Abstract
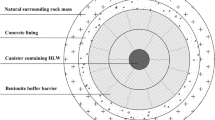
Gaomiaozi (GMZ) bentonite has been recognized as the first choice for using as buffer/backfill material in deep geological repository for the disposal of high-level nuclear waste in China. High salinity and high pH of the pore solutions may cause changes in the mineralogical composition, and the swelling capacity of the bentonite results in affecting the long-term performance of the engineering barrier system. In the present work, a series of hydrothermal reactivity experiments were performed using batch reactors at 20, 35 and 80 °C for evaluating the chemical and mineralogical responses of GMZ bentonites. The results show that the dissolution of smectite releases Si and Al under the conditions of 1 M KOH at 35 and 80 °C and the released Si and Al may work as a cementing agent in GMZ bentonite. XRD pattern results show that alteration of the GMZ bentonite is expected to be insignificant for reaction with NaCl, KCl and NaOH solutions under low temperatures. However, it is obviously reacted with KOH solutions especially at 80 °C, during which cementitious material was produced leading to kaolinitization. When contacted with KOH solutions, the basal spacing (d001) of the main primary diffraction peaks (001) value of GMZ bentonite increases with increasing temperature. Salinity also can influence the smectite stability and accordingly loss of swelling capacity. This conclusion could be explained by the diffusing double-layer effects induced by salt solutions and ion exchange.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso EE, Vaunat J, Gens A (1999) Modelling the mechanical behaviour of expansive clay. Eng Geol 54:173–183
Altaner SP, Ylagan RF (1997) Comparison of structural models of mixed-layer illite/smectite andreaction mechanisms of smectiteillitization. Clay Clay Miner 45(4):517–533
Amram K, Ganor J (2005) The combined effect of pH and temperature on the smectite dissolution rate under acidic conditions. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 69:2535–2546
Bauer A, Berger G (1998) Kaolinite and smectite dissolution rate in high molar KOH solutions at 35° and 80 °C. Appl Geo chem 13:905–916
Bauer A, Velde B (1999) Smectite transformation in high molar KOH solutions. Clay Miner 34:259–273
Bauer A, Lanson B, Ferrage E, Emmerich K, Taubald H, Schild D, Velde B (2006) The fate of smectite in KOH solution. Am Mineral 91:1313–1322
Boles JR, Franks SG (1979) Clay diagenesis in Wilcox sandstones of southwest Texas: implications of smectitediagenesis on sandstone cementation. J Sediment Petrol 49:55–70
Bouchet A, Cassagnabère A, Parneix JC (2004) Batch experiments: results on MX80. In Ecoclay II:Effect of cement on clay barrier performance phase II. Final report. (ANDRA) European contractFIKW-CT-2000-0028, (ed. N. Michau)
Cama J, Ganor J, Ayora C, Lasaga A (2000) Smectite dissolution kinetics at 80 °C and pH 8.8. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 64:2701–2717
Cuevas J (2004) Geochemical reactions between the FEBEX bentonite and Portland-type cement porewater. InEcoclay II: Effect of cement on clay barrier performance phase II. Final report. (ANDRA) Europeancontract FIKW-CT-2000-0028, (ed. N. Michau)
de la Villa Cuevas RVJ, Ramirez S, Leguey S (2001) Zeolite formation during the alkaline reaction ofbentonite. Eur J Miner 13:635–644
Dixon D, Chandler N, Graham J, Gray MN (2002) Two large-scale sealing tests conducted at Atomic Energy of Canada’s underground research laboratory: the buffer-container experiment and the isothermal test. Can Geo J 39(3):503–518
Fernández R, Ruiz AI, Cuevas J (2014) The role of smectite composition on the hyperalkaline alteration of bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 95:83–94
Furrer G, Zysset M, Schindler P (1993) Weathering kinetics of montmorillonite: Investigation in batch and mixed-flow reactors. In: Manning D, Hall P, Hughes C (eds) Geochemistry of clay-pore fluid interaction, vol 4. Chapman & Hall, Boca Raton, pp 243–262
Gates WP, Bouazza A (2010) Bentonite transformations in strongly alkaline solutions. GeotextGeomembranes 28:219–225
Gaucher EC, Blanc P (2006) Cement/clay interactions-a review: experiments, natural analogues, and modeling. Waste Manage 26:776–788
Glasser FP (2001) Mineralogical aspects of cement in radioactive waste disposal. Miner Mag 65:621–633
