Abstract
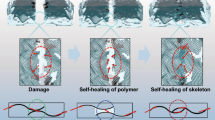
Thermal conducting materials may be damaged during long-term use, resulting in the increase of thermal resistance and therefore inefficient heat dissipation. The introduction of self-healing ability may solve this problem, but the realization of fast and room-temperature self-healing in thermal conducting composites is quite challenging. Herein, we choose a flexible poly(dimethylsiloxane) polymer material (PDMS-COOH) as the matrix and graphene nanosheets as the thermal conductive filler to prepare a new kind of thermal conductive polymer composite (PDMS-COOH-CG) that can quickly self-heal at room temperature. The thermal conductivity of PDMS-COOH-CG10 with 10% of graphene content is 0.48 W·m−1·K−1, which is 16 times that of PDMS-COOH (0.03 W·m−1·K−1). At room temperature, self-healing efficiency of PDMS-COOH-CG10 based on tensile strength can be 53.8% for 30 s and 84.6% for 24 h. Dynamic infrared thermal imaging dipicted that after 2 min of self-healing at room temperature, the thermal conduction temperature near the damage was basically restored to the level of the pristine sample.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mack, C. A. Fifty years of Moore’s law. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2011, 24, 202–207.
Krishnan, S.; Garimella, S. V.; Chrysler, G. M.; Mahajan, R. V. Towards’a thermal Moore’s law. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 2007, 30, 462–474.
Lin, S. C.; Banerjee, K. Cool chips: opportunities and implications for power and thermal management. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2008, 55, 245–255.
Zhang, F.; Feng, Y.; Feng, W. Three-dimensional interconnected networks for thermally conductive polymer composites: design, preparation, properties, and mechanisms. Mater. Sci. Eng. R-Rep. 2020, 142.
Xie, B. H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G. J. High thermal conductive polyvinyl alcohol composites with hexagonal boron nitride microplatelets as fillers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 85, 98–103.
Thermal Contact Conductance. In Encyclopedia of thermal stresses, Hetnarski, R. B., Ed. Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2014; pp 4948–4948.
Yovanovich, M. M. Four decades of research on thermal contact, gap, and joint resistance in microelectronics. IEEE T. Compon. Pack. T. 2005, 28, 182–206.
Lewis, J. S.; Perrier, T.; Barani, Z.; Kargar, F.; Balandin, A. A. Thermal interface materials with graphene fillers: review of the state of the art and outlook for future applications. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 142003.
Prasher, R. Thermal interface materials: historical perspective, status, and future directions. Proc. IEEE 2006, 94, 1571–1586.
Sarvar, F.; Whalley, D. C.; Conway, P. P. In Thermal interface materials-a review of the state of the art, 2006 1st Electronic Systemintegration Technology Conference, 5–7 Sep. 2006; pp. 1292–1302.
Chung, D. D. L. Thermal interface materials. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2001, 10, 56–59.
Gwinn, J. P.; Webb, R. L. Performance and testing of thermal interface materials. Millpress Science Publishers: Rotterdam, 2002, p. 201–210.
Guo, Y. Q.; Ruan, K. P.; Shi, X. T.; Yang, X. T.; Gu, J. W. Factors affecting thermal conductivities of the polymers and polymer composites: a review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 193, 25.
He, X. H.; Wang, Y. C. Recent advances in the rational design of thermal conductive polymer composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 1137–1154.
Zhang, Z. X.; Qu, J. Y.; Feng, Y. Y.; Feng, W. Assembly of graphenealigned polymer composites for thermal conductive applications. Compos. Commun. 2018, 9, 33–41.
Zhu, Z.; Li, C.; Songfeng, E.; Xie, L.; Geng, R.; Lin, C. T.; Li, L.; Yao, Y. Enhanced thermal conductivity of polyurethane composites via engineering small/large sizes interconnected boron nitride nanosheets. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 170, 93–100.
Xu, X. F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, B. W. Thermal conductivity of polymers and their nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705544.
