Abstract
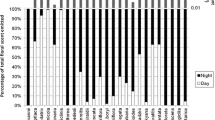
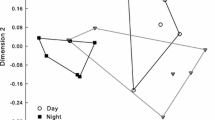
We examined the contribution of diurnal and nocturnal pollination to male and female reproductive success in Lilium auratum. Plants were bagged for either 12 h during the day or at night to allow either only nocturnal or only diurnal visitors to forage throughout the flowering period. We found that there was no significant difference in the seed:ovule ratio among diurnally pollinated, nocturnally pollinated, or control flowers. However, in terms of male reproductive success, it was more advantageous for the plants to be pollinated both diurnally and nocturnally: the numbers of pollen grains remaining in diurnally pollinated or nocturnally pollinated flowers were significantly greater than those in control flowers. The total amount of floral volatiles of L. auratum was significantly higher at night than during the day. The constituents of floral scent of all time series examined were mostly monoterpenoids, many of which serve as attractants for nocturnal hawkmoths. Such nocturnally biased floral scent emission of L. auratum might achieve male reproductive success by attracting nocturnal visitors, which may suggest that the relative contribution of floral scent in this species is biased towards male reproductive success.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenburger R, Matile P (1990) Further observation of rhythmic emission of fragrances in flowers. Planta 180:194–197. doi:10.1007/BF00193995
Arizaga S, Ezcurra E, Peters E, de Arellano FR, Vega E (2000) Pollination ecology of Agave macroacantha (Agavaceae) in a Mexican tropical desert. I. Floral biology and pollination mechanisms. Am J Bot 87:1004–1010. doi:10.2307/2657000
Bell G (1985) On the function of flowers. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 224:223–265
Bertin RI, Willson MF (1980) Effectiveness of diurnal and nocturnal pollination of two milkweeds. Can J Bot 58:1744–1746
Cruden RW (1973) Reproductive biology of weedy and cultivated Mirabilis (Nyctaginaceae). Am J Bot 60:802–809. doi:10.2307/2441173
Dötterl S, Wolfe LM, Jürgens A (2005) Qualitative and quantitative analyses of flower scent in Silene latifolia. Phytochemistry 66:203–213. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.12.002
Dudareva N, Murfitt LM, Mann CJ, Gorenstein N, Kolosova N, Kish CM et al (2000) Developmental regulation of methyl benzoate biosynthesis and emission in snapdragon flowers. Plant Cell 12:949–961
Fleming TH, Holland JN (1998) The evolution of obligate pollination mutualisms: senita cactus and senita moth. Oecologia 114:368–375. doi:10.1007/s004420050459
Galen C (1996) Rates of floral evolution: adaptation to bumble bee pollination in an alpine wild flower, Polemonium viscosum. Evol Int J Org Evol 50:120–125. doi:10.2307/2410786
Gershenzon J (1994) Metabolic costs of terpenoid accumulation in higher plants. J Chem Ecol 20:1281–1328. doi:10.1007/BF02059810
Groman JD, Pellmyr O (1999) The pollination biology of Manfreda virginica (Agavaceae): relative contribution of diurnal and nocturnal visitors. Oikos 87:373–381. doi:10.2307/3546753
Guitian P, Guitian J, Navarro L (1993) Pollen transfer and diurnal versus nocturnal pollination in Lonicera etrusca. Acta Oecol 14:219–227
Haber WA, Frankie GW (1982) Pollination of Luehea (Tiliaceae) in Costa Rican deciduous forest. Ecology 63:1740–1750. doi:10.2307/1940116
Helsper JPFG, Davies JA, Bouwmeester HJ, Korl AF, van Kampen MH (1998) Circadian rhythmicity in emission of volatile compounds by flowers of Rosa hybrida L. cv. Honesty. Planta 207:88–95. doi:10.1007/s004250050459
Hoballah ME, Koellner TG, Degenhardt J, Turlings TCJ (2004) Costs of induced volatile production in maize. Oikos 105:168–180. doi:10.1111/j.0030-1299.2004.12831.x
Ishii HS, Sakai S (2000) Optimal timing of corolla abscission: experimental study on Erythronium japonicum (Liliaceae). Funct Ecol 14:122–128. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2435.2000.00401.x
Jennersten O (1988) Pollination of Viscaria vulgaris (Caryophyllaceae): the contributions of diurnal and nocturnal insects to seed set and seed predation. Oikos 52:319–327. doi:10.2307/3565205
Jennersten O, Morse DH (1991) The quality of pollination by diurnal and nocturnal insects visiting common milkweed Asclepias syriaca. Am Midl Nat 125:18–28. doi:10.2307/2426365
Jürgens A, Witt T, Gottsberger G (2002) Flower scent composition in night-flowering Silene species (Caryophyllaceae). Biochem Syst Ecol 30:383–397. doi:10.1016/S0305-1978(01)00106-5
