Abstract
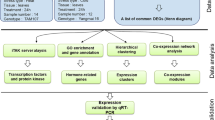
To identify salt-responsive genes in wheat, global expression analysis of transcripts was carried out using oligo-DNA microarrays. Microarrays have been designed from approximately 32,000 unique wheat genes classified from a large number of expressed sequence tags (ESTs). Two-week-old seedlings of wheat were treated with 150 mM NaCl for 1, 6, and 24 h, and their roots and shoots were separately subjected to analyses. Consequently, 5,996 genes showed changes in expression of more than twofold and were classified into 12 groups according to correlations in expression patterns. These salt-responsive genes were assigned functions using the Gene Ontology (GO). Genes assigned to transcription factor, transcription-regulator activity, and DNA-binding functions were preferentially classified into early response groups. On the other hand, those assigned transferase and transporter activity were classified into late response groups. These data suggest that multiple signal transduction pathways in response to salinity exist in wheat. Transcription factors (TFs) which have been reported as participants in salt-tolerant pathway changed their expression levels in response to salt treatment. Among them, only a few TFs show high sequence homologies to genes in rice. These investigations suggest that salt-responsive genes identified by this study are candidates for salt-stress tolerance uniquely in wheat.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berardini T, Mundodi S, Reiser R, Huala E, Garcia-Hernandez M, Zhang P, Mueller L, Yoon J, Doyle A, Lander G, Moseyko N, Yoo D, Xu I, Zoeckler B, Montoya M, Miller N, Weems D, Rhee S (2004) Functional annotation of the Arabidopsis genome using controlled vocabularies. Plant Physiol 135:1–11
Chao D, Luo Y, Shi M, Luo D, Lin H (2005) Salt-responsive genes in rice revealed by cDNA microarray analysis. Cell Research 15:796–810
Chao S, Lazo G, You F, Crossman C, Hummel D, Lui N, Laudencia-Chingcuanco D, Anderson JA, Close T, Dubcovsky J, Gill B, Gill K, Gustafson J, Kianian S, Lapitan N, Nguyen H, Sorrells M, McGuire P, Qualset C, Anderson O (2006) Use of a large-scale Triticeae expressed sequence tag resource to reveal gene expression profiles in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome 49:531–544
Chen W, Provart NJ, Glazebrook J, Katagiri F, Chang H, Eulgem T, Mauch F, Luan S, Zou G, Whitham SA, Budworth PR, Tao Y, Xie Z, Chen X, Lam S, Kreps JA, Harper JF, Si-Ammour A, Mauch-Mani B, Heinlein M, Kobayashi K, Hohn T, Dangl J, Wang X, Zhu T (2002) Expression profile matrix of Arabidopsis transcription factor genes suggests their putative functions in response to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 14:559–574
Crismani W, Baumann U, Sutton T, Shirley N, Webster T, Spangenberg G, Langridge P, Able J (2006) Microarray expression analysis of meiosis and microsporogenesis in hexaploid bread wheat. BMC Genomics 7:267
Dai X, Xu Y, Ma Q, Xu W, Wang T, Xue Y, Chong K (2007) Overexpression of a R1R2R3 MYB Gene, OsMYB3R-2, Increases Tolerance to Freezing, Drought, and Salt Stress in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1739–1751
Devos K, Ma J, Pontaroli A, Pratt L, Bennetzen J (2005) Analysis and mapping of randomly chosen bacterial artificial chromosome clones from hexaploid bread wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:19243–19248
Eisen M, Spellman P, Brown P, Botstein D (1998) Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14863–14868
Finn R, Mistry J, Schuster-Bockler B, Griffiths-Jones S, Hollich V, Lassmann T, Moxon S, Marshall M, Khanna A, Durbin R, Eddy SR, Sonnhammer E, Bateman A (2006) Pfam: clans, web tools and services. Nucleic Acid Research 34:D247–251
Flowers T, Koyama M, Flowers S, Sudhakar C, Singh K, Yeo A (2000) QTL: their place in engineering tolerance of rice to salinity. J Exp Bot 51:99–106
Flowers T (2004) Improving crop salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 55:307–319