Huang, C. L.; Qian, X.; Yang, R. G. Thermal conductivity of polymers and polymer nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R-Rep. 2018, 132, 1–22.
Han, Z.; Fina, A. Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes and their polymer nanocomposites: a review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 914–944.
Billiet, S.; Hillewaere, X. K. D.; Teixeira, R. F. A.; Du Prez, F. E. Chemistry of crosslinking processes for self-healing polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 290–309.
Williams, K. A.; Dreyer, D. R.; Bielawski, C. W. The underlying chemistry of self-healing materials. MRS Bull. 2008, 33, 759–765.
Wang, S. Y.; Urban, M. W. Self-healing polymers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 562–583.
Blaiszik, B. J.; Kramer, S. L. B.; Olugebefola, S. C.; Moore, J. S.; Sottos, N. R.; White, S. R. Self-healing polymers and composites. In Annual review of materials research, Vol 40, Clarke, D. R.; Ruhle, M.; Zok, F., Eds. Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, 2010; Vol. 40, pp. 179–211.
Xu, Z. G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. G.; Lin, T. A thermally healable polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocomposite based on Diels-Alder chemistry. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6755–6757.
Lin, C. H.; Sheng, D. K.; Liu, X. D.; Xu, S. B.; Ji, F.; Dong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y. M. NIR induced self-healing electrical conductivity polyurethane/graphene nanocomposites based on Diels-Alder reaction. Polymer 2018, 140, 150–157.
Jia, Z.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, B.; Jia, D. Recyclable and self-healing rubber composites based on thermorevesible dynamic covalent bonding. Pt. A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 129, 105709.
Yoon, J. A.; Kamada, J.; Koynov, K.; Mohin, J.; Nicolay, R.; Zhang, Y. Z.; Balazs, A. C.; Kowalewski, T.; Matyjaszewski, K. Self-healing polymer films based on thiol-disulfide exchange reactions and self-healing kinetics measured using atomic force microscopy. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 142–149.
Banerjee, S. L.; Bhattacharya, K.; Samanta, S.; Singha, N. K. Self-healable antifouling zwitterionic hydrogel based on synergistic phototriggered dynamic disulfide metathesis reaction and ionic interaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27391–27406.
Xiang, H.; Yin, J.; Lin, G.; Liu, X.; Rong, M.; Zhang, M. Photo-crosslinkable, self-healable and reprocessable rubbers. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 878–890.
Lai, J. C.; Mei, J. F.; Jia, X. Y.; Li, C. H.; You, X. Z.; Bao, Z. A. A stiff and healable polymer based on dynamic-covalent boroxine bonds. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8277–8282.
Chen, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Guo, B. Covalently cross-linked elastomers with self-healing and malleable abilities enabled by boronic ester bonds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24224–24231.
Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Duong, N. T.; Li, X.; Nishiyama, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Sun, P. Using dynamic bonds to enhance the mechanical performance: from microscopic molecular interactions to macroscopic properties. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 5014–5025.
Yang, X.; Guo, Y.; Luo, X.; Zheng, N.; Ma, T.; Tan, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, J. Self-healing, recoverable epoxy elastomers and their composites with desirable thermal conductivities by incorporating BN fillers via in-situ polymerization. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 164, 59–64.
Feng, Z.; Hu, J.; Zuo, H.; Ning, N.; Zhang, L.; Yu, B.; Tian, M. Photothermal-induced self-healable and reconfigurable shape memory bio-based elastomer with recyclable ability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1469–1479.
Wang, D. P.; Zhao, Z. H.; Li, C. H.; Zuo, J. L. An ultrafast self-healing polydimethylsiloxane elastomer with persistent sealing performance. Mat. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 1411–1421.
Lei, X.; Huang, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, L. Preparation of highly transparent, room-temperature self-healing and recyclable silicon elastomers based on dynamic imine bond and their ion responsive properties. Mater. Lett. 2020, 268, 127598.
Li, C. H.; Wang, C.; Keplinger, C.; Zuo, J. L.; Jin, L.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, P.; Cao, Y.; Lissel, F.; Linder, C.; You, X. Z.; Bao, Z. A. A highly stretchable autonomous self-healing elastomer. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 619–625.