Guo YH, Yang TX, Liu SF (2001) Hydro-geological characteristics of Beishan preselected area, Gansu province for China’s high-level radioactive waste repository. Uranium Geol 17(3):184–189 (in Chinese)
Guo YH, Su R, Ji RL, Wang HL, Liu SF, Zong ZH, Dong JN, Zhang M (2014) Synthetic hydrogeological study on Beishan preselected area for high-level radioactive waste repository in China. World Nucl Geo 31(4):587–593 (in Chinese)
Herbert HJ, Kasbohm J, Moog HC, Henning KH (2003) Long term behaviour of the Wyoming bentonite MX-80 in high saline solutions. Appl Clay Sci 26:275–291
Herbert HJ, Kasbohm J, Sprenger H, Fernández AM, Reichelt C (2008) Swelling pressures of MX-80 bentonite in solutions of different ionic strength. PhysChem Earth 33:S327–S342
Hökmark H, Fälth B (2003) Thermal dimentioning of the deep repository. Technical Report, TR-03-09, SvenskKärnbränslehantering AB 2003
Hower J, Eslinger E, Hower M, Perry E (1976) Mechanism of burial metamorphism of argillaceous sediment. 1. Mineralogical and chemical evidence. GeolSoc Am Bull 87:725–737
Hurel C, Marmier N (2010) Sorption of europium on a MX-80 bentonite sample: experimental and modelling results. J Radioanal Nucl Ch 284(1):225–230
Inoue A (1995) Formation of clay minerals in hydrothermal environments. In: Velde B (ed) Origin and mineralogy of clays. Springer, Berlin, pp 268–329
Jennings S, Thompson GR (1986) Diagenesis of Plio-Pleistocene sediments of the Colorado River Delta, southern California. J Sed Pet 56:89–98
Karnland O (2004) Laboratory experiments concerning compacted bentonite contacted to high pH solutions. In Ecoclay II: Effect of cement on clay barrier performance phase II. Final Report. (ANDRA) Europeancontract FIKW-CT-2000-0028, (ed. N. Michau)
Karnland O, Olsson S, Nilsson U, Sellin P (2007) Experimentally determined swelling pressures and geochemical interactions of compacted Wyoming bentonite with highly alkaline solutions. Phys Chem Earth 32:275–286
Kaufhold S, Dohrmann R (2009) Stability of bentonites in salt solutions I: sodium chloride. Appl Clay Sci 45:171–177
Kaufhold S, Dohrmann R (2010) Stability of bentonites in salt solutionsII. Potassium chloride solution—Initial step of illitization? Appl Clay Sci 49:98–107
Kaufhold S, Dohrmann R (2011) Stability of bentonites in salt solutions III: calcium hydroxide. Appl Clay Sci 51:300–307
Laine H, Karttunen P (2010) Long-term stability of bentonite: a literature review. POSIVA, Working Report 2010-53, Finland
Lee JO, Kang IM, Cho WJ (2010) Smectite alteration and its influence on the barrier properties of smectite clay for a repository. Appl Clay Sci 47:99–104
Lehikoinen J (2009) Bentonite-cement interaction-preliminary results from model calculations. Posiva Working Report 2009-37. PosivaOy, Eurajoki, Finland
Liu YM, Xu GQ, Liu SF (2001) Study on compatibility and swelling property of buffer/backfill material for HLW repository. Uranium Geol 17(1):44–47 (in Chinese)
Lloret A, Villar MV (2007) Advances on the knowledge of the therm-hydro-mechanical behaviour of heavily compacted “FEBEX” bentonite. Phys Chem Earth 32(8–14):701–715
Marcial D (2003) Comportementhydromécaniqueet microstructural des matériaux de barrierouvragée. PhD Thesis. Paris: ÉcoleNationale des PontsetChausées
Mitchell JK (1993) Fundamentals of Soil Behavior, 2nd edn. John Wiley, New York
MosseR-Ruck R, Cathelineau M (2004) Experimental transformation of Na, Ca-smectite under basicconditions at 150°C. Appl Clay Sci 26:259–273
Muurinen A, Lehikoinen J (1999) Pore-water chemistry in compacted bentonite. Eng Geol 54:207–214
Nakashima Y (2004) Nuclear magnetic resonance properties of water-rich gels of Kunigel-V1 bentonite. J Nucl Sci Technol 41:981–992
Nakayama S, Sakamoto Y, Yamaguchi T, Akai M, Tanaka T, Sato T, Lida Y (2004) Dissolution of montmorillonite in compacted bentonite by highly alkaline aqueous solutions and diffusivity of hydroxide ions. Appl Clay Sci 27:53–65
Pastina B, Hellä P (2006) Expected evolution of a spent nuclear fuel repository at Olkiluoto. POSIVA Report 2006-05. PosivaOy, Olkiluoto, Finland
Plançon A, Drits VA (2000) Phase analysis of clays using an expert system and calculation programs for X-ray diffraction by two- and three- component mixed-layer minerals. Clay Clay Miner 48:57–62
Pusch R (2001) The Buffer and Backfill Handbook Part 2: Materials and techniques. SKB Technical Report TR-02-12. Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co (SKB), Stockholm, Sweden
