Abstract
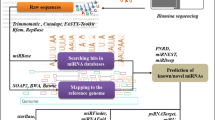
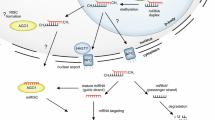
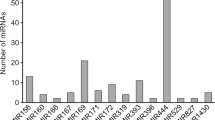
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding small endogenous RNAs with lengths of ~22 nucleotides (nt) that have been shown to regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional levels by targeting mRNAs for degradation or by inhibiting protein translation. Although thousands of miRNAs have been identified in many species, miRNAs have not yet been identified in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum), one of the most important bioenergy crops in the United States and around the world. In this study, we identified 121 potential switchgrass miRNAs, belonging to 44 families, using a well-defined comparative genome-based computational approach. We also identified miRNA clusters and antisense miRNAs in switchgrass expressed sequences tags. These identified miRNAs potentially target 839 protein-coding genes, which can act as transcription factors, and take part in multiple biological and metabolic processes including sucrose and fat metabolism, signal transduction, stress response, and plant development. Gene ontology (GO) analysis, based on these targets, showed that 527 biological processes were involved. Twenty-five of these processes were demonstrated to participate in the metabolism of carbon, glucose, starch, fatty acid, and lignin and in xylem formation. According to pathway enrichment analysis based on Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), 118 metabolism networks were found. These networks are involved in sucrose metabolism, fat metabolism, carbon fixation, hormone regulation, oxidative stress response, and the processing of other secondary metabolites.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DCL1:
-
Dicer-like 1
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- MFE:
-
Minimal folding free energy
- MFEI:
-
Minimal folding free energy index
- nt:
-
Nucleotide
- pre-miRNAs:
-
miRNA precursor
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- RISC:
-
RNA-induced silencing complex
- SBP:
-
Squamosa-promoter-binding protein-like protein
- TAF:
-
TBP-associated factors
- TBP:
-
TATA-binding protein
References
Altuvia Y, Landgraf P, Lithwick G, Elefant N, Pfeffer S, Aravin A, Brownstein MJ, Tuschl T, Margalit H (2005) Clustering and conservation patterns of human microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 33:2697–2706
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
Ashburner M, Bergman CM (2005) Drosophila melanogaster: a case study of a model genomic sequence and its consequences. Genome Res 15:1661–1667
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bender W (2008) MicroRNAs in the Drosophila bithorax complex. Genes Dev 22:14–19
Bouton JH (2007) Molecular breeding of switchgrass for use as a biofuel crop. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17:553–558
Chen B, Schnoor JL (2009) Role of suberin, suberan, and hemicellulose in phenanthrene sorption by root tissue fractions of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) seedlings. Environ Sci Technol 43:4130–4136
Chiou TJ (2007) The role of microRNAs in sensing nutrient stress. Plant Cell Environ 30:323–332
Cler E, Papai G, Schultz P, Davidson I (2009) Recent advances in understanding the structure and function of general transcription factor TFIID. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:2123–2134
Fattash I, Voss B, Reski R, Hess WR, Frank W (2007) Evidence for the rapid expansion of microRNA-mediated regulation in early land plant evolution. BMC Plant Biol 7:13
Floyd SK, Bowman JL (2004) Gene regulation: ancient microRNA target sequences in plants. Nature 428:485–486
Gleave AP, Ampomah-Dwamena C, Berthold S, Dejnoprat S, Karunairetnam S, Nain B, Wang Y-Y, Crowhurst RN, MacDiarmid RM (2008) Identification and characterization of primary microRNAs from apple (Malus domestica cv. Royal Gala) expressed sequence tags. Tree Genet Genomes 4:343–358
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ (2008) miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D154–D158
Hofacker IL (2003) Vienna RNA secondary structure server. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3429–3431
Jagadeeswaran G, Saini A, Sunkar R (2009) Biotic and abiotic stress down-regulate miR398 expression in Arabidopsis. Planta 229:1009–1014
Jia X, Wang WX, Ren L, Chen QJ, Mendu V, Willcut B, Dinkins R, Tang X, Tang G (2009) Differential and dynamic regulation of miR398 in response to ABA and salt stress in Populus tremula and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 71:51–59
Jin H, Martin C (1999) Multifunctionality and diversity within the plant MYB-gene family. Plant Mol Biol 41:577–585
Jin WB, Li NN, Zhang B, Wu FL, Li WJ, Guo AG, Deng ZY (2008) Identification and verification of microRNA in wheat (Triticum aestivum). J Plant Res 121:351–355
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP (2004) Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol Cell 14:787–799
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B (2006) MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:19–53
Jung HJ, Kang H (2007) Expression and functional analyses of microRNA417 in Arabidopsis thaliana under stress conditions. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:805–811
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30
Lu SF, Sun YH, Shi R, Clark C, Li LG, Chiang VL (2005) Novel and mechanical stress-responsive microRNAs in Populus trichocarpa that are absent from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:2186–2203
