Abstract
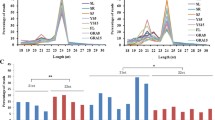
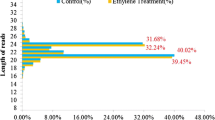
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are recently discovered, noncoding, small regulatory RNA molecules that negatively regulate gene expression. Although many miRNAs are identified and validated in many plant species, they remain largely unknown in Brassica rapa (AA 2n =, 20). B. rapa is an important Brassica crop with wide genetic and morphological diversity resulting in several subspecies that are largely grown for vegetables, oilseeds, and fodder crop production. In this study, we identified 186 miRNAs belonging to 55 families in B. rapa by using comparative genomics. The lengths of identified mature and pre-miRNAs ranged from 18 to 22 and 66 to 305 nucleotides, respectively. Comparison of 4 nucleotides revealed that uracil is the predominant base in the first position of B. rapa miRNA, suggesting that it plays an important role in miRNA-mediated gene regulation. Overall, adenine and guanine were predominant in mature miRNAs, while adenine and uracil were predominant in pre-miRNA sequences. One DNA sequence producing both sense and antisense mature miRNAs belonging to the BrMiR 399 family, which differs by 1 nucleotide at the, 20th position, was identified. In silico analyses, using previously established methods, predicted 66 miRNA target mRNAs for 33 miRNA families. The majority of the target genes were transcription factors that regulate plant growth and development, followed by a few target genes that are involved in fatty acid metabolism, glycolysis, biotic and abiotic stresses, and other cellular processes. Northern blot and qRT-PCR analyses of RNA samples prepared from different B. rapa tissues for 17 miRNA families revealed that miRNAs are differentially expressed both quantitatively and qualitatively in different tissues of B. rapa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros, V., and Chen, X.M. (2007). The regulation of genes and genomes by small RNAs. Development 134, 1635–1641.
Alves-Junior, L., Niemeier, S., Hauenschild, A., Rehmsmeier, M., and Merkle, T. (2009). Comprehensive prediction of novel microRNA targets in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 4010–4021.
Bartel, D.P. (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297.
Bazzini, A.A., Hopp, H.E., Beachy, R.N., and Asurmendi, S. (2007). Infection and coaccumulation of tobacco mosaic virus proteins alter microRNA levels, correlating with symptom and plant development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 12157–12162.
Bender, W. (2008). MicroRNAs in the Drosophila bithorax complex. Genes Dev. 22, 14–19.
Bollman, K.M., Aukerman, M.J., Park, M.Y., Hunter, C., Berardini, T.Z., and Poethig, R.S. (2003). HASTY, the Arabidopsis ortholog of exportin 5/MSN5, regulates phase change and morphogenesis. Development 130, 1493–1504.
Bonnet, E., Wuyts, J., Rouzé, P., and Van de Peer, Y. (2004a). Detection of 91 potential conserved plant microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa identifies important target genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 11511–11516.
Bonnet, E., Wuyts, J., Rouze, P., and Van de Peer, Y. (2004b). Evidence that microRNA precursors, unlike other non-coding RNAs, have lower folding free energies than random sequences. Bioinformatics 20, 2911–2917. formatics 20, 2911–2917.
Buhtz, A., Springer, F., Chappell, L., Baulcombe, D.C., and Kehr, J. (2008). Identification and characterization of small RNAs from the phloem of Brassica napus. Plant J. 53, 739–749.
Camacho, C., Coulouris, G., Avagyan, V., Ma, N., Papadopoulos, J., Bealer, K., and Madden, T.L. (2009). BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics 10, 421.
Carrington, J.C., and Ambros, V. (2003). Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 301, 336–338.
Carthew, R.W., and Sontheimer, E.J. (2009). Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136, 642–655.
Chen, X. (2004). A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science 303, 2022–2025.
Chiou, T.J., Aung, K., Lin, S.I., Wu, C.C., Chiang, S.F., and Su, C.L. (2006). Regulation of phosphate homeostasis by microRNA in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18, 412–421.
Depicker, A., and Montagu, M.V. (1997). Post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 373–382.
Dugas, D.V., and Bartel, B. (2004). MicroRNA regulation of gene expression in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 7, 512–520.
Floyd, S.K., and Bowman, J.L. (2004). Gene regulation: ancient microRNA target sequences in plants. Nature 428, 485–486.
Fujii, H., Chiou, T.J., Lin, S.I., Aung, K., and Zhu, J.K. (2005). A miRNA involved in phosphate-starvation response in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 15, 2038–2043.
