Abstract
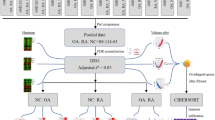
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is recognized as the most crippling or disabling type of arthritis, and osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis. These diseases severely reduce the quality of life, and cause high socioeconomic burdens. However, the molecular mechanisms of RA and OA development remain elusive despite intensive research efforts. In this study, we aimed to identify the potential transcription regulatory relationships between transcription factors (TFs) and differentially co-expressed genes (DCGs) in RA and OA, respectively. We downloaded the gene expression profiles of RA and OA from the Gene Expression Omnibus and analyzed the gene expression using computational methods. We identified a set of 4,076 DCGs in pairwise comparisons between RA and OA patients, RA and normal donors (NDs), or OA and ND. After regulatory network construction and regulatory impact factor analysis, we found that EGR1, NFE2L1, and NFYA were crucial TFs in the regulatory network of RA and NFYA, CBFB, CREB1, YY1 and PATZ1 were crucial TFs in the regulatory network of OA. These TFs could regulate the DCGs expression to involve RA and OA by promoting or inhibiting their expression. Altogether, our work may extend our understanding of disease mechanisms and may lead to an improved diagnosis. However, further experiments are still needed to confirm these observations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delgado M, Abad C, Martinez C, Leceta J, Gomariz RP (2001) Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents experimental arthritis by downregulating both autoimmune and inflammatory components of the disease. Nat Med 7(5):563–568. doi:10.1038/8788787887
Silman AJ, Pearson JE (2002) Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res 4(Suppl 3):S265–S272
Prevalence of disabilities and associated health conditions among adults—United States, 1999 (2001). MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 50 (7):120–125
Wong JB, Ramey DR, Singh G (2001) Long-term morbidity, mortality, and economics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 44(12):2746–2749
Firestein GS (2003) Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423(6937):356–361. doi:10.1038/nature01661
Muller-Ladner U, Pap T, Gay RE, Neidhart M, Gay S (2005) Mechanisms of disease: the molecular and cellular basis of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 1(2):102–110, ncprheum004710.1038/ncprheum0047
Majithia V, Geraci SA (2007) Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis and management. Am J Med 120(11):936–939, doi:S0002-9343(07)00361-010.1016/j.amjmed.2007.04.005
Batliwalla FM, Baechler EC, Xiao X, Li W, Balasubramanian S, Khalili H, Damle A, Ortmann WA, Perrone A, Kantor AB, Gulko PS, Kern M, Furie R, Behrens TW, Gregersen PK (2005) Peripheral blood gene expression profiling in rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun 6(5):388–397, doi:636420910.1038/sj.gene.6364209
Meugnier E, Coury F, Tebib J, Ferraro-Peyret C, Rome S, Bienvenu J, Vidal H, Sibilia J, Fabien N (2011) Gene expression profiling in peripheral blood cells of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in response to anti-TNF-alpha treatments. Physiol Genomics 43(7):365–371, physiolgenomics.00127.201010.1152/physiolgenomics.00127.2010
Bovin LF, Rieneck K, Workman C, Nielsen H, Sorensen SF, Skjodt H, Florescu A, Brunak S, Bendtzen K (2004) Blood cell gene expression profiling in rheumatoid arthritis. Discriminative genes and effect of rheumatoid factor. Immunol Lett 93(2–3):217–226. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2004.03.018S0165247804000872
Neumann E, Kullmann F, Judex M, Justen HP, Wessinghage D, Gay S, Scholmerich J, Muller-Ladner U (2002) Identification of differentially expressed genes in rheumatoid arthritis by a combination of complementary DNA array and RNA arbitrarily primed-polymerase chain reaction. Arthritis Rheum 46(1):52–63. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200201)46:1<52::AID-ART10048>3.0.CO;2-1
Aigner T, Fundel K, Saas J, Gebhard PM, Haag J, Weiss T, Zien A, Obermayr F, Zimmer R, Bartnik E (2006) Large-scale gene expression profiling reveals major pathogenetic pathways of cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54(11):3533–3544. doi:10.1002/art.22174
Hopwood B, Tsykin A, Findlay DM, Fazzalari NL (2007) Microarray gene expression profiling of osteoarthritic bone suggests altered bone remodelling, WNT and transforming growth factor-beta/bone morphogenic protein signalling. Arthritis Res Ther 9(5):R100, ar230110.1186/ar2301
Ungethuem U, Haeupl T, Witt H, Koczan D, Krenn V, Huber H, von Helversen TM, Drungowski M, Seyfert C, Zacher J, Pruss A, Neidel J, Lehrach H, Thiesen HJ, Ruiz P, Blass S (2010) Molecular signatures and new candidates to target the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Physiol Genomics 42A(4):267–282, physiolgenomics.00004.201010.1152/physiolgenomics.00004.2010
