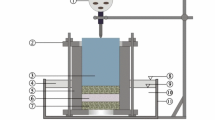
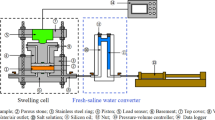
Abstract
Compacted bentonite is used as a buffer or backfill material in deep geological repositories. However, the seepage of pore water containing various salt and minerals can affect the hydro-mechanical performance of the bentonite. To investigate these effects, samples of compacted bentonite with initial dry densities of 1.50 Mg·m−3 and 1.70 Mg·m−3 were subject to saturation by distilled water, and solutions of NaCl and NaOH (0.1 M and 1.0 M), and the changes in swelling pressure and microstructure were monitored. The swelling pressure was seen to reduce with greater concentrations of the salt solution or when the initial dry density was decreased. At lower salt concentrations, the variation of the swelling pressure exhibited a double-peak, while further increases in the salt concentration caused the swelling pressure curve to exhibit only a single-peak. Compared to samples with a 1.7 Mg·m−3 dry density, the large swelling pressure decreased following the initial peak, and a smaller second peak was observed for samples with a 1.5 Mg·m−3dry density. The swelling pressure of samples saturated with NaOH solutions was notably lower, particularly after the second peak in the double-peaked curves. Applicable empirical kinetic equations were proposed to fit the relationship between the swelling pressure (p, MPa) and time (t, h) of the compacted sample saturated with DW and aqueous NaCl and NaOH. Microscopic analyses provide evidence that this reduction of swelling pressure could be attributed to the osmotic consolidation, ionic exchange, and mineral dissolution of bentonite.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso EE, Romero E, Hoffmann C, García-Escudero E (2005) Expansive bentonite–sand mixtures in cyclic controlled-suction drying and wetting. Eng Geol 81:213–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.06.009
An N, Zagorščak R, Thomas HR (2022) Adsorption characteristics of rocks and soils, and their potential for mitigating the environmental impact of underground coal gasification technology: A review, J Environ Manage 305, 114390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114390
Andersson P, Stark K, Xu S, Nordén M, Dverstorp B (2017) The Swedish radiological environmental protection regulations applied in a review of a license application for a geological repository for spent nuclear fuel. J Environ Radioactiv 178–179:439–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2017.04.001
Bauer A, Velde B (1999) Smectite transformation in high molar KOH solutions. Clay Miner 34:259–273. https://doi.org/10.1180/000985599546226
Bradbury MH, Baeyens B (2003) Porewater chemistry in compacted re-saturated MX-80 bentonite. J Contam Hydrol 61:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7722(02)00125-0
Castellanos E, Villar MV, Romero E, Lloret A, Gens A (2008) Chemical impact on the hydro-mechanical behaviour of high-density FEBEX bentonite. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 33:S516–S526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2008.10.056
Chen G, Gallipoli D, Ledesma A (2007) Chemo-hydro-mechanical coupled consolidation for a poroelastic clay buffer in a radioactive waste repository. Transport Porous Med 69:189–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-006-9083-2
Chen WC, Huang WH (2013) Effect of groundwater chemistry on the swelling behavior of a Ca-bentonite for deep geological repository. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 65:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2013.05.012
Chen YG, He Y, Ye WM, Jia LY (2015) Competitive adsorption characteristics of Na(I)/Cr(III) and Cu(II)/Cr(III) on GMZ bentonite in their binary solution. J Ind Eng Chem 26:335–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.12.006
Cui LY, Ye WM, Wang Q, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2021) Insights into gas migration behavior in saturated GMZ bentonite under flexible constraint conditions. Constr Build Mater 287:123070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123070
Cuisinier O, Deneele D, Masrouri F, Abdallah A, Conil N (2014) Impact of high-pH fluid circulation on long term hydromechanical behaviour and microstructure of compacted clay from the laboratory of Meuse-Haute Marne (France). Appl Clay Sci 88–89:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2013.12.008
Delage P (2010) A microstructure approach to the sensitivity and compressibility of some Eastern Canada sensitive clays. Géotechnique 60:353–368. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2010.60.5.353
Elkady TY, Shaker AA (2018) Role of cementation and suction in the swelling behavior of lime-treated expansive soils. J Mater Civil Eng 30:04018073. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002140
Estabragh AR, Moghadas M, Javadi AA (2013) Effect of different types of wetting fluids on the behaviour of expansive soil during wetting and drying. Soils Found 53:617–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2013.08.001
