Abstract
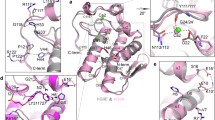
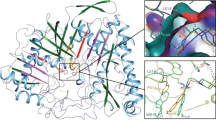
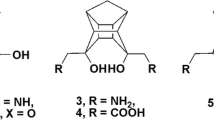
Structure and analog based analysis of 3D-QSAR, CoMFA and CoMSIA, along with different docking protocols were used to evaluate the structure activity relationship of 26 analogues of 1-aryl sulfamido-2-alkyl piperazines to model the activities of group I and II secreted phospholipases A2 (sPLA2s) and probe into the chemical space and nature of receptor — ligand interactions. The best CoMFA model yields cross-validated (q2) and conventional correlation coefficients (r2) of 0.703 and 0.962 respectively whereas CoMSIA model yields q2 and r2 values of 0.408 and 0.922 respectively, followed by docking analysis using FlexX and GOLD methodologies on the X-ray structure of human and bovine PLA2s. A comparative study was made to find out the differences in the active site residues of both PLA2s. The information enunciated from the analysis of CoMFA and CoMSIA maps and docking results were analyzed and employed in the design of 29 new ligands using molecules 4, 21, 22 from the initial set as templates. New ligands for group I and II secreted phospholipases A2 (sPLA2s) have been thus designed based on the 32 analogues of 1-aryl sulfamido-2-alkyl piperazine with a cursory note on its synthetic feasibility. Molecular modeling studies indicate that the newly designed ligands are expected to show high affinity and experimental efforts in this direction is highly rewarding.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heinrikson RL, Krueger ET, Keim PS (1977) Amino acid sequence of phospholipase A2-alpha from the venom of Crotalus adamanteus. A new classification of phospholipases A2 based upon structural determinants. J Biol Chem 252:4913–4921
Waite M (ed) (1987) The phospholipases in handbook of lipid research. Plenum, New York, pp 1–332
Valentin E, Lambeau G (2000) Increasing molecular diversity of secreted phospholipase A2 and their receptor and protein binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta — Mol Cell Bio Lip 1488:59–70
Dennis EA (1994) Diversity of group types, regulation, and function of phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem 269:13057–13060
Uhl W, Nevalainen TJ, Buchler MW (eds) (1997) Phospholipase A2: basic and clinical aspects in inflammatory diseases. Karger, Basel
Kovanen PT, Pentikainen MO (2000) Secretory group II phospholipase A2: a newly recognized acute-phase reactant with a role in atherogenesis. Circ Res 86:610–612
Forster S, Ilderton E, Norris JFB, Summerly R, Yardley HJ (1985) Characterization and activity of phospholipase A2 in normal human epidermis and in lesion-free epidermis of patients with psoriasis or eczema. Br J Dermatol 112:135–147
Minami T, Tojo H, Shinomura Y, Matsuzawa Y, Okamoto M (1994) Increased group II phospholipase A2 in colonic mucosa of patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut 35:1593–1598
Meyer MC, Rastogi P, Beckett CS, McHowat J (2005) Phospholipase A2 inhibitors as potential anti-inflammatory agents. Curr Pharm Des 11:1301–1312
Dong CZ, Himidi AA, Plocki S, Aoun D, Touaibia M, Habich NM, Huet J, Redeuilh C, Ombetta JE, Godfroid JJ, Massicota F, Heymans F (2005) Bioorg Med Chem 13:1989–2007
Jabeen T, Singh N, Singh RK, Sharma S, Somvanshi RK, Dey S, Singh TP (2005) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as potent inhibitors of phospholipase A2: structure of the complex of phospholipase A2 with niflumic acid at 2.5 angstroms resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 61:1579–1586
Muller P, Lena G, Boilard E, Bezzine S, Lambeau G, Guichard G, Rognan D (2006) In silico-guided target identification of a scaffold-focused library: 1, 3, 5-triazepan-2, 6-diones as novel phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J Med Chem 49:6768–6778
Dillard RD, Bach NJ, Draheim SE, Berry DR, Carlson DG, Chirgadze NY, Clawson DK, Hartley LW, Johnson LM, Jones ND, McKinney ER, Mihelich ED, Olkowski JL, Schevitz RW, Smith AC, Snyder DW, Sommers CD, Wery J-P (1996) Indole inhibitors of human nonpancreatic secretory phospholipase A2. 1. Indole-3-acetamides. J Med Chem 39:5119–5136
Dillard RD, Bach NJ, Draheim SE, Berry DR, Carlson DG, Chirgadze NY, Clawson DK, Hartley LW, Johnson LM, Jones ND, McKinney ER, Mihelich ED, Olkowski JL, Schevitz RW, Smith AC, Snyder DW, Sommers CD, Wery J-P (1996) Indole inhibitors of human nonpancreatic secretory phospholipase A2. 2. Indole-3-acetamides with additional functionality. J Med Chem 39:5137–5158
