Abstract
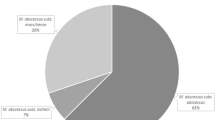
The rapidly growing mycobacterium Mycobacterium abscessus is a clinically important organism causing pulmonary and skin diseases. The M. abscessus complex is comprised of three subspecies: M. abscessus subsp. abscessus, M. abscessus subsp. massiliense, and M. abscessus subsp. bolletii. Here, we aimed to develop a Cas12a/sgRNA-based nucleic acid detection platform to identify M. abscessus species and subspecies. By designing specific sgRNA probes targeting rpoB and erm(41), we demonstrated that M. abscessus could be differentiated from other major mycobacterial species and identified at the subspecies level. Using this platform, a total of 38 clinical M. abscessus isolates were identified, 18 as M. abscessus subsp. abscessus and 20 as M. abscessus subsp. massiliense. We concluded that the Cas12a/sgRNA-based nucleic acid detection platform provides an easy-to-use, quick, and cost-effective approach for identification of M. abscessus species and subspecies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donohue MJ, Wymer L (2016) Increasing prevalence rate of nontuberculous mycobacteria infections in five states, 2008–2013. Annals of the American Thoracic Society 13:AnnalsATS.201605-353OC
Donohue MJ (2018) Increasing nontuberculous mycobacteria reporting rates and species diversity identified in clinical laboratory reports. BMC Infect Dis 18:163
Yu X, Liu P, Liu G, Zhao L, Hu Y, Wei G, Luo J, Huang H (2016) The prevalence of non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections in mainland China: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Infect 73:558
Harris KA, Kenna DTD, Cornelis B, Hartley JC, Turton JF, Paul A, Dixon GLJ (2012) Molecular fingerprinting of Mycobacterium abscessus strains in a cohort of pediatric cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol 50:1758–1761
Won-Jung K, Kyeongman J, Nam Yong L, Bum-Joon K, Yoon-Hoh K, Seung-Heon L, Young Kil P, Ki KC, Sung Jae S, Huitt GA (2011) Clinical significance of differentiation of Mycobacterium massiliense from Mycobacterium abscessus. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183:405
Rebecca G, Byrd TF (2008) Differential antibiotic susceptibility of Mycobacterium abscessus variants in biofilms and macrophages compared to that of planktonic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:2019–2026
Toidi A, Pierre B, Didier R, Michel D (2006) rpoB gene sequence-based characterization of emerging non-tuberculous mycobacteria with descriptions of Mycobacterium bolletii sp. nov., Mycobacterium phocaicum sp. nov. and Mycobacterium aubagnense sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:133
Toidi A, Martine RG, Gilbert G, Marie-José G, Bernard LS, Didier R, Michel D (2004) Amoebal coculture of “Mycobacterium massiliense” sp. nov. from the sputum of a patient with hemoptoic pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol 42:5493
Hee-Youn K, Byoung Jun K, Yoonwon K, Yeo-Jun Y, Jeong Hwan S, Bum-Joon K, Yoon-Hoh K (2010) Mycobacterium massiliense is differentiated from Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium bolletii by erythromycin ribosome methyltransferase gene (erm) and clarithromycin susceptibility patterns. Microbiol Immunol 54:347–353
Toshiyuki H, Yasushi A, Atsuyuki K, Hideaki N, Kazunari T, Takashi F, Syuichi Y, Eriko S, Toshihiko K, Akira K (2012) Clinical and microbiological differences between Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium massiliense lung diseases. J Clin Microbiol 50:3556–3561
Macheras E, Konjek J, Roux AL, Thiberge JM, Bastian S, Leão SC, Palaci M, Sivadon-Tardy V, Gutierrez C, Richter E (2014) Multilocus sequence typing scheme for the Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Res Microbiol 165:82–90
Theofano P, Pincus DH, Dorothy G, Melissa J, Josephine B, Julian P, R Andres F, Peter G. (2015) Mycobacterium abscessus complex identification with matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol 53:2355–2358
Mellmann A, Cloud J, Maier T, Keckevoet U, Ramminger I, Iwen P, Dunn J, Hall G, Wilson D, Lasala P (2008) Evaluation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry in comparison to 16S rRNA gene sequencing for species identification of nonfermenting bacteria. J Clin Microbiol 46:1946–1954
Fangous MS, Mougari F, Gouriou S, Calvez E, Raskine L, Cambau E, Payan C, Héry-Arnaud G (2014) Classification algorithm for subspecies identification within the Mycobacterium abscessus species, based on matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol 52:3362–3369
