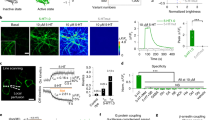
Abstract
Serotonin (5-HT) regulates a wide range of behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans, including egg laying, male mating, locomotion and pharyngeal pumping. So far, four serotonin receptors have been described in the nematode C. elegans, three of which are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), (SER-1, SER-4 and SER-7), and one is an ion channel (MOD-1). By searching the C. elegans genome for additional 5-HT GPCR genes, we identified five further genes which encode putative 5-HT receptors, based on sequence similarities to 5-HT receptors from other species. Using loss-of-function mutants and RNAi, we performed a systematic study of the role of the eight GPCR genes in serotonin-modulated behaviors of C. elegans (F59C12.2, Y22D7AR.13, K02F2.6, C09B7.1, M03F4.3, F16D3.7, T02E9.3, C24A8.1). We also examined their expression patterns. Finally, we tested whether the most likely candidate receptors were able to modulate adenylate cyclase activity in transfected cells in a 5-HT-dependent manner. This paper is the first comprehensive study of G protein-coupled serotonin receptors of C. elegans. It provides a direct comparison of the expression patterns and functional roles for 5-HT receptors in C. elegans.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amlaiky N, Ramboz S, Boschert U, Plassat JL, Hen R (1992) Isolation of a mouse “5HT1E-like” serotonin receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampus. J Biol Chem 267:19761–19764
Angers A, Storozhuk MV, Duchaine T, Castellucci VF, DesGroseillers L (1998) Cloning and functional expression of an Aplysia 5-HT receptor negatively coupled to adenylate cyclase. J Neurosci 18:5586–5593
Bard JA, Zgombick J, Adham N, Vaysse P, Branchek TA, Weinshank RL (1993) Cloning of a novel human serotonin receptor (5-HT7) positively linked to adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem 268:23422–23426
Bastiani CA, Gharib S, Simon MI, Sternberg PW (2003) Caenorhabditis elegans Galphaq regulates egg-laying behavior via a PLCbeta-independent and serotonin-dependent signaling pathway and likely functions both in the nervous system and in muscle. Genetics 165:1805–1822
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carnell L, Illi J, Hong SW, McIntire SL (2005) The G-protein-coupled serotonin receptor SER-1 regulates egg laying and male mating behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 25:10671–10681
Chao MY, Komatsu H, Fukuto HS, Dionne HM, Hart AC (2004) Feeding status and serotonin rapidly and reversibly modulate a Caenorhabditis elegans chemosensory circuit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15512–15517
Chen A, Holmes SP, Pietrantonio PV (2004) Molecular cloning and functional expression of a serotonin receptor from the Southern cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Insect Mol Biol 13:45–54
Colas JF, Launay JM, Kellermann O, Rosay P, Maroteaux L (1995) Drosophila 5-HT2 serotonin receptor: coexpression with fushi-tarazu during segmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5441–5445
Dempsey CM, Mackenzie SM, Gargus A, Blanco G, Sze JY (2005) Serotonin (5HT), fluoxetine, imipramine and dopamine target distinct 5HT receptor signaling to modulate Caenorhabditis elegans egg-laying behavior. Genetics 169:1425–1436
Dubin AE, Huvar R, D’Andrea MR, Pyati J, Zhu JY, Joy KC, Wilson SJ, Galindo JE, Glass CA, Luo L, Jackson MR, Lovenberg TW, Erlander MG (1999) The pharmacological and functional characteristics of the serotonin 5-HT(3A) receptor are specifically modified by a 5-HT(3B) receptor subunit. J Biol Chem 274:30799–30810
Foguet M, Hoyer D, Pardo LA, Parekh A, Kluxen FW, Kalkman HO, Stuhmer W, Lubbert H (1992a) Cloning and functional characterization of the rat stomach fundus serotonin receptor. Embo J 11:3481–3487
Foguet M, Nguyen H, Le H, Lubbert H (1992b) Structure of the mouse 5-HT1C, 5-HT2 and stomach fundus serotonin receptor genes. Neuroreport 3:345–348
Gerald C, Adham N, Kao HT, Olsen MA, Laz TM, Schechter LE, Bard JA, Vaysse PJ, Hartig PR, Branchek TA et al (1995) The 5-HT4 receptor: molecular cloning and pharmacological characterization of two splice variants. Embo J 14:2806–2815