Jürgens A, Witt T, Gottsberger G (2003) Flower scent composition in Dianthus and Saponaria species (Caryophyllaceae) and its relevance for pollination biology and taxonomy. Biochem Syst Ecol 31:345–357. doi:10.1016/S0305-1978(02)00173-4
Kelber A, Balkenius A, Warrant EJ (2002) Scotopic colour vision in nocturnal hawkmoths. Nature 419:922–925. doi:10.1038/nature01065
Knudsen JT, Tollsten L (1993) Trends in floral scent chemistry in pollination syndromes: floral scent composition in moth-pollinated taxa. Bot J Linn Soc 113:263–284
Kolosova N, Gorenstein N, Kish CM, Dudareva N (2001) Regulation of circadian methyl benzoate emission in diurnally and nocturnally emitting plants. Plant Cell 13:2333–2347
Loughrin JH, Hamilton-Kemp TR, Andersen RA, Hildebrand DF (1990) Volatiles from flowers of Nicotiana sylvestris, N. otophora, and Malus domestica: headspace components and day/night changes in their relative concentrations. Phytochemistry 29:2473–2477. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(90)85169-G
Matile P, Altenburger R (1988) Rhythms of fragrance emission in flowers. Planta 174:242–247. doi:10.1007/BF00394777
Miyake T, Yahara T (1998) Why does the flower of Lonicera japonica open at dusk? Can J Bot 76:1806–1811. doi:10.1139/cjb-76-10-1806
Miyake T, Yahara T (1999) Theoretical evaluation of pollen transfer by nocturnal and diurnal pollinators: when should a flower open? Oikos 86:233–240. doi:10.2307/3546441
Miyake T, Yamaoka R, Yahara T (1998) Floral scents of hawkmoth-pollinated flowers in Japan. J Plant Res 111:199–205. doi:10.1007/BF02512170
Morse DH, Fritz RS (1983) Contributions of diurnal and nocturnal insects to the pollination of common milkweed (Asclepias syriaca L.) in a pollen-limited system. Oecologia 60:190–197. doi:10.1007/BF00379521
Nilsson LA (1985) Characteristics and distribution of intermediates between Platantera bifolia and P. chlorantha (Orchidaceae) in the Nordic countries. Nord J Bot 5:407–419. doi:10.1111/j.1756-1051.1985.tb01696.x
Raguso RA, Pichersky E (1995) Floral volatiles from Clarkia breweri and C. concinna (Onagraceae): recent evolution of floral scent and moth pollination. Plant Syst Evol 194:55–67. doi:10.1007/BF00983216
Raguso RA, Pichersky E (1999) A day in the life of a linalool molecule: chemical communication in a plant-pollinator system. Part 1: Linalool biosynthesis in flowering plants. Plant Species Biol 14:95–120. doi:10.1046/j.1442-1984.1999.00014.x
Raguso RA, Willis MA (2002) Synergy between visual and olfactory cues in nectar feeding by naive hawkmoths, Manduca sexta. Anim Behav 64:685–695. doi:10.1006/anbe.2002.4010
Raguso RA, Willis MA (2005) Synergy between visual and olfactory cues in nectar feeding by wild hawkmoths, Manduca sexta. Anim Behav 69:407–418. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2004.04.015
Raguso RA, Levin RA, Foose SE, Holmberg MW, McDade LA (2003) Fragrance chemistry, nocturnal rhythms and pollination “syndromes” in Nicotiana. Phytochemistry 63:265–284. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00113-4
Slauson LA (2000) Pollination biology of two chiropterophilous agaves in Arizona. Am J Bot 87:825–836. doi:10.2307/2656890
Tollsten L (1993) A multivariate approach to post-pollination changes in the floral scent of Platanthera bifolia (Orchidaceae). Nord J Bot 13:495–499. doi:10.1111/j.1756-1051.1993.tb00088.x
Tollsten L, Knudsen JT, Bergström LG (1994) Floral scent in generalistic Angelica (Apiaceae): an adaptive character? Biochem Syst Ecol 22:161–169. doi:10.1016/0305-1978(94)90006-X
Young HJ (2002) Diurnal and nocturnal pollination of Silene alba (Caryophyllaceae). Am J Bot 89:433–440. doi:10.3732/ajb.89.3.433
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank T. Nakashizuka, J. Urabe, K. Hikosaka, J. Yokoyama and H. Ota for their valuable suggestions; T. Itagaki, T. Makino, H. Tsujisawa and M. Kimura for their assistance in the design of experiments; and Y. Suzuki, M. Oguro, S. Horie, T. Yamada, A. Shigeno and K. Kubota for assistance in the field work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morinaga, SI., Kumano, Y., Ota, A. et al. Day–night fluctuations in floral scent and their effects on reproductive success in Lilium auratum . Popul Ecol 51, 187–195 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10144-008-0097-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10144-008-0097-1