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tagiri A, Tanaka H, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Tanaka Y (2004) Function, intracellular localization and the importance in salt tolerance of a vacuolar Na(+)/H(+) antiporter from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:146–159
Gill B, Appels R, Botha-Oberholster A, Buell C, Bennetzen J, Chalhoub B, Chumley F, Dvorak J, Iwanaga M, Keller B, Li W, McCombie W, Ogihara Y, Quetier F, Sasaki T (2004) A workshop report on wheat genome sequencing: International Genome Research on Wheat Consortium. Genetics 168:1087–1096
Golkari S, Gilbert J, Prashar S, Procunier JD (2007) Microarray analysis of Fusarium graminearum-induced wheat genes: identification of organ-specific and differentially expressed genes. Plant Biotechnol J 5:38–49
Gregersen PL, Holm PB (2007) Transcriptome analysis of senescence in the flag leaf of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Biotechnol J 5:192–206
Gregersen PL, Brinch-Pedersen H, Holm P (2005) A microarray-based comparative analysis of gene expression profiles during grain development in transgenic and wild type wheat. Transgenic Res 14:887–905
He XJ, Mu RL, Cao WH, Zhang ZG, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2005) AtNAC2, a transcription factor downstream of ethylene and auxin signaling pathways, is involved in salt stress response and lateral root development. Plant J 44:903–916
Houde M, Belcaid M, Ouellet F, Danyluk J, Monroy AF, Dryanova A, Gulick P, Bergeron A, Laroche A, Links MG, MacCarthy L, Crosby WL, Sarhan F (2006) Wheat EST resources for functional genomics of abiotic stress. BMC Genomics 7:149
Hu H, Dai M, Yao J, Xiao B, Li X, Zhang Q, Xiong L (2006) Overexpressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:12987–12992
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (2005) The map based sequence of rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
Ito Y, Katsura K, Maruyama K, Taji T, Kobayashi M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Functional analysis of rice DREB1/CBF-type transcription factors involved in cold-responsive gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Physiol 47:141–153
Jiang Y, Deyholos MK (2006) Comprehensive transcriptional profiling of NaCl-stressed Arabidopsis roots reveals novel classes of responsive genes. BMC Plant Biol 6:25
Kader M, Seidel T, Golldack D, Lindberg S (2006) Expressions of OsHKT1, OsHKT2, and OsVHA are differentially regulated under NaCl stress in salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J Exp Bot 15:4257–4268
Karlin S, Altschul S (1993) Applications and statistics for multiple high-scoring segments in molecular sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5873–5877
Kasuga M, Liu Q, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1999) Improving plant drought, salt, and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nat Biotechnol 17:287–291
Kawasaki S, Borchert C, Deyholos M, Wang H, Brazille S, Kawai K, Galbraith D, Bohnert H (2001) Gene expression profiles during the initial phase of salt stress in rice. Plant Cell 13:889–905
Kawaura K, Mochida K, Yamazaki Y, Ogihara Y (2006) Transcriptome analysis of salinity stress responses in common wheat using a 22 k oligo-DNA microarray. Funct Integr Genomics 6:132–142
Kikuchi S, Satoh K, Nagata T, Kawagashira N, Doi K, Kishimoto N, Yazaki J, Ishikawa M, Yamada H, Ooka H, Hotta I, Kojima K, Namiki T, Ohneda E, Yahagi W, Suzuki K, Li C, Ohtsuki K, Shishiki T, Otomo Y, Murakami K, Iida Y, Sugano S, Fujimura T, Suzuki Y, Tsunoda Y, Kurosaki T, Kodama T, Masuda H, Kobayashi M, Xie Q, Lu M, Narikawa R, Sugiyama A, Mizuno K, Yokomizo S, Niikura J, Ikeda R, Ishibiki J, Kawamata M, Yoshimura A, Miura J, Kusumegi T, Oka M, Ryu R, Ueda M, Matsubara K, Kawai J, Carninci P, Adachi J, Aizawa K, Arakawa T, Fukuda S, Hara A, Hashizume W, Hayatsu N, Imotani K, Ishii Y, Itoh M, Kagawa I, Kondo S, Konno H, Miyazaki A, Osato N, Ota Y, Saito R, Sasaki D, Sato K, Shibata K, Shinagawa A, Shiraki T, Yoshino M, Hayashizaki Y, Yasunishi A, Rice Full-Length cDNA Project TeamFoundation of Agrobiological International Science Genome Sequencing and Analysis Group RIKEN (2003) Collection, mapping, and annotation of over 28,000 cDNA clones from japonica rice. Science 301:376–379