Gerhardt CC, Leysen JE, Planta RJ, Vreugdenhil E, Van Heerikhuizen H (1996) Functional characterisation of a 5-HT2 receptor cDNA cloned from Lymnaea stagnalis. Eur J Pharmacol 311:249–258
Hamdan FF, Ungrin MD, Abramovitz M, Ribeiro P (1999) Characterization of a novel serotonin receptor from Caenorhabditis elegans: cloning and expression of two splice variants. J Neurochem 72:1372–1383
Hanna MC, Davies PA, Hales TG, Kirkness EF (2000) Evidence for expression of heteromeric serotonin 5-HT(3) receptors in rodents. J Neurochem 75:240–247
Hartig P (1997) Molecular biology and transductional characteristics of 5-HT receptors. In: Baumgarten H (eds) Serotoninergic neurons and 5-HT receptors in the CNS. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 175–212
Hobert O (2002) PCR fusion-based approach to create reporter gene constructs for expression analysis in transgenic C. elegans. Biotechniques 32:728–730
Hobson RJ, Geng J, Gray AD, Komuniecki RW (2003) SER-7b, a constitutively active Galphas coupled 5-HT7-like receptor expressed in the Caenorhabditis elegans M4 pharyngeal motorneuron. J Neurochem 87:22–29
Hobson RJ, Hapiak VM, Xiao H, Buehrer KL, Komuniecki PR, Komuniecki RW (2006) SER-7, a Caenorhabditis elegans 5-HT7-like receptor, is essential for the 5-HT stimulation of pharyngeal pumping and egg laying. Genetics 172:159–169
Horvitz HR, Chalfie M, Trent C, Sulston JE, Evans PD (1982) Serotonin and octopamine in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 216:1012–1014
Huang X, Duran E, Diaz F, Xiao H, Messer WS Jr, Komuniecki R (1999) Alternative-splicing of serotonin receptor isoforms in the pharynx and muscle of the parasitic nematode, Ascaris suum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 101:95–106
Keating CD, Kriek N, Daniels M, Ashcroft NR, Hopper NA, Siney EJ, Holden-Dye L, Burke JF (2003) Whole-genome analysis of 60 G protein-coupled receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans by gene knockout with RNAi. Curr Biol 13:1715–1720
Kim SK, Lund J, Kiraly M, Duke K, Jiang M, Stuart JM, Eizinger A, Wylie BN, Davidson GS (2001) A gene expression map for Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 293:2087–2092
Komuniecki RW, Hobson RJ, Rex EB, Hapiak VM, Komuniecki PR (2004) Biogenic amine receptors in parasitic nematodes: what can be learned from Caenorhabditis elegans? Mol Biochem Parasitol 137:1–11
Li XC, Giot JF, Kuhl D, Hen R, Kandel ER (1995) Cloning and characterization of two related serotonergic receptors from the brain and the reproductive system of Aplysia that activate phospholipase C. J Neurosci 15:7585–7591
Loer CM, Kenyon CJ (1993) Serotonin-deficient mutants and male mating behavior in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 13:5407–5417
Maroteaux L, Saudou F, Amlaiky N, Boschert U, Plassat JL, Hen R (1992) Mouse 5HT1B serotonin receptor: cloning, functional expression, and localization in motor control centers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:3020–3024
McKay SJ, Johnsen R, Khattra J, Asano J, Baillie DL, Chan S, Dube N, Fang L, Goszczynski B, Ha E, Halfnight E, Hollebakken R, Huang P, Hung K, Jensen V, Jones SJ, Kai H, Li D, Mah A, Marra M, McGhee J, Newbury R, Pouzyrev A, Riddle DL, Sonnhammer E, Tian H, Tu D, Tyson JR, Vatcher G, Warner A, Wong K, Zhao Z, Moerman DG (2003) Gene expression profiling of cells, tissues, and developmental stages of the nematode C. elegans. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 68:159–169
Meyerhof W, Obermuller F, Fehr S, Richter D (1993) A novel rat serotonin receptor: primary structure, pharmacology, and expression pattern in distinct brain regions. DNA Cell Biol 12:401–409
Monsma FJ Jr, Shen Y, Ward RP, Hamblin MW, Sibley DR (1993) Cloning and expression of a novel serotonin receptor with high affinity for tricyclic psychotropic drugs. Mol Pharmacol 43:320–327
Olde B, McCombie WR (1997) Molecular cloning and functional expression of a serotonin receptor from Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Neurosci 8:53–62
Plassat JL, Boschert U, Amlaiky N, Hen R (1992) The mouse 5HT5 receptor reveals a remarkable heterogeneity within the 5HT1D receptor family. Embo J 11:4779–4786
