Abstract
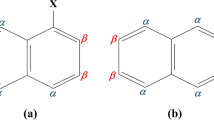
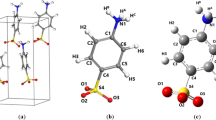
“Proton sponges,” derivatives of prototypic 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene (DMAN), exhibit remarkable basicity, which made them interesting for various experimental and theoretical studies. The details of bridged proton dynamics in protonated DMAN and its derivative denoted as TMGN (1,8-bis(tetramethylguanidino)naphthalene) were investigated on the basis of density functional theory (DFT) and Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics (CPMD) methods. Special attention was paid to the effects of symmetry of the molecular skeleton and the type of substituent on the bridged proton neighborhood statistics and dynamics. The metric parameter analyses of hydrogen bridge provided us with a conclusion that proton migration events in TMGNH+ are less numerous than in DMANH+, which can be rationalized by noticing the slower dynamics of large substituents of TMGN with respect to the smaller –N(Me)2 groups of DMAN. The atomic velocity power spectra served as computational models of the vibrational signatures associated with the presence of the intramolecular hydrogen bond. A broad feature was registered for hydrogen bonds present in both compounds. The computations were verified by experimental data available.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alder RW, Bowman PS, Steele RS, Winterman DR (1968) The remarkable basicity of 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene. Chem Commun 452:723–724
Raab V, Gauchenova E, Merkoulov A, Harms K, Sundermeyer J, Kovačević B, Maksić ZB (2005) 1,8-bis(hexamethyltriaminophosphazenyl)naphthalene, HMPN: a superbasic bisphosphazene “proton sponge”. J Am Chem Soc 127:15738–15743
Alder RW (1989) Strain effects on amine basicities. Chem Rev 89:1215–1223
Saupe T, Krieger C, Staab HA (1986) 4,5-bis(dimethylamino)phenanthrene and 4,5-bis(dimethylamino)-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene: syntheses and “proton sponge” properties. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 25:451–453. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.198604511
Kögel JF, Xie X, Baal E, Gesevičius D, Oelkers B, Kovačević B, Sundermeyer J (2014) Superbasic alkyl-substituted bisphosphazene proton sponges: synthesis, structural features, thermodynamic and kinetic basicity, nucleophilicity and coordination chemistry. Chem Eur J 20:7670–7685. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201402226
Alder RW, Orpen AG, Sessions RB (1983) The structure of I ,6-diazabicyclo[4.4.4]tetradecane and of its inside protonated ion. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 999–1000
Ozeryanskii VA, Pozharskii AF, Antonov AS, Filarowski A (2014) Out-basicity of 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)-naphthalene: the experimental and theoretical challenge. Org Biomol Chem 12:2360–2369. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ob41986j
Schwesinger R, Mißfeldt M, Peters K, von Schnering HG (1987) Novel, very strongly basic, pentacyclic “proton sponges” with vinamidine structure. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 26:1165–1167. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.198711651
Katz HE (1985) Hydride sponge: 1,8-naphtalenediylbis(dimethylborane). J Am Chem 107:1420–1421. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00291a057
Staab HA, Saupe T (1988) “Proton sponges” and the geometry of hydrogen bonds: aromatic nitrogen bases with exceptional basicities. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 27:865–879. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.198808653
Llamas-Saiz AL, Foces-Foces C, Elguero J (1994) Proton sponges. J Mol Struct 328:297–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2860(94)08367-3
Raczyńska ED, Gal J-F, Maria P-C (2016) Enhanced basicity of push–pull nitrogen bases in the gas phase. Chem Rev 116:13454–13511. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00224
Mallinson PR, Woźniak K, Wilson CC, McCormack KL, Yufit DS (1999) Charge density distribution in the “proton sponge” compound1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene. J Am Chem Soc 121:4640–4646. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja983393z
Bieńko AJ, Latajka Z, Sawka-Dobrowolska W, Sobczyk L, Ozeryanskii VA, Pozharskii AF, Grech E, Nowicka-Scheibe J (2003) Low barrier hydrogen bond in protonated proton sponge. X-ray diffraction, infrared, and theoretical ab initio and density functional theory studies. J Chem Phys 119:4313–4319. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1594171
