Abstract
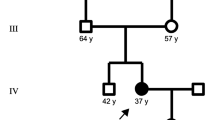
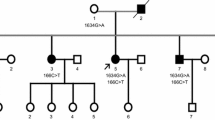
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a motor neuron disease eventually leading to death from respiratory failure. Recessive inheritance is very rare. Here, we describe the clinical findings in a consanguineous family with five men afflicted with recessive ALS and the identification of the homozygous mutation responsible for the disorder. The onset of the disease ranged from 12 to 35 years of age, with variable disease progressions. We performed clinical investigations including metabolic and paraneoplastic screening, cranial and cervical imaging, and electrophysiology. We mapped the disease gene to 9p21.1-p12 with a LOD score of 5.2 via linkage mapping using genotype data for single-nucleotide polymorphism markers and performed exome sequence analysis to identify the disease-causing gene variant. We also Sanger sequenced all coding sequences of SIGMAR1, a gene reported as responsible for juvenile ALS in a family. We did not find any mutation in SIGMAR1. Instead, we identified a novel homozygous missense mutation p.(His705Arg) in GNE which was predicted as damaging by online tools. GNE has been associated with inclusion body myopathy and is expressed in many tissues. We propose that the GNE mutation underlies the pathology in the family.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiò A, Logroscino G, Traynor BJ, Collins J, Simeone JC, Goldstein LA, White LA (2013) Global epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review of the published literature. Neuroepidemiology 41(2):118–130
Siddique T, Deng HX (1996) Genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 5 Spec No:1465–1470
Mulder DW, Kurland LT, Offord KP, Beard CM (1986) Familial adult motor neuron disease: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 36(4):511–517
Chen S, Sayana P, Zhang X, Le W (2013) Genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an update. Mol Neurodegener 8:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-8-28
Sreedharan J, Brown RH Jr (2013) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: problems and prospects. Ann Neurol 74(3):309–316. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24012
Zufiria M, Gil-Bea FJ, Fernandez-Torron R, Poza JJ, Munoz-Blanco JL, Rojas-Garcia R, Riancho J, de Munain AL (2016) ALS: a bucket of genes, environment, metabolism and unknown ingredients. Prog Neurobiol 142:104–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.05.004
Powers JM, Horoupian DS, Schaumburg HH (1974) Wetherbee Ail. Documentation of a neurological disease in a Vermont family 90 years later. Can J Neurol Sci 1(2):139–140
Veltema AN, Roos RA, Bruyn GW (1990) Autosomal dominant adult amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A six generation Dutch family. J Neurol Sci 97(1):93–115
Hentati A, Ouahchi K, Pericak-Vance MA, Nijhawan D, Ahmad A, Yang Y, Rimmler J, Hung W, Schlotter B, Ahmed A, Ben Hamida M, Hentati F, Siddique T (1998) Linkage of a commoner form of recessive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis to chromosome 15q15-q22 markers. Neurogenetics 2(1):55–60
Chen YZ, Bennett CL, Huynh HM, Blair IP, Puls I, Irobi J, Dierick I, Abel A, Kennerson ML, Rabin BA, Nicholson GA, Auer-Grumbach M, Wagner K, De Jonghe P, Griffin JW, Fischbeck KH, Timmerman V, Cornblath DR, Chance PF (2004) DNA/RNA helicase gene mutations in a form of juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS4). Am J Hum Genet 74(6):1128–1135. https://doi.org/10.1086/421054
Alter M, Schaumann B (1976) Hereditary amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A report of two families. Eur Neurol 14(4):250–265
Turner MR, Bakker M, Sham P, Shaw CE, Leigh PN, Al-Chalabi A (2002) Prognostic modelling of therapeutic interventions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 3(1):15–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/146608202317576499
Sabatelli M, Madia F, Conte A, Luigetti M, Zollino M, Mancuso I, Lo Monaco M, Lippi G, Tonali P (2008) Natural history of young-adult amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 71(12):876–881. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000312378.94737.45