Draheim SE, Bach NJ, Dillard RD, Berry DR, Carlson DG, Chirgadze NY, Clawson DK, Hartley LW, Johnson LM, Jones ND, McKinney ER, Mihelich ED, Olkowski JL, Schevitz RW, Smith AC, Snyder DW, Sommers CD, Wery J-P (1996) Indole inhibitors of human nonpancreatic secretory phospholipase A2. 3. Indole-3-glyoxamides. J Med Chem 39:5159–5175
Bernard P, Pintore M, Berthon JY, Chretien JR (2001) A molecular modeling and 3D QSAR study of a large series of indole inhibitors of human non-pancreatic secretory phospholipase A2. Eur J Med Chem 36:1–19
Binisti C, Assogba L, Touboul E, Mounier C, Huet J, Ombetta JE, Dong CZ, Redeuilh C, Heymans F, Goldfroid JJ (2001) Structure—activity relationships in platelet-activating factor (PAF). 11-From PAF-antagonism to phospholipase A2 inhibition: syntheses and structure—activity relationships in 1-arylsulfamido-2-alkylpiperazines. Eur J Med Chem 36:809–828
Cramer RD, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J Med Chem 37:4130–4146
Vellarkad N, Viswanadhan VN, Ghose AK, Revenkar R, Robins RN (1989) Atomic physicochemical parameters for three dimensional structure directed quantitative structure-activity relationships. 4. Additional parameters for hydrophobic and dispersive interactions and their application for an automated superposition of certain naturally occurring nucleoside antibiotics. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 29:163–172
Srivani P, Kiran K, Sastry GN (2006) Understanding the structural requirements of triarylethane analogues towards PDE IV inhibitors: a molecular modeling study. Ind J Chem A 45A:68–76
Janardhan S, Srivani P, Sastry GN (2006) 2D and 3D quantitative structure-activity relationship studies on a series of bis-pyridinium compounds as choline kinase inhibitors. QSAR Comb Sci 25:860–872
Srivani P, Srinivas E, Raghu R, Sastry GN (2007) Molecular modeling studies of pyridopurinone derivatives — Potential phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors. J Mol Graph Model 26:378–390
Kulkarni RG, Srivani P, Achaiah G, Sastry GN (2007) Strategies to design of pyrazolyl urea derivatives for p38 kinase inhibition: a molecular modeling study. J Comput Aided Mol Design 25:155–166
Kulkarni RG, Achaiah G, Sastry GN (2008) Molecular modeling studies of phenoxypyrimidinyl imidazoles as p38 kinase inhibitors using QSAR and docking. Eur J Med Chem 43:830–838
Srivani P, Sastry GN (2009) Potential choline kinase inhibitors: a molecular modeling study of bis-quinolinium compounds. J Mol Graph Model 27:676–688
SYBYL 6.9. Molecular Modeling Software, Tripos Inc, 1699 Hanley Road, St Louis, MO 63144
Rarey M, Kramer B, Lengauer T, Klebe G (1996) A fast flexible docking method using an incremental construction algorithm. J Mol Biol 261:470–489
GOLD, version 2.1; Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre: Cambridge, UK
Jones G, Willet P, Glen RC, Leach AR, Taylor R (1997) Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J Mol Biol 267:727–748
Reddy AS, Priyadarshini PS, Kumar PP, Pradeep HN, Sastry GN (2007) Virtual screening in drug discovery — A computational perspective. Curr Prot Pept Sci 8:329–351
Jin ZM, Pan YJ, He L, Li ZG, Yu KB (2003) Crystal structure of the 1:2:2 adduct of piperazine, o-phthalic acid and water. Anal Sci 19:333–334
Coupar PI, Ferguson G, Glidewell C (1996) Piperazine-4, 4′-sulfonyldiphenol (1/2): a self-assembled channel structure. Acta Crystallogr 52:3052–3055
Wouters J, Haming L, Sheldrick G (1996) HEPES. Acta Crystallogr 52:1687–1688
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Alessandro P, Vistoli G, Gaillard P, Carrupt PA, Testa B, Boudon A (1994) Molecular lipophilicity potential, a tool in 3D QSAR: method and applications. J Comput Aided Mol Des 8:83–96
Accelrys Discovery Studio v2.1.0.8130
Acknowledgments
Department of Biotechnology (DBT), New Delhi is thanked for the financial support. DST is thanked for the women scientist award to PB and Swarnajayanthi Fellowship to GNS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 43 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badrinarayan, P., Srivani, P. & Narahari Sastry, G. Design of 1-arylsulfamido-2-alkylpiperazine derivatives as secreted PLA2 inhibitors. J Mol Model 17, 817–831 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0752-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0752-2