Sobczyk L, Chudoba D, Tolstoy PM, Filarowski A (2016) Some brief notes on theoretical and experimental investigations of intramolecular hydrogen bonding. Molecules 21:1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121657
Korzhenevska NG, Rybachenko VI, Schroeder G (2002) The basicity of 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene and the hybrid state of the nitrogen atoms of its dimethylamino groups. Tetrahedron Lett 43:6043–6045
Perrin CL (2010) Are short, low-barrier hydrogen bonds unusually strong? Acc Chem Res 43:1550–1557
Mazaleyrat J-P, Wright K (2008) Binaphthyl substituted 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalenes, the first chiral, atropisomeric, proton sponges. Tetrahedron Lett 49:4537–4541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.05.042
Mallinson PR, Woźniak K, Smith GT, MCCormack KL (1997) A charge density analysis of cationic and anionic hydrogen bonds in a “proton sponge” complex. J Am Chem Soc 119:11502–11509
Eitner K, Schroeder G, Rybachenko VI, Brzezinski B (2000) NHN+ intramolecular hydrogen bonds: heat of formation and parameters of some proton sponges. J Mol Struct 525:247–251
Ozeryanskii VA, Shevchuk DA, Pozharskii AF, Kazheva ON, Chekhlov AN, Dyachenko OA (2008) Protonation of naphthalene proton sponges containing higher N-alkyl groups. Structural Consequences on Proton Accepting Properties and Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding. J Mol Struct 892:63–67
Sobczyk L (2010) The specificity of the [NHN]+ hydrogen bonds in protonated naphthalene proton sponges. J Mol Struct 972:59–63
Pozharskii AF, Ozeryanskii VA (2012) Proton sponges and hydrogen transfer phenomena. Mendeleev Commun 22:117–124
Ozeryanskii VA, Pozharskii AF (2013) Simple and hydrolytically stable proton sponge based organic cation displaying hydrogen bonding and a number of related phenomena. Thtrahedron 69:2107–2112
Bernatowicz P, Kowalewski J, Sandström D (2005) NMR relaxation study of the protonated form of 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene in isotropic solution: anisotropic motion outside of extreme narrowing and ultrafast proton transfer. J Phys Chem A 109:57–63
Degtyarev AV, Ryabtsova OV, Pozharskii AF, Ozeryanskii VA, Starikova ZA, Sobczyk L, Filarowski A (2008) 2,7-Disubstituted proton sponges as borderline systems for investigating barrier-free intramolecular hydrogen bonds. Protonated 2,7-bis-(trimethylsilyl)- and 2,7-di(hydroxymethyl)-1,8-bis(dimethylamino)-naphthalenes. Tetrahedron 64:6209–6214
Gilli G, Gilli P (2000) Towards an unified hydrogen-bond theory. J Mol Struct 552:1–15
Boer SA, Wang P-X, MacLachlan MJ, White NG (2019) Open pentiptycene networks assembled through charge-assisted hydrogen bonds. Cryst Growth Des 19:4829–4835
Meot-Ner (Mautner) M (2005) The ionic hydrogen bond. Chem Rev 105:213–284
Raab V, Kipke J, Gschwind RM, Sundermeyer J (2002) 1,8-Bis(tetramethylguanidino)naphthalene (TMGN): a new, superbasic and kinetically active “proton sponge”. Chem Eur J 8:1682–1693
Kovačević B, Maksić ZB (2002) The proton affinity of the superbase 1,8-bis(tetramethylguanidino)naphthalene (TMGN) and some related compounds: a theoretical study. Chem Eur J 8:1694–1702
Hohenberg P, Kohn W (1964) Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys Rev 136:B864–B871
Kohn W, Sham LJ (1965) Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys Rev 140:A1133–A1138
Car R, Parrinello M (1985) Unified approach for molecular dynamics and density-functional theory. Phys Rev Lett 55:2471–2474
Jezierska A, Panek JJ (2015) “Zwitterionic proton sponge” hydrogen bonding investigations on the basis of Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics. J Chem Inf Model 55:1148–1157
Jezierska A, Panek JJ, Koll A (2008) Spectroscopic properties of a strongly anharmonic Mannich base N-oxide. Chem Phys Chem 9:839–846
Jezierska A, Panek JJ (2008) First-principle molecular dynamics study of selected Schiff and Mannich bases: application of two-dimensional potential of mean force to systems with strong intramolecular hydrogen bonds. J Chem Theory Comput 4:375–384
Ditchfield R, Hehre WJ, Pople JA (1971) Self-consistent molecular-orbital methods. IX. An extended Gaussian-type basis for molecular-orbital studies of organic molecules. J Chem Phys 54:724–728. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1674902