Estabragh AR, Soltani A, Javadi AA (2020) Effect of pore water chemistry on the behaviour of a kaolin–bentonite mixture during drying and wetting cycles. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 24:895–914. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2018.1428691
Fernández AM, Baeyens B, Bradbury M, Rivas P (2004) Analysis of the porewater chemical composition of a Spanish compacted bentonite used in an engineered barrier. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 29:105–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2003.12.001
Fernández R, Cuevas J, Sánchez L, de la Villa RV, Leguey S (2006) Reactivity of the cement–bentonite interface with alkaline solutions using transport cells. Appl Geochem 21:977–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.02.016
Fernández R, Mäder UK, Rodríguez M, Vigil De La Villa R, Cuevas J (2009) Alteration of compacted bentonite by diffusion of highly alkaline solutions. Eur J Mineral 21:725–735. https://doi.org/10.1127/0935-1221/2009/0021-1947
Fredlund DG, Rahardjo H (1993) Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils. John Wiley & Sons
Gajo A, Maines M (2007) Mechanical effects of aqueous solutions of inorganic acids and bases on a natural active clay. Géotechnique 57:687–699. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2007.57.8.687
Gates WP, Bouazza A (2010) Bentonite transformations in strongly alkaline solutions. Geotext Geomembranes 28:219–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2009.10.010
Glasser FP (2001) Mineralogical aspects of cement in radioactive waste disposal. Mineral Mag 65:621–633. https://doi.org/10.1180/002646101317018442
Guimarães LDN, Gens A, Olivella S (2007) Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical and chemical analysis of expansive clay subjected to heating and hydration. Transport Porous Med 66:341–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-006-0014-z
Guzman J, Maximov S, Escarela-Perez R, López-García I, Moranchel M (2015) Analytical solution to the diffusion, sorption and decay chain equation in a saturated porous medium between two reservoirs. J Environ Radioactiv 139:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2014.10.003
He Y, Ye WM, Chen YG, Chen B, Ye B, Cui YJ (2016a) Influence of pore fluid concentration on water retention properties of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 129:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.05.020
He Y, Chen YG, YeChen WMB, Cui YJ (2016b) Influence of salt concentration on volume shrinkage water retention characteristics of compacted GMZ bentonite. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5228-3
He Y, Cui YJ, Ye WM, Conil N (2017) Effects of wetting-drying cycles on the air permeability of compacted Téguline clay. Eng Geol 228:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.08.015
He Y, Wang MM, Wu DY, Zhang KN, Chen YG, Ye WM (2021) Effects of chemical solutions on the hydromechanical behavior of a laterite/bentonite mixture used as an engineered barrier. B Eng Geol Environ 80:1169–1180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-02003-6
He Y, Ye WM, Chen YG, Cui YJ (2019) Effects of K+ solutions on swelling behavior of compacted GMZ bentonite. Eng Geol 249:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.12.020
He Y, Ye WM, Chen YG, Zhang KN, Wu DY (2020) Effects of NaCl solution on the swelling and shrinkage behavior of compacted bentonite under one-dimensional conditions. B Eng Geol Environ 79:399–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01568-1
He Y, Lu PH, Ye WM, Chen YG, Zhang KN (2022) Coupled chemo-hydro-mechanical effects on volume change behaviour of compacted bentonite used as buffer/backfill material in high-level radioactive waste repository. J Nucl Sci Technol. 2022-03-21. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223131.2022.2044930
Herbert HJ, Kasbohm J, Moog HC, Henning KH (2004) Long-term behaviour of the Wyoming bentonite MX-80 in high saline solutions. Appl Clay Sci 26:275–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2003.12.028
Herbert HJ, Kasbohm J, Sprenger H, Fernández AM, Reichelt C (2008) Swelling pressures of MX-80 bentonite in solutions of different ionic strength. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 33:S327–S342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2008.10.005
Karnland O, Birgersson M (2006) Montmorillonite stability with special respect to KBS-3 conditions. Sweden
Karnland O, Olsson S, Nilsson U (2006) Mineralogy and sealing properties of various bentonites and smectite-rich clay materials. Sweden
Karnland O, Olsson S, Nilsson U, Sellin P (2007) Experimentally determined swelling pressures and geochemical interactions of compacted Wyoming bentonite with highly alkaline solutions. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 32:275–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2006.01.012
Kasar S, Kumar S, Bajpai RK, Tomar BS (2016) Diffusion of Na(I), Cs(I), Sr(II) and Eu(III) in smectite rich natural clay. J Environ Radioactiv 151:218–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2015.10.012
Kaufhold S, Dohrmann R (2010) Stability of bentonites in salt solutions: II. Potassium chloride solution — Initial step of illitization. Appl Clay Sci 49:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.04.009