Griffiths-Jones, S. (2006). MiRBase: the microRNA sequence database. Methods Mol. Biol. 342, 129–138.
Griffiths-Jones, S., Saini, H.K., Van, D.S., and Enright, A.J. (2008). miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D154–D158.
Guo, H.S., Xie, Q., Fei, J.F., and Chua, N.H. (2005). MicroRNA directs mRNA cleavage of the transcription factor NAC1 to downregulate auxin signals for Arabidopsis lateral root development. Plant Cell 17, 1376–1386.
He, X.F., Fang, Y.Y., Feng, L., and Guo, H.S. (2008). Characterization of conserved and novel microRNAs and their targets, including a TuMV-induced TIR-NBS-LRR class R gene-derived novel miRNA in Brassica. FEBS Lett. 582, 2445–2452.
Jagadeeswaran, G., Zheng, Y., Li, Y.F., Shukla, L.I., Matts, J., Hoyt, P., Macmil, S.L., Wiley, G.B., Roe, B.A., Zhang, W., et al. (2009). Cloning and characterization of small RNAs from Medicago truncatula reveals four novel legume-specific microRNA families. New Phytol. 184, 85–98.
Jin, W., Li, N., Zhang, B., Wu, F., Li, W., Guo, A., and Deng, Z. (2008). Identification and verification of microRNA in wheat (Triticum aestivum). J. Plant Res. 121, 351–355.
Jones-Rhoades, M.W., and Bartel, D.P. (2004). Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress induced miRNA. Mol. Cell 14, 787–799.
Kim, J., Jung, J.-H., Reyes, J.L., Kim, Y.-S., Kim, S.Y., Chung, K.-S., Kim, J.A., Lee, M., Lee, Y., Kim, V.N., et al. (2005). microRNA-directed cleavage of ATHB15 mRNA regulates vascular development in Arabidopsis inflorescence stems. Plant J. 42, 84–94.
Klevebring, D., Street, N.R., Fahlgren, N., Kasschau, K.D., Carrington, J.C., Lundeberg, J., and Jansson, S. (2009). Genome-wide profiling of Populus small RNAs. BMC Genomics 10, 620.
Lauter, N., Kampani, A., Carlson, S., Goebel, M., and Moose, S.P. (2005). microRNA172 down-regulates glossy15 to promote vegetative phase change in maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 9412–9417.
Livak, K.J., and Schmittgen, T.D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402–408.
Llave, C., Xie, Z.X., Kasschau, K.D., and Carrington, J.C. (2002a). Cleavage of Scarecrow-like mRNA targets directed by a class of Arabidopsis miRNA. Science 297, 2053–2056.
Llave, C., Kasschau, K.D., Rector, M., and Carrington, J.C. (2002b). Endogeneous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell 14, 1605–1619.
Lu, S., Sun, Y.H., Shi, R., Clark, C., Li, L., and Chiang, V.L. (2005). Novel and mechanical stress-responsive microRNAs in Populus trichocarpa that are absent from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17, 2186–2203.
Lu, S., Sun, Y.H., Amerson, H., and Chiang, V.L. (2007). MicroRNAs in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) and their association with fusiform rust gall development. Plant J. 51, 1077–1098.
Mallory, A.C., Dugas, D.V., Bartel, D.P., and Bartel, B. (2004). MicroRNA regulation of NAC domain targets is required for proper formation and separation of adjacent embryonic, vegetative, and floral organs. Curr. Biol. 14, 1035–1046.
Meyers, B.C., Axtell, M.J., Bartel, B., Bartel, D.P., Baulcombe, D., Bowman, J.L., Cao, X.F., Carrington, J.C., Chen, X., Green, P.J., et al. (2008). Criteria for annotation of plant MicroRNAs. Plant Cell 20, 3186–3190.
Mi, S., Cai, T., Hu, Y., Chen, Y., Hodges, E., Ni, F., Wu, L., Li. S., Zhou, H., Long, C., et al. (2008). Sorting of small RNAs into Arabidopsis argonaute complexes is directed by the 5′ terminal nucleotide. Cell 133, 116–127.
Montgomery, T.A., Howell, M.D., Cuperus, J.T., Li, D., Hansen, J.E., Alexander, A.L., Chapman, E.J., Fahlgren, N., Allen, E., and Carrington, J.C. (2008). Specificity of ARGONAUTE7-miR390 interaction and dual functionality in TAS3 trans-acting siRNA formation. Cell 133, 128–141.