Becke AD (1993) Density-functional thermochemistry. III The role of exact exchange. J Chem Phys 98:5648–5652
Lee C, Yang W, Parr RG (1988) Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys Rev B 37:785–789
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77:3865–3868. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865
Tao JM, Perdew JP, Staroverov VN, Scuseria GE (2003) Climbing the density functional ladder: nonempirical meta-generalized gradient approximation designed for molecules and solids. Phys Rev Lett 91:146401. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.146401
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian HP, Izmaylov AF, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Montgomery Jr. JA, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark M, Heyd JJ, Brothers E, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Keith T, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell A, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Rega N, Millam JM, Klene M, Knox JE, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Zakrzewski VG, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Farkas O, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cioslowski J, Fox DJ. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford 2010
Hockney RW (1970) The potential calculation and some applications. Methods Comput Phys 9:136–211
Trouiller N, Martins JS (1991) Efficient pseudopotentials for plane-wave calculations. Phys Rev B 43:8861–8869
Jezierska-Mazzarello A, Panek JJ, Vuilleumier R, Koll A, Ciccotti G (2011) Direct observation of the substitution effects on the hydrogen bridge dynamics in selected Schiff bases – a comparative molecular dynamics study. J Chem Phys 134:034308
Jezierska A, Panek JJ, Koll A, Mavri J (2007) Car-Parrinello simulation of an O-H stretching envelope and potential of mean force of an intramolecular hydrogen bonded system: application to a Mannich base in solid state and in vacuum. J Chem Phys 126:205101
Martyniak A, Panek J, Jezierska-Mazzarello A, Filarowski A (2012) Triple hydrogen bonding in a circular arrangement: ab initio, DFT and first-principles MD studies of tris-hydroxyaryl enamines. J Comput Aid Mol Des 26:1045–1053
Panek JJ, Jezierska-Mazzarello A, Lipkowski P, Martyniak A, Filarowski A (2014) Comparison of resonance assisted and charge assisted effects in strengthening of hydrogen bonds in dipyrrins. J Chem Inf Model 54:86–95
Nosé S (1984) A molecular dynamics method for simulations in the canonical ensemble. Mol Phys 52:255–268
Nosé S (1984) A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods. J Chem Phys 81:511–519
Hoover WG (1985) Canonical dynamics: equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys Rev A 31:1695–1697
CPMD, Copyright IBM Corp., Zurich, Switzerland, 1990–2004; Copyright MPI fuer Festkoerperforschung Stuttgart, Stuttgart. Germany, 1997–2001
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD - visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14:33–38
Gnuplot, Copyright (C) 1986–1993, 1998, 2004. Williams T, Kelley C. Copyright (C) 2004-2007. Broeker HB, Campbell J, Cunningham R, Denholm D, Elber G, Fearick R, Grammes C, Hart L et al.
Sobczyk L, Grabowski SJ, Krygowski TM (2005) Interrelation between H-bond and Pi-electron delocalization. Chem Rev 105:3513–3560
Grech E, Malarski Z, Sobczyk L (1985) IR spectroscopic properties of hydrogen bonding in 1:1 salts of 1,8-bis(N,N-dimethylamino)naphthalene. J Mol Struct 129:35–43
Grech E, Malarski Z, Sobczyk L (1986) Isotopic effects in NH…N hydrogen bonds. Chem Phys Lett 128:259–263
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank the Wrocław Centre for Networking and Supercomputing (WCSS), the Academic Computer Center (TASK) in Gdańsk for generous computing time grants and the use of computational facilities.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the National Science Centre (Poland) which supported this work under the grant no. UMO-2015/17/B/ST4/03568.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This paper belongs to the Topical Collection Zdzisław Latajka 70th Birthday Festschrift
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jezierska, A., Panek, J.J. Theoretical study of intramolecular hydrogen bond in selected symmetric “proton sponges” on the basis of DFT and CPMD methods. J Mol Model 26, 37 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-020-4296-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-020-4296-9