Komine H (2004) Simplified evaluation on hydraulic conductivities of sand–bentonite mixture backfill. Appl Clay Sci 26:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2003.09.006
Komine H, Ogata N (1996) Prediction for swelling characteristics of compacted bentonite. Can Geotech J 33:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1139/t96-021
Laine H, Karttunen P (2010) Long-term stability of bentonite. A literature review. Finland
Lee JO, Lim JG, Kang IM, Kwon S (2012) Swelling pressures of compacted Ca-bentonite. Eng Geol 129–130:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.01.005
Liu LN, Chen YG, Ye WM, Cui YJ, Wu DB (2018) Effects of hyperalkaline solutions on the swelling pressure of compacted Gaomiaozi (GMZ) bentonite from the viewpoint of Na+ cations and OH– anions. Appl Clay Sci 161:334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.04.023
Lloret A, Villar MV, Sánchez M, Gens A, Pintado X, Alonso EE (2003) Mechanical behaviour of heavily compacted bentonite under high suction changes. Géotechnique 53:27–40. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2003.53.1.27
Lu PH, He Y, Zhang Z, Ye WM (2021) Predicting chemical influence on soil water retention curves with models established based on pore structure evolution of compacted clay. Comput Geotech 138, 104360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104360
Marcial D, Delage P, Cui YJ (2002) On the high stress compression of bentonites. Can Geotech J 39:812–820. https://doi.org/10.1139/t02-019
Mata Mena C, Romero E, Ledesma A (2002) Hydro-chemical effects on water retention in bentonite-sand mixtures
Medved I, Černý R (2013) Osmosis in porous media: a review of recent studies. Micropor Mesopor Mat 170:299–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.12.009
Mokni N (2011) Deformation and flow driven by osmotic processes in porous materials. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya
Molinero-Guerra A, Delage P, Cui YJ, Mokni N, Tang AM, Aimedieu P, Bernier F, Bornert M (2020) Water-retention properties and microstructure changes of a bentonite pellet upon wetting/drying; application to radioactive waste disposal. Géotechnique 70(3): 199–209. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.17.P.291
Monroy R, Zdravkovic L, Ridley A (2010) Evolution of microstructure in compacted London Clay during wetting and loading. Géotechnique 60:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.8.P.125
Musso G, Romero E, Vecchia GD (2013) Double-structure effects on the chemo-hydro-mechanical behaviour of a compacted active clay. Géotechnique 63:206–220. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.SIP13.P.011
Musso G, Romero Morales E, Gens A, Castellanos E (2003) The role of structure in the chemically induced deformations of FEBEX bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 23:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1317(03)00107-8
Nowamooz H, Jahangir E, Masrouri F, Tisot JP (2016) Effective stress in swelling soils during wetting drying cycles. Eng Geol 210:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.05.021
Nowamooz H, Masrouri F (2010) Relationships between soil fabric and suction cycles in compacted swelling soils. Eng Geol 114:444–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.06.005
Ouhadi VR, Yong RN (2003) Impact of clay microstructure and mass absorption coefficient on the quantitative mineral identification by XRD analysis. Appl Clay Sci 23:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1317(03)00096-6
Pusch R (2002) The Buffer and Backfill Handbook Part 1: Definitions, basic relationships and laboratory methods. Sweden
Pusch R, Yong RN (2006) Microstructure of smectite clays and engineering performance (1st ed.). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781482265675
Ravi K, Rao SM (2013) Influence of infiltration of sodium chloride solutions on SWCC of compacted bentonite–sand specimens. Geotech Geol Eng 31:1291–1303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-013-9650-6
Romero E, Vecchia GD, Jommi C (2011) An insight into the water retention properties of compacted clayey soils. Géotechnique 61:313–328. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2011.61.4.313
Sasanian S, Newson TA (2013) Use of mercury intrusion porosimetry for microstructural investigation of reconstituted clays at high water contents. Eng Geol 158:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.03.002
Savage D (2005) The effects of high salinity groundwater on the performance of clay barriers. Sweden
Savage D, Arthur R, Watson C, Wilson J, Strömberg B (2011) Testing geochemical models of bentonite pore water evolution against laboratory experimental data. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 36:1817–1829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2011.07.025
Savage D, Walker C, Arthur R, Rochelle C, Oda C, Takase H (2007) Alteration of bentonite by hyperalkaline fluids: a review of the role of secondary minerals. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 32:287–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2005.08.048