Langridge P, Paltridge N, Fincher G (2006) Functional genomics of abiotic stress tolerance in cereals. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 4:343–354
Lee S, Ahn J, Cha Y, Yun D, Lee M, Ko J, Lee K, Eun M (2006) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for salt tolerance at the seedling stage in rice. Mol Cells 21:192–196
Liu Q, Kasuga M, Sakuma Y, Abe H, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1998) Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1391–1406
Maruyama K, Sakuma Y, Kasuga M, Ito Y, Seki M, Goda H, Shimada Y, Yoshida S, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2004) Identification of cold-inducible downstream genes of the Arabidopsis DREB1A/CBF3 transcriptional factor using two microarray systems. Plant J 38:982–993
Mochida K, Kawaura K, Shimosaka E, Kawakami N, Shin-i T, Kohara Y, Yamazaki Y, Ogihara Y (2006) Tissue expression map of a large number of expressed sequence tags and its application to in silico screening of stress response genes in common wheat. Mol Genet Genomes 276:304–312
Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Regulons involved in osmotic stress-responsive and cold stress-responsive gene expression in plants. Pysiologia Plantarum 126:62–71
Ogihara Y, Mochida K, Nemoto Y, Murai K, Yamazaki Y, Shin-i T, Kohara Y (2003) Correlated clustering and virtual display of gene expression patterns in the wheat life cycle by large-scale statistical analyses of expressed sequence tags. Plant J 33:1001–1011
Oh S, Song S, Kim Y, Jang H, Kim S, Kim M, Kim Y, Nahm B, Kim J (2005) Arabidopsis CBF3/DREB1A and ABF3 in transgenic rice increased tolerance to abiotic stress without stunting growth. Plant Physiol 138:341–351
Ouyang S, Zhu W, Hamilton J, Lin H, Campbell M, Childs K, Thibaud-Nissen F, Malek RL, Lee Y, Zheng L, Orvis J, Haas B, Wortman J, Buell CR (2007) The TIGR Rice Genome Annotation Resource: improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Research 35:D883–D887
Pellegrineschi A, Reynolds M, Pacheco M, Brito R, Almeraya R, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Hoisington D (2004) Stress-induced expression in wheat of the Arabidopsis thaliana DREB1A gene delays water stress symptoms under greenhouse conditions. Genome 47:493–500
Qu LJ, Zhu YX (2006) Transcription factor families in Arabidopsis: major progress and outstanding issues for future research. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 9:544–549
Quarrie S, Steed A, Calestani C, Semikhodskii A, Lebreton C, Chinoy C, Steele N, Pljevljakusic D, Waterman E, Weyen J, Schondelmaier J, Habash D, Farmer P, Saker L, Clarkson D, Abugalieva A, Yessimbekova M, Turuspekov Y, Abugalieva S, Tuberosa R, Sanguineti M, Hollington P, Aragues R, Royo A, Dodig D (2005) A high-density genetic map of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) from the cross Chinese Spring x SQ1 and its use to compare QTLs for grain yield across a range of environments. Theor Appl Genet 110:865–880
Rabbani M, Maruyama K, Abe H, Khan M, Katsura K, Ito Y, Yoshiwara K, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Monitoring expression profiles of rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA gel-blot analyses. Plant Physiol 133:1755–1767
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li LG, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY, Zhu MZ, Wang ZY, Luan S, Lin HX (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nature Genet 37:1141–1146
Sahi C, Singh A, Kumar K, Blumwald E, Grover A (2006) Salt stress response in rice: genetics, molecular biology, and comparative genomics. Funct Integr Genomics 6:263–284