Pan XP, Zhang BH, SanFrancisco M, Cobb GP (2007) Characterizing viral microRNAs and its application on identifying new microRNAs in viruses. J Cell Physiol 211:10–18
Peng L, Kawagoe Y, Hogan P, Delmer D (2002) Sitosterol-beta-glucoside as primer for cellulose synthesis in plants. Science 295:147–150
Pilcher RLR, Moxon S, Pakseresht N, Moulton V, Manning K, Seymour G, Dalmay T (2007) Identification of novel small RNAs in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Planta 226:709–717
Schwab R, Palatnik JF, Riester M, Schommer C, Schmid M, Weigel D (2005) Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev Cell 8:517–527
Seitz H, Royo H, Bortolin ML, Lin SP, Ferguson-Smith AC, Cavaille J (2004) A large imprinted microRNA gene cluster at the mouse Dlkl-Gtl2 domain. Genome Res 14:1741–1748
Smith TF, Waterman MS (1981) Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol 147:195–197
Song CN, Fang JG, Li XY, Liu H, Chao CT (2009) Identification and characterization of 27 conserved microRNAs in citrus. Planta 230:671–685
Stark A, Bushati N, Jan CH, Kheradpour P, Hodges E, Brennecke J, Bartel DP, Cohen SM, Kellis M (2008) A single Hox locus in Drosophila produces functional microRNAs from opposite DNA strands. Genes Develop 22:8–13
Sunkar R, Zhu JK (2004) Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2001–2019
Sunkar R, Girke T, Jain PK, Zhu JK (2005) Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from rice. Plant Cell 17:1397–1411
Sunkar R, Kapoor A, Zhu JK (2006) Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Cell 18:2051–2065
Sunkar R, Chinnusamy V, Zhu JH, Zhu JK (2007) Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci 12:301–309
Talmor-Neiman M, Stav R, Frank W, Voss B, Arazi T (2006) Novel micro-RNAs and intermediates of micro-RNA biogenesis from moss. Plant J 47:25–37
Tanzer A, Stadler PF (2004) Molecular evolution of a microRNA cluster. J Mol Biol 339:327–335
Tanzer A, Amemiya CT, Kim CB, Stadler PF (2005) Evolution of microRNAs located within Hox gene clusters. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 304B:75–85
Tyler DM, Okamura K, Chung WJ, Hagen JW, Berezikov E, Hannon GJ, Lai EC (2008) Functionally distinct regulatory RNAs generated by bidirectional transcription and processing of microRNA loci. Genes Develop 22:26–36
Unver T, Budak H (2009) Conserved microRNAs and their targets in model grass species Brachypodium distachyon. Planta 230:659–669
Uppugundla N, Engelberth A, Vandhana Ravindranath S, Clausen EC, Lay JO, Gidden J, Carrier DJ (2009) Switchgrass water extracts: extraction, separation and biological activity of rutin and quercitrin. J Agric Food Chem 57:7763–7770
Wang XJ, Reyes JL, Chua NH, Gaasterland T (2004) Prediction and identification of Arabidopsis thaliana microRNAs and their mRNA targets. Genome Biol 5:R65
Xie FL, Huang SQ, Guo K, Xiang AL, Zhu YY, Nie L, Yang ZM (2007) Computational identification of novel microRNAs and targets in Brassica napus. FEBS Lett 581:1464–1474
Yao YY, Guo GG, Ni ZF, Sunkar R, Du JK, Zhu JK, Sun QX (2007) Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome Biol 8:R96
Yu J, Wang F, Yang GH, Wang FL, Ma YN, Du ZW, Zhang JW (2006) Human microRNA clusters: genomic organization and expression profile in leukemia cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349:59–68
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Wang QL, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2005) Identification and characterization of new plant microRNAs using EST analysis. Cell Res 15:336–360
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Anderson TA (2006a) Identification of 188 conserved maize microRNAs and their targets. FEBS Lett 580:3753–3762
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Cannon CH, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2006b) Conservation and divergence of plant microRNA genes. Plant J 46:243–259
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Cox SB, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2006c) Evidence that miRNAs are different from other RNAs. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:246–254
Zhang BH, Wang QL, Pan XP (2007a) MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in animals and plants. J Cell Physiol 210:279–289
Zhang BH, Wang QL, Wang KB, Pan XP, Liu F, Guo TL, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2007b) Identification of cotton microRNAs and their targets. Gene 397:26–37
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Stellwag EJ (2008) Identification of soybean microRNAs and their targets. Planta 229:161–182
Zhang WW, Luo YP, Gong X, Zeng WH, Li SG (2009) Computational identification of 48 potato microRNAs and their targets. Comput Biol Chem 33:84–93
Zhong R, Pena MJ, Zhou GK, Nairn CJ, Wood-Jones A, Richardson EA, Morrison WH 3rd, Darvill AG, York WS, Ye ZH (2005) Arabidopsis fragile fiber8, which encodes a putative glucuronyltransferase, is essential for normal secondary wall synthesis. Plant Cell 17:3390–3408
Zuker M, Stiegler P (1981) Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res 9:133–148
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by a grant from the North Carolina Biotechnology Center (2009-BRG-1202) and a grant from DuPont Science & Engineering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, F., Frazier, T.P. & Zhang, B. Identification and characterization of microRNAs and their targets in the bioenergy plant switchgrass (Panicum virgatum). Planta 232, 417–434 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1182-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1182-1