Tseng SP, Teng SH, Lee PS, Wang CF, Yu JS, Lu PL (2013) Rapid identification of M. abscessus and M. massiliense by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry with a comparison to sequencing methods and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns. Future Microbiol 8:1381–1389
Kehrmann J, Wessel S, Murali R, Hampel A, Bange FC, Buer J, Mosel F (2016) Principal component analysis of MALDI TOF MS mass spectra separates M. abscessus (sensu stricto) from M. massiliense isolates. BMC Microbiol 16:24
Kehrmann J, Kurt N, Rueger K, Bange FC, Buer J (2016) GenoType NTM-DR for identifying Mycobacterium abscessus subspecies and determining molecular resistance. J Clin Microbiol 54:JCM.00147–JCM.00116
Mougari F, Loiseau J, Veziris N, Bernard C, Bercot B, Sougakoff W, Jarlier V, Raskine L, Cambau E (2017) Evaluation of the new GenoType NTM-DR kit for the molecular detection of antimicrobial resistance in non-tuberculous mycobacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother 72
Li SY, Cheng QX, Wang JM, Li XY, Zhang ZL, Gao S, Cao RB, Zhao GP, Wang J (2018) CRISPR-Cas12a-assisted nucleic acid detection. Cell Discovery 4:20
Li SY, Cheng QX, Liu JK, Nie XQ, Zhao GP, Wang J (2018) CRISPR-Cas12a has both cis- and trans-cleavage activities on single-stranded DNA. Cell Res
Chen JS, Ma E, Harrington LB, Costa MD, Doudna JA. 2018. CRISPR-Cas12a target binding unleashes indiscriminate single-stranded DNase activity. Science 360:eaar6245
Toidi A, Philippe C, Michel D (2003) rpoB-based identification of nonpigmented and late-pigmenting rapidly growing mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol 41:5699–5708
Mikaeili F, Kia EB, Sharbatkhori M, Sharifdini M, Jalalizand N, Heidari Z, Zarei Z, Stensvold CR, Mirhendi H (2013) Comparison of six simple methods for extracting ribosomal and mitochondrial DNA from Toxocara and Toxascaris nematodes. Exp Parasitol 134:155–159
Blauwendraat C, Dixon GLJ, Hartley JC, Foweraker J, Harris KA (2012) The use of a two-gene sequencing approach to accurately distinguish between the species within the Mycobacterium abscessus complex and Mycobacterium chelonae. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31:1847–1853
Leung JM, Olivier KN (2013) Nontuberculous mycobacteria: the changing epidemiology and treatment challenges in cystic fibrosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med 19:662–669
De Zwaan R, van Ingen J, van Soolingen D (2014) Utility of rpoB gene sequencing for identification of nontuberculous mycobacteria in the Netherlands. J Clin Microbiol 52:2544–2551
Nie W, Duan H, Huang H, Lu Y, Bi D, Chu N (2014) Species identification of Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. abscessus and Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. bolletii using rpoB and hsp65, and susceptibility testing to eight antibiotics. Int J Infect Dis 25:170–174
Hee-Youn K, Yoonwon K, Yeo-Jun Y, Geun PC, Nam Yong L, Tae Sun S, Bum-Joon K, Yoon-Hoh K (2008) Proportions of Mycobacterium massiliense and Mycobacterium bolletii strains among Korean Mycobacterium chelonae-Mycobacterium abscessus group isolates. J Clin Microbiol 46:3384
Funding
This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019 M653108), the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81873958), the National Science and Technology Major Project for Control and Prevention of Major Infectious Diseases of China (No. 2017ZX10103004), the State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Diseases Open Project (No. SKLRD-OP-201919), the Key Laboratory of Tropical Disease Control of the Ministry of Education Open Project (No.2019kfkt01, 2019kfkt04), the Shenzhen Scientific and Technological Foundation (JCYJ20180306170510974, JCYJ20180228162453330, and JCYJ20180228162511084), and the Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (No. SZSM201911009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Shenzhen Third People’s Hospital.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, G., Zhang, S., Liang, Z. et al. Identification of Mycobacterium abscessus species and subspecies using the Cas12a/sgRNA-based nucleic acid detection platform. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39, 551–558 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03757-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03757-y