Lai, J. C.; Li, L.; Wang, D. P.; Zhang, M. H.; Mo, S. R.; Wang, X.; Zeng, K. Y.; Li, C. H.; Jiang, Q.; You, X. Z.; Zuo, J. L. A rigid and healable polymer cross-linked by weak but abundant Zn(II)-carboxylate interactions. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2725.
Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Tu, Z.; Huang, J.; Qiu, X. Lignin-Reinforced nitrile rubber/poly(vinyl chloride) composites via metal coordination interactions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 23114–23123.
Lai, J. C.; Jia, X. Y.; Wang, D. P.; Deng, Y. B.; Zheng, P.; Li, C. H.; Zuo, J. L.; Bao, Z. Thermodynamically stable whilst kinetically labile coordination bonds lead to strong and tough self-healing polymers. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1164.
Sordo, F.; Mougnier, S. J.; Loureiro, N.; Tournilhac, F.; Michaud, V. Design of self-healing supramolecular rubbers with a tunable number of chemical cross-links. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 4394–4402.
Kang, J.; Son, D.; Wang, G. J. N.; Liu, Y.; Lopez, J.; Kim, Y.; Oh, J. Y.; Katsumata, T.; Mun, J.; Lee, Y.; Jin, L.; Tok, J. B. H.; Bao, Z. Tough and water-insensitive self-healing elastomer for robust electronic skin. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706846.
Ogliani, E.; Yu, L.; Javakhishvili, I.; Skov, A. L. A thermo-reversible silicone elastomer with remotely controlled self-healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 8285–8291.
Lai, H. Y.; Wang, H. Q.; Lai, J. C.; Li, C. H. A self-healing and shape memory polymer that functions at body temperature. Molecules 2019, 24, 12.
Qiao, H.; Qi, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Luan, Z.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Sui, K. Multiple weak H-bonds lead to highly sensitive, stretchable, self adhesive, and self-healing ionic sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7755–7763.
Zhang, M. H.; Li, C. H.; Zuo, J. L. A supramolecular polymer formed by small molecules. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100144.
Das, A.; Sallat, A.; Böhme, F.; Suckow, M.; Basu, D.; Wießner, S.; Stöckelhuber, K. W.; Voit, B.; Heinrich, G. Ionic modification turns commercial rubber into a self-healing material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20623–20630.
Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, D.; Cao, J.; Huang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X. Scalable manufacturing of real-time self-healing strain sensors based on brominated natural rubber. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124448.
Zhao, L.; Shi, X.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, B.; Huang, Y. A self-healing silicone/BN composite with efficient healing property and improved thermal conductivities. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 186, 107919.
Yu, H.; Feng, Y.; Gao, L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, W. Self-healing high strength and thermal conductivity of 3D graphene/PDMS composites by the optimization of multiple molecular interactions. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 7161–7170.
Liu, M.; Liu, P.; Lu, G.; Xu, Z.; Yao, X. Multiphase-assembly of siloxane oligomers with improved mechanical strength and water-enhanced healing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11242–11246.
Shahil, K. M.; Balandin, A. A. Graphene-multilayer graphene nanocomposites as highly efficient thermal interface materials. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 861–867.
Yu, A.; Ramesh, P.; Itkis, M. E.; Bekyarova, E.; Haddon, R. C. Graphite nanoplatelet-epoxy composite thermal interface materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 7565–7569.
Gu, J.; Xie, C.; Li, H.; Dang, J.; Geng, W.; Zhang, Q. Thermal percolation behavior of graphene nanoplatelets/polyphenylene sulfide thermal conductivity composites. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 1087–1092.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21631006 and 21771100) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 020514380212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, DW., Wang, HQ., Tao, HQ. et al. A Fast and Room-temperature Self-healing Thermal Conductive Polymer Composite. Chin J Polym Sci 39, 1328–1336 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-021-2620-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-021-2620-1