Stuart JM, Segal E, Koller D, Kim SK (2003) A gene-coexpression network for global discovery of conserved genetic modules. Science 302(5643):249–255. doi:10.1126/science.10874471087447
Lee HK, Hsu AK, Sajdak J, Qin J, Pavlidis P (2004) Coexpression analysis of human genes across many microarray data sets. Genome Res 14(6):1085–1094. doi:10.1101/gr.191090414/6/1085
Bergmann S, Ihmels J, Barkai N (2004) Similarities and differences in genome-wide expression data of six organisms. PLoS Biol 2(1):E9. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020009
Liu BH, Yu H, Tu K, Li C, Li YX, Li YY (2010) DCGL: an R package for identifying differentially coexpressed genes and links from gene expression microarray data. Bioinformatics 26(20):2637–2638, btq47110.1093/bioinformatics/btq471
Yu H, Liu BH, Ye ZQ, Li C, Li YX, Li YY (2011) Link-based quantitative methods to identify differentially coexpressed genes and gene pairs. BMC Bioinforma 12:315, 1471-2105-12-31510.1186/1471-2105-12-315
Team RDC (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. http://www.gbif.org/orc/?doc_id=3297
Benjamini YH, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Methodological) 57:289–300
Reverter A, Hudson NJ, Nagaraj SH, Perez-Enciso M, Dalrymple BP (2010) Regulatory impact factors: unraveling the transcriptional regulation of complex traits from expression data. Bioinformatics 26(7):896–904, btq05110.1093/bioinformatics/btq051
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504. doi:10.1101/gr.123930313/11/2498
Rachlin J, Cohen DD, Cantor C, Kasif S (2006) Biological context networks: a mosaic view of the interactome. Mol Syst Biol 2:66, msb410010310.1038/msb4100103
Wang L, Tang H, Thayanithy V, Subramanian S, Oberg AL, Cunningham JM, Cerhan JR, Steer CJ, Thibodeau SN (2009) Gene networks and microRNAs implicated in aggressive prostate cancer. Cancer Res 69(24):9490–9497, 0008-5472.CAN-09-218310.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2183
Vaquerizas JM, Kummerfeld SK, Teichmann SA, Luscombe NM (2009) A census of human transcription factors: function, expression and evolution. Nat Rev Genet 10(4):252–263, nrg253810.1038/nrg2538
Aicher WK, Dinkel A, Grimbacher B, Haas C, Seydlitz-Kurzbach EV, Peter HH, Eibel H (1999) Serum response elements activate and cAMP responsive elements inhibit expression of transcription factor Egr-1 in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int Immunol 11(1):47–61
Aicher WK, Heer AH, Trabandt A, Bridges SL Jr, Schroeder HW Jr, Stransky G, Gay RE, Eibel H, Peter HH, Siebenlist U et al (1994) Overexpression of zinc-finger transcription factor Z-225/Egr-1 in synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Immunol 152(12):5940–5948
Alexander D, Judex M, Meyringer R, Weis-Klemm M, Gay S, Muller-Ladner U, Aicher WK (2002) Transcription factor Egr-1 activates collagen expression in immortalized fibroblasts or fibrosarcoma cells. Biol Chem 383(12):1845–1853. doi:10.1515/BC.2002.208
Kim J, Xing W, Wergedal J, Chan JY, Mohan S (2010) Targeted disruption of nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 1 in osteoblasts reduces bone size and bone formation in mice. Physiol Genomics 40(2):100–110, 00105.200910.1152/physiolgenomics.00105.2009
Lee MS, Sun MT, Pang ST, Ueng SW, Chen SC, Hwang TL, Wang TH (2009) Evaluation of differentially expressed genes by shear stress in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes in vitro. Chang Gung Med J 32(1):42–50, 3201/320105
Singal DP, Ye M, Fleisig H, Buchanan WW, Qiu X (1996) Y box-binding trans-regulatory nuclear proteins and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 14(6):669–672
Johnson K, Zhu S, Tremblay MS, Payette JN, Wang J, Bouchez LC, Meeusen S, Althage A, Cho CY, Wu X, Schultz PG (2012) A stem cell-based approach to cartilage repair. Science 336(6082):717–721. doi:10.1126/science.1215157
Perez-Garcia S, Juarranz Y, Carrion M, Gutierrez-Canas I, Margioris A, Pablos JL, Tsatsanis C, Gomariz RP (2011) Mapping the CRF–urocortins system in human osteoarthritic and rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts: effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide. J Cell Physiol 226(12):3261–3269. doi:10.1002/jcp.22687
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the foundation of Pudong District (PW2011B-2 and PWRq2012-13).
Disclosures
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
G. Li and N. Han should be regarded as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Han, N., Li, Z. et al. Identification of transcription regulatory relationships in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 32, 609–615 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2143-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2143-9