Cudkowicz ME, McKenna-Yasek D, Sapp PE, Chin W, Geller B, Hayden DL, Schoenfeld DA, Hosler BA, Horvitz HR, Brown RH (1997) Epidemiology of mutations in superoxide dismutase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 41(2):210–221. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410410212
Juneja T, Pericak-Vance MA, Laing NG, Dave S, Siddique T (1997) Prognosis in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: progression and survival in patients with glu100gly and ala4val mutations in Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase. Neurology 48(1):55–57
Luigetti M, Madia F, Conte A, Marangi G, Zollino M, Del Grande A, Dileone M, Tonali PA, Sabatelli M (2009) SOD1 G93D mutation presenting as paucisymptomatic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 10(5–6):479–482. https://doi.org/10.3109/17482960802302261
Orban P, Devon RS, Hayden MR, Leavitt BR (2007) Chapter 15 Juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Handb Clin Neurol 82:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0072-9752(07)80018-2
Fecto F, Siddique T (2011) Making connections: pathology and genetics link amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with frontotemporal lobe dementia. J Mol Neurosci 45(3):663–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9637-9
Orlacchio A, Babalini C, Borreca A, Patrono C, Massa R, Basaran S, Munhoz RP, Rogaeva EA, St George-Hyslop PH, Bernardi G, Kawarai T (2010) SPATACSIN mutations cause autosomal recessive juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 133(Pt 2):591–598. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp325
Andersen PM, Nilsson P, Ala-Hurula V, Keränen ML, Tarvainen I, Haltia T, Nilsson L, Binzer M, Forsgren L, Marklund SL (1995) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated with homozygosity for an Asp90Ala mutation in CuZn-superoxide dismutase. Nat Genet 10(1):61–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0595-61
Maruyama H, Morino H, Ito H, Izumi Y, Kato H, Watanabe Y, Kinoshita Y, Kamada M, Nodera H, Suzuki H, Komure O, Matsuura S, Kobatake K, Morimoto N, Abe K, Suzuki N, Aoki M, Kawata A, Hirai T, Kato T, Ogasawara K, Hirano A, Takumi T, Kusaka H, Hagiwara K, Kaji R, Kawakami H (2010) Mutations of optineurin in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 465(7295):223–226. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08971
Yang Y, Hentati A, Deng HX, Dabbagh O, Sasaki T, Hirano M, Hung WY, Ouahchi K, Yan J, Azim AC, Cole N, Gascon G, Yagmour A, Ben-Hamida M, Pericak-Vance M, Hentati F, Siddique T (2001) The gene encoding alsin, a protein with three guanine-nucleotide exchange factor domains, is mutated in a form of recessive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet 29(2):160–165. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1001-160
Hadano S, Hand CK, Osuga H, Yanagisawa Y, Otomo A, Devon RS, Miyamoto N, Showguchi-Miyata J, Okada Y, Singaraja R, Figlewicz DA, Kwiatkowski T, Hosler BA, Sagie T, Skaug J, Nasir J, Brown RH Jr, Scherer SW, Rouleau GA, Hayden MR, Ikeda JE (2001) A gene encoding a putative GTPase regulator is mutated in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2. Nat Genet 29(2):166–173. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1001-166
Kress JA, Kuhnlein P, Winter P, Ludolph AC, Kassubek J, Müller U, Sperfeld AD (2005) Novel mutation in the ALS2 gene in juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 58(5):800–803. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20665
Al-Saif A, Al-Mohanna F, Bohlega S (2011) A mutation in sigma-1 receptor causes juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 70(6):913–919. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22534
Kwiatkowski TJ Jr, Bosco DA, Leclerc AL, Tamrazian E, Vanderburg CR, Russ C, Davis A, Gilchrist J, Kasarskis EJ, Munsat T, Valdmanis P, Rouleau GA, Hosler BA, Cortelli P, de Jong PJ, Yoshinaga Y, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Yan J, Ticozzi N, Siddique T, McKenna-Yasek D, Sapp PC, Horvitz HR, Landers JE, Brown RH Jr (2009) Mutations in the FUS/TLS gene on chromosome 16 cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 323(5918):1205–1208. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1166066