Saijo Y, Hata S, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K, Izui K (2000) Over-expression of a single Ca2+ -dependent protein kinase confers both cold and salt/drought tolerance on rice plants. Plant J 23:319–327
Seki M, Narusaka M, Ishida J, Nanjo T, Fujita M, Oono Y, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Sakurai T, Satou M, Akiyama K, Taji T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Carninci P, Kawai J, Hayashizaki Y, Shinozaki K (2002) Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J 31:279–292
Seki M, Satou M, Sakurai T, Akiyama K, Iida K, Ishida J, Nakajima M, Enju A, Narusaka M, Fujita M, Oono Y, Kamei A, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2004) RIKEN Arabidopsis full-length (RAFL) cDNA and its applications for expression profiling under abiotic stress conditions. J Exp Bot 55:213–223
Shukla R, Raha S, Tripathi V, Chattopadhyay D (2006) Expression of CAP2, and APETALA2-family transcription factor fron chickpea, enhances growth and tolerance to dehydration and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol 142:113–123
The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 480:796–815
The Gene Ontology Consortium (2000) Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nature Genet 25:25–29
Ueda A, Kathiresan A, Bennett J, Takabe T (2006) Comparative transcriptome analyses of barley and rice under salt stress. Theor Appl Genet 112:1286–1294
Walia H, Wilson C, Condamine P, Liu X, Ismail A, Zeng L, Wanamaker S, Mandal J, Xu J, Cui X, Close T (2005) Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage. Plant Physiol 139:822–835
Walia H, Wilson C, Zeng L, Ismail A, Condamine P, Close T (2007) Genome-wide transcriptional analysis of salinity stressed japonica and indica rice genotypes during panicle initiation stage. Plant Mol Biol 63:609–623
Xiong L, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Cell signaling during Cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell 14:S165–S183
Xu D, Duan X, Wang B, Hong B, Ho T, Wu R (1996) Expression of a late embryogenesis abundant protein gene, HVA1, from barley confers tolerance to water deficit and salt stress in transgenic rice. Plant Physiol 110:249–257
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Organization of cis-acting regulatory elements in osmotic- and cold-stress-responsive promoters. Trends Plant Sci 10:88–94
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas “Comparative Genomics” and the National Bioresource Project of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan. The data discussed in this publication have been deposited in NCBIs Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/), GSM198948, GSM198949, GSM198952, GSM198955, GSM198961, GSM198962, GSM198969, GSM198970, GSM198971, GSM198972, GSM-198973, GSM199012, GSM199013, GSM199014, GSM199015, GSM199016, GSM199017, GSM199018, GSM199019, GSM199020, GSM199021, GSM199022 and GSM199023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Table S1
Experimental design for microarray hybridizations. (doc 35 KB)
Table S2
Primer pairs using for qRT-PCR in wheat. (doc 30 KB)
Fig. S1
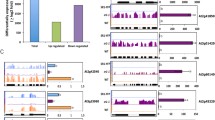
Validation of microarray data by qPCR. Vertical axis indicates log-transformed ratio of expression level. Solid black bar shows log-transformed ratio from qPCR, and gray bar shows log-transformed ratio from microarrays. Probe IDs and definitions are as follows: a w15334 dehydrin, b 23lib_15343 transcription factor AP2D23-like, c 23lib_11009 RAV1-like, d w9701 NAC domain containing protein, e w15821 alcohol dehydrogenase, f w14201 thiamine biosynthesis protein, g w13500 fructokinase, h w12804 chalcone synthase. Primer pairs using for qPCR are listed in Supplemental Table 2. (doc 240 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawaura, K., Mochida, K. & Ogihara, Y. Genome-wide analysis for identification of salt-responsive genes in common wheat. Funct Integr Genomics 8, 277–286 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-008-0076-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-008-0076-9