Stoltz G, Cuisinier O, Masrouri F (2012) Multi-scale analysis of the swelling and shrinkage of a lime-treated expansive clayey soil. Appl Clay Sci 61:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2012.04.001
Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Company (SKB) (1999) SR 97 - Waste, repository design and sites Background report to SR 97 SKB. Sweden
Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Company (SKB) (2012) Aespoe Hard Rock Laboratory Annual Report 2011. Sweden
Tang AM, Cui YJ (2009) Modelling the thermomechanical volume change behaviour of compacted expansive clays. Géotechnique 59:185–195. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2009.59.3.185
Taylor HFW (1987) A method for predicting alkazi ion concentrations in cement pore solutions. Adv Cem Res 1:5–17. https://doi.org/10.1680/adcr.1987.1.1.5
Van Genuchten M (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
Villar MV, Lloret A (2004) Influence of temperature on the hydro-mechanical behaviour of a compacted bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 26:337–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2003.12.026
Villar MV, Lloret A (2008) Influence of dry density and water content on the swelling of a compacted bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 39:38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2007.04.007
Wang J, Chen L, Su R, Zhao X (2018) The Beishan underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China: planning, site selection, site characterization and in situ tests. J Rock Mech Geotech 10:411–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.03.002
Wang Q, Su W, Ye W, Zhang Y, Chen Y (2021) Analysing the volume change behaviour of compacted bentonites upon THM processes based on the framework of BExM model. Environ Earth Sci 80:615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09885-z
Wen ZJ (2006) Physical property of china’s buffer material for high-level radioactive waste repositories. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 25(4):794–800
Ye WM, Cui YJ, Qian LX, Chen B (2009) An experimental study of the water transfer through confined compacted GMZ bentonite. Eng Geol 108:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.08.003
Ye WM, He Y, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2016) Thermochemical effects on the smectite alteration of GMZ bentonite for deep geological repository. Environ Earth Sci 75:906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5716-0
Ye WM, Wan M, Chen B, Chen YG, Cui YJ, Wang J (2012) Temperature effects on the unsaturated permeability of the densely compacted GMZ01 bentonite under confined conditions. Eng Geol 126:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.10.011
Ye WM, Wan M, Chen B, Chen YG, Cui YJ, Wang J (2013) Temperature effects on the swelling pressure and saturated hydraulic conductivity of the compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Environ Earth Sci 68:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1738-4
Ye WM, Zhang F, Chen B, Chen YG, Wang Q, Cui YJ (2014) Effects of salt solutions on the hydro-mechanical behavior of compacted GMZ01 Bentonite. Environ Earth Sci 72:2621–2630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3169-x
Ye WM, Zhang F, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2017) Influences of salt solutions and salinization-desalinization processes on the volume change of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Eng Geol 222:140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.04.002
Zhu CM, Ye WM, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2013) Influence of salt solutions on the swelling pressure and hydraulic conductivity of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Eng Geol 166:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.09.001
Zhu CM, Ye WM, Chen YG, Chen B, Cui YJ (2015) Impact of cyclically infiltration of CaCl2 solution and de-ionized water on volume change behavior of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Eng Geol 184:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.005
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Projects No. 42072318 & 42030714 & 41972282 & 41807253) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Project No. 2019JJ50763) for the financial support. The authors also wish to acknowledge the support of European Commission via the Marie Curie IRSES project GREAT – Geotechnical and geological Responses to climate change: Exchanging Approaches and Technologies on a worldwide scale (FP7-PEOPLE-2013-IRSES-612665), and also to grateful to the research fund program of the State Key Laboratory of Environmental Geochemistry (Project No. SKLEG2021208).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Ph., He, Y., Ye, Wm. et al. Experimental investigations and microscopic analyses of chemical effects and dry density on the swelling behavior of compacted bentonite. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 243 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02736-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02736-6