Navarro, L., Dunoyer, P., Jay, F., Arnold, B., Dharmasiri, N., Estelle, M., Voinnet, O., and Jones, J.D. (2006). A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science 21, 436–439.
Palatnik, J.F., Allen, E., Wu, X., Schommer, C., Schwab, R., Carrington, J.C., and Weigel, D. (2003). Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature 425, 257–263.
Panjabi, P., Jagannath, A., Bisht, N.C., Padmaja, K.L., Sharma, S., Gupta, V., Pradhan, A.K., and Pental, D. (2008). Comparative mapping of Brassica juncea and Arabidopsis thaliana using intron polymorphism (IP) markers: homoeologous relationships, diversification and evolution of the A, B and C Brassica genomes. BMC Genomics 9, 113.
Park, W., Li, J.J., Song, R.T., Messing, J., and Chen, X.M. (2002). CARPEL FACTORY, a Dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 12, 1484–1495.
Park, M.Y., Wu, G., Gonzalez-Sulser, A., Vaucheret, H., and Poethig, R.S. (2005). Nuclear processing and export of microRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 3691–3696.
Parkin, I.A.P., Gulden, S.M., Sharpe, A.G., Lukens, L., Trick, M., Osborn, T.C., and Lydiate, D.J. (2005). Segmental structure of the Brassica napus genome based on comparative analysis with Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 171, 765–781.
Pulido, A., and Laufs, P. (2010). Co-ordination of developmental processes by small RNAs during leaf development. J. Exp. Bot. 61, 1277–1291.
Qiu, C.X., Xie, F.L., Zhu, Y.Y., Guo, K., Huang, S.Q., Nie, L., and Yang, Z.M. (2007). Computational identification of microRNAs and their targets in Gossypium hirsutum expressed sequence tags. Gene 395, 49–61.
Reinhart, B.J., Weinstein, E.G., Rhoades, M.W., Bartel, B., and Bartel, D.P. (2002). Micro-RNAs in plants. Genes Dev. 16, 1616–1626.
Rhoades, M.W., Reinhart, B.J., Lim, L.P., Burge, C.B., Bartel, B., and Bartel, D.P. (2002). Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110, 513–520.
Ruiz-Ferrer, V., and Voinnet, O. (2009). Roles of plant small RNAs in biotic stress responses. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 60, 485–510.
Schwab, R., Palatnik, J.F., Riester, M., Schommer, C., Schmid, M., and Weigel, D. (2005). Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev. Cell 8, 517–527.
Shi, R., and Chiang, V.L. (2005). Facile means for quantifying microRNA expression by real-time PCR. BioTechniques 39, 519–524.
Song, C., Fang, J., Li, X., Liu, H., and Chao, C.T. (2009). Identification and characterization of 27 conserved microRNAs in citrus. Planta 230, 671–685.
Stark, A., Bushati, N., Jan, C.H., Kheradpour, P., Hodges, E., Brennecke, J., Bartel, D.P., Cohen, S.M., and Kellis, M. (2008). A single Hox locus in Drosophila produces functional microRNAs from opposite DNA strands. Genes Dev. 22, 8–13.
Sunkar, R., and Jagadeeswaran, G. (2008). In silico identification of conserved microRNAs in large number of diverse plant species. BMC Plant Biol. 8, 37.
Sunkar, R., and Zhu, J.K. (2004). Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabdopsis. Plant Cell 16, 2001–2019.
Sunkar, R., Girke, T., Jain, P.K., and Zhu, J.K. (2005). Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from rice. Plant Cell 17, 1397–1411.
Sunkar, R., Kapoor, A., and Zhu, J.K. (2006). Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Cell 18, 2051–2065.
Sunkar, R., Chinnusamy, V., Zhu, J., and Zhu, J.K. (2007). Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci. 12, 301–309.
Sunkar, R., Zhou, X., Zheng, Y., Zhang, W., and Zhu, J.K. (2008). Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 8, 25.
Szittya, G., Moxon, S., Santos, D.M., Jing, R., Fevereiro, M.P., Moulton, V., and Dalmay, T. (2008). High-throughput sequencing of Medicago truncatula short RNAs identifies eight new miRNA families. BMC Genomics 9, 593.
Takeda, A., Iwasaki, S., Watanabe, T., Utsumi, M., and Watanabe, Y. (2008). The mechanism selecting the guide strand from small RNA duplexes is different among argonaute proteins. Plant Cell Physiol. 49, 493–500.