Pusch R, Karnland O, Sandén T (1996) Final report on physical testing programme concerning Spanish clays (saponites and bentonites). Enresa Technical Report, 02/96
Pusch R, Kasbohm J, Hoang MT (2007) Evolution of clay buffer under repository. Reprints of the contributions to the workshop on long-term performance of smectitic clays embedding canisters with highly radioactive waste, Lund, Sweden, pp. 1–12
Ramírez S, Cuevas J, Vigil de la Villa R, Leguey S (2002) Hydrothermal alteration of “LaSerrata” bentonite (Almeria, Spain) by alkaline solutions. Appl Clay Sci 21:257–269
Roaldset E, Wei H, Grimstad S (1998) Smectite to illite conversion by hydrouspyrolysis. Clay Miner 33:147–158
Sánchez L, Cuevas J, Ramírez S, Riuiz De León D, Fernández R, Vigil Dela Villa R, Leguey S (2006) Reaction kinetics of FEBEX bentonite in hyperalkaline conditions resembling the cement-bentonite interface. Appl Clay Sci 33:125–141
Sato T, Kuroda M, Yokoyama S, Tsutsui M, Pacau C, Ringor C, Fukushi K, Tanaka T, Nakayama S (2005) Dissolution kinetics of smectite under alkaline conditions. International meeting: clays in natural and engineering barriers for nuclear waste confinement, Tours, France
Savage D, Bateman K, Hill P, Hughes C, Milodowski A, Pearce J, Rae E, Rochelle C (1992) Rate and mechanism of the reaction of silicates with cement pore fluids. Appl Clay Sci 7:33–45
Savage D, Walker C, Arthur R, Rochelle C, Oda C, Takase H (2007) Alteration of bentonite by hyperalkaline fluids: a review of the role of secondary minerals. Phys Chem Earth 32:287–297
Suzuki S, Sazarashi M, Akimoto T, Haginuma M, Suzuki K (2008) A study of the mineralogical alteration of bentonite in saline water. Appl Clay Sci 41:190–198
Taylor HFW (1987) A method for predicting alkali ion concentrations in cement pore solutions. Adv Cem Res 1:5–16
Villar MV, Lloret A (2004) Influence of temperature on the hydro-mechanical behavior of a compacted bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 26:337–350
Wersin P, Johnson L, McKinley I (2007) Performance of the bentonite barrier at temperatures beyond 100 °C: a critical review. Phys Chem Earth 32:780–788
Whitney G, Northrop HR (1988) Experimental investigation of the smectite to illite reaction: dual reaction mechanisms and oxygen isotope systematics. Am Miner 73:77–90
Wood M (1983) Experimental investigation of sodium bentonite stability in Hanford basalt. In: Bookins DC (ed) Material research society symposium, Amsterdam 15, 727–743
Ye WM, Schanz T, Qian LX, Wang J, Arifin YF (2007) Characteristics of swelling pressure of densely compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 26:3861–3865
Ye WM, Cui YJ, Qian LX, Chen B (2009a) An experimental study of the water transfer through confined compacted GMZ bentonite. Eng Geol 108(3–4):169–176
Ye WM, Wan M, Chen B, Chen YG, Cui YJ, Wang J (2009b) Effect of temperature on soil-water characteristics and hysteresis of compacted Gaomiaozi bentonite. J Cent South Univ Technol 16(5):821–826
Ye WM, Wan M, Chen B, Chen YG, Cui YJ, Wang J (2012) Temperature effects on the unsaturated permeability of the densely compacted GMZ01 bentonite under confined conditions. Eng Geol 126:1–7
Ye WM, Zheng ZJ, Chen B, Chen YG, Cui YJ, Wang J (2014a) Effects of pH and temperature on the swelling pressure and hydraulic conductivity of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 101:192–198
Ye WM, Zhang F, Chen B, Chen YG, Wang Q, Cui YJ (2014b) Effects of salt solutions on the hydro-mechanical behavior of compacted GMZ01 Bentonite. Environ Earth Sci 72(7):2621–2630
Zhu CM, Ye WM, Chen Y, Chen B, Cui YJ (2013) Influence of salt solutions on the swelling pressure and hydraulic conductivity of compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Eng Geol 166:74–80
Zysset M, Schindler P (1996) The proton promoted dissolution kinetics of K montmorillonite. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 60:921–936
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to China Atomic Energy Authority [Project (2011)1051], the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Projects No. 41272287, 41030748), for the financial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, W.M., He, Y., Chen, Y.G. et al. Thermochemical effects on the smectite alteration of GMZ bentonite for deep geological repository. Environ Earth Sci 75, 906 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5716-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5716-0