Huizing M, Carrillo-Carrasco N, Malicdan MC, Noguchi S, Gahl WA, Mitrani-Rosenbaum S, Argov Z, Nishino I (2014) GNE myopathy: new name and new mutation nomenclature. Neuromuscul Disord 24(5):387–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2014.03.004
Dimachkie MM, Barohn RJ (2014) Distal myopathies. Neurol Clin 32(3):817–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2014.04.004
Nishino I, Noguchi S, Murayama K, Driss A, Sugie K, Oya Y, Nagata T, Chida K, Takahashi T, Takusa Y, Ohi T, Nishimiya J, Sunohara N, Ciafaloni E, Kawai M, Aoki M, Nonaka I (2002) Distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles is allelic to hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Neurology 59(11):1689–1693
de Dios JK, Shrader JA, Joe GO, McClean JC, Williams K, Evers R, Malicdan MC, Ciccone C, Mankodi A, Huizing M, McKew JC, Bluemke DA, Gahl WA, Carrillo-Carrasco N (2014) Atypical presentation of GNE myopathy with asymmetric hand weakness. Neuromuscul Disord 24(12):1063–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2014.07.006
Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL, World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases (2000) El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1(5):293–299
Eisenberg I, Avidan N, Potikha T, Hochner H, Chen M, Olender T, Barash M, Shemesh M, Sadeh M, Grabov-Nardini G, Shmilevich I, Friedmann A, Karpati G, Bradley WG, Baumbach L, Lancet D, Asher EB, Beckmann JS, Argov Z, Mitrani-Rosenbaum S (2001) The UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase gene is mutated in recessive hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Nat Genet 29(1):83–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng718
Keppler OT, Hinderlich S, Langner J, Schwartz-Albiez R, Reutter W, Pawlita M (1999) UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase: a regulator of cell surface sialylation. Science 284(5418):1372–1376
Acknowledgements
We thank the family members for their cooperation, Dr. Aslıhan Tolun for supervising the genetic studies and her contribution to writing the manuscript, and TÜBITAK Advanced Genomics and Bioinformatics Group (IGBAM) for sharing with us the Turkish Exome Database.
Funding
This work was supported by the Boğaziçi University Research Fund grant number 5708 and the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey grant number 110T252 (to AT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study protocol was approved by the Boğaziçi University Institutional Review Board for Research with Human Participants. Informed consent was obtained from all the subjects according to the regulations of the board.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
Simplified pedigree used for the initial whole-genome multipoint linkage analysis on Allegro. Because of the limitations in the program, unaffected siblings were not included and consanguinity between 407 and 408 was disregarded. (GIF 11 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
Multipoint LOD scores for chromosomes that yielded positive scores. A, initial calculations for autosomes and pseudoautosomal regions using Allegro. B, detailed calculations using SimWalk at loci that yielded LOD scores > 3 in the initial analysis. (PDF 4733 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
Chromatograms showing the candidate variant GNE c.2114A>G (p.His705Arg). (GIF 39 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
The list of all exonic and splicing variants detected at the disease locus 9p21.1-p12. False calls as indicated by IGV inspection, as well as variants with allele frequencies > 0.05, were filtered out. Novel, homozygous variant c.A2114G (p.His705Arg) in GNE was selected as the candidate mutation. (XLS 58 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köroğlu, Ç., Yılmaz, R., Sorgun, M.H. et al. GNE missense mutation in recessive familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurogenetics 18, 237–243 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-017-0527-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-017-0527-3