Pritchett DB, Bach AW, Wozny M, Taleb O, Dal Toso R, Shih JC, Seeburg PH (1988) Structure and functional expression of cloned rat serotonin 5HT-2 receptor. Embo J 7:4135–4140
Ranganathan R, Cannon SC, Horvitz HR (2000) MOD-1 is a serotonin-gated chloride channel that modulates locomotory behaviour in C. elegans. Nature 408:470–475
Saudou F, Boschert U, Amlaiky N, Plassat JL, Hen R (1992) A family of Drosophila serotonin receptors with distinct intracellular signalling properties and expression patterns. Embo J 11:7–17
Sawin ER, Ranganathan R, Horvitz HR (2000) C. elegans locomotory rate is modulated by the environment through a dopaminergic pathway and by experience through a serotonergic pathway. Neuron 26:619–631
Schloss P, Williams DC (1998) The serotonin transporter: a primary target for antidepressant drugs. J Psychopharmacol 12:115–121
Segalat L, Elkes DA, Kaplan JM (1995) Modulation of serotonin-controlled behaviors by Go in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 267:1648–1651
Sugamori KS, Sunahara RK, Guan HC, Bulloch AG, Tensen CP, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Van Tol HH (1993) Serotonin receptor cDNA cloned from Lymnaea stagnalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:11–15
Sugiura M, Fuke S, Suo S, Sasagawa N, Van Tol HH, Ishiura S (2005) Characterization of a novel D2-like dopamine receptor with a truncated splice variant and a D1-like dopamine receptor unique to invertebrates from Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurochem 94:1146–1157
Sze JY, Victor M, Loer C, Shi Y, Ruvkun G (2000) Food and metabolic signalling defects in a Caenorhabditis elegans serotonin-synthesis mutant. Nature 403:560–564
Thacker C, Sheps JA, Rose AM (2006) Caenorhabditis elegans dpy-5 is a cuticle procollagen processed by a proprotein convertase. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1193–204
Tierney AJ (2001) Structure and function of invertebrate 5-HT receptors: a review. Comp Biochem Physiol A 128:791–804
Timmons L, Court DL, Fire A (2001) Ingestion of bacterially expressed dsRNAs can produce specific and potent genetic interference in Caenorhabditis elegans. Gene 263:103–112
Trent C, Tsuing N, Horvitz HR (1983) Egg-laying defective mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 104:619–647
Tsalik EL, Niacaris T, Wenick AS, Pau K, Avery L, Hobert O (2003) LIM homeobox gene-dependent expression of biogenic amine receptors in restricted regions of the C. elegans nervous system. Dev Biol 263:81–102
Waggoner LE, Zhou GT, Schafer RW, Schafer WR (1998) Control of alternative behavioral states by serotonin in Caenorhabditis elegans. Neuron 21:203–214
Weiger WA (1997) Serotonergic modulation of behaviour: a phylogenetic overview. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 72:61–95
Witz P, Amlaiky N, Plassat JL, Maroteaux L, Borrelli E, Hen R (1990) Cloning and characterization of a Drosophila serotonin receptor that activates adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:8940–8944
Xie J, Dernovici S, Ribeiro P (2005) Mutagenesis analysis of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor and a Caenorhabditis elegans 5-HT2 homologue: conserved residues of helix 4 and helix 7 contribute to agonist-dependent activation of 5-HT2 receptors. J Neurochem 92:375–387
Zhang Y, Lu H, Bargmann CI (2005) Pathogenic bacteria induce aversive olfactory learning in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 438:179–184
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Theresa Stiernagle and the Caenorhabditis Genetic Center (CGC) for providing various strains used in this study, and J. Starck, G. Mouchiroud and F. Morlé for technical advice. The authors thank P.O. Barome, P. Vernier, D. Rognan, and F. Bonneton for phylogenetic analysis. This work was supported by grants from the Association Française contre les Myopathies (AFM) and the European Community (MYORES) to L.S., and grants from Genome Canada and Genome BC, NSERC, and a CRC Chair to D.L.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carre-Pierrat, M., Baillie, D., Johnsen, R. et al. Characterization of the Caenorhabditis elegans G protein-coupled serotonin receptors. Invert Neurosci 6, 189–205 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-006-0033-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-006-0033-z