Teutonico, R.A., and Osborn, T.C. (1994). Mapping of RFLP and quantitative trait loci in Brassica rapa and comparison to the linkage maps of B. napus, B. oleracea, and Arabidopsis thaliana. Theor. Appl. Genet. 89, 885–894.
Truco, M.J., Hu, J., Sadowski, J., and Quiros, C.F. (1996). Interand intra-genomic homology of the Brassica genomes: implications for their origin and evolution. Theor. Appl. Genet. 93, 1225–1233.
Tyler, D.M., Okamura, K., Chung, W.J., Hagen, J.W., Berezikov, E., Hannon, G.J., and Lai, E.C. (2008). Functionally distinct regulatory RNAs generated by bidirectional transcription and processing of microRNA loci. Genes Dev. 22, 26–36.
Vaucheret, H., and Fagard, M. (2001). Transcriptional gene silencing in plants: targets, inducers and regulators. Trends Genet. 17, 29–35.
Voinnet, O. (2009). Origin, biogenesis, and activity of plant microRNAs. Cell 136, 669–687.
Wang, J.F., Zhou, H., Chen, Y.Q., Luo, Q.J., and Qu, L.H. (2004a). Identification of, 20 microRNAs from Oryza sativa. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1688–1695.
Wang, X.L., Reyes, J.L., Chua, N.H., and Gaasterland, T. (2004b). Prediction and identification of Arabidopsis thaliana microRNAs and their mRNA targets. Genome Biol. 5, R65.
Wu, G., and Poethig, R.S. (2006). Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thaliana by miR156 and its target SPL3. Development 133, 3539–3547.
Xie, F.L., Huang, S.Q., Guo, K., Xiang, A.L., Zhu, Y.Y., Nie, L., and Yang, Z.M. (2007). Computational identification of novel microRNAs and targets in Brassica napus. FEBS Lett. 581, 1464–1474.
Xie, F., Frazier, T.P., and Zhang, B. (2010). Identification and characterization of microRNAs and their targets in the bioenergy plant switchgrass (Panicum virgatum). Planta 232, 417–434.
Yang, T.J., Kim, J.S., Lim, K.B., Kwon, S.J., Kim, J.A., Jin, M., Park, J.Y., Lim, M.H., Kim, H.I., Kim, S.H., et al. (2005). The Korea Brassica Genome Project: A glimpse of the Brassica genome based on comparative genome analysis with Arabidopsis. Comp. Funct. Genom. 6, 138–146.
Zhang, Y. (2005). miRU: an automated plant miRNA target prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, W701–W704.
Zhang, B.H., Pan, X.P., Cobb, G.P., and Anderson, T.A. (2006a). Plant microRNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact. Dev. Biol. 289, 3–16.
Zhang, B.H., Pan, X.P., and Anderson T.A. (2006b). Identification of 188 conserved maize microRNAs and their targets. FEBS Lett. 580, 3753–3762.
Zhang, B.H., Pan, X.P., Cox, S.B., Cobb, G.P., and Anderson, T.A. (2006c). Evidence that miRNAs are different from other RNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 246–254.
Zhang, B.H., Wang, Q., Wang, K., Pan, X., Liu, F., Guo, T., Cobb, G.P., and Anderson, T.A. (2007a). Identification of cotton microRNAs and their targets. Gene 397, 26–37.
Zhang, B.H., Pan, X.P., Cobb, G.P., and Anderson, T.A. (2007b). microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev. Biol. 302, 1–12.
Zhang, B.H., Wang, Q.L., and Pan, X.P. (2007c). MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in animals and plants. J. Cell. Physiol. 210, 279–289.
Zhang, B.H., Pan, X.P., and Stellwag, E.J. (2008). Identification of soybean microRNAs and their targets. Planta 229, 161–182.
Zhao, B., Liang, R., Ge, L., Li, W., Xiao, H., Lin, H., Ruan, K., and Jin, Y. (2007). Identification of drought-induced microRNAs in rice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 354, 585–590.
Zhou, X., Wang, G., and Zhang, W. (2007). UV-B responsive micro-RNA genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3, 103.
Zuker, M. (2003). Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3406–3415.
Zuker, M., Mathews, D.H., and Turner, D.H. (1998). Algorithms and thermodynamics for RNA secondary structure prediction: a practical guide. In RNA Biochemistry and Biotechnology, J. Barciszewski, and C.C. Brian Frederic, eds. (NATO Science series), Vol. 70, pp. 11–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Dhandapani, V., Ramchiary, N., Paul, P. et al. Identification of potential microRNAs and their targets in Brassica rapa L.. Mol Cells 32, 21–37 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-2313-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-2313-7