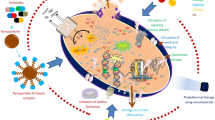
Abstract
Arsenic and its various forms have been in use in ancient Chinese medicine for more than 2000 years. Arsenicals have gained importance for having remedial effects for various diseases from syphilis to cancer thus highlighting its role as a therapeutic agent even though it has been labelled as a potential ‘poison’. The ability of arsenic, specifically arsenic trioxide, to treat acute promyelocytic leukaemia has radically changed the perception of this poison and has been the main factor for the re-emergence of this candidate to Western medicine for the treatment of leukaemia and other solid tumours. This review highlights the glorious history of arsenic and its various forms with major emphasis on arsenic trioxide as a therapeutic agent. The mechanism of action, pathogenesis, pharmacokinetic profile, safety concerns, ongoing clinical trials and various new forms of arsenic trioxide are discussed. The review also outlines the therapeutic ability of this drug, discusses the latest developments and recent investigations and potential advancement of arsenic trioxide as nanoformulations that has made it emerge as a potential remedial agent.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen CJ, Wang CJ (1990) Ecological correlation between arsenic level in well water and age-adjusted mortality from malignant neoplasms. Cancer Res 50:5470–5474
Waxman S, Anderson K (2001) History of the development of arsenic derivatives in cancer therapy. Oncologist 6:3–10
Gawkrodger DJ (2004) Occupational skin cancers. Occup Med 54(7):458–463
Miller WH, Schipper HM, Lee JS, Singer J, Waxman S (2002) Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res 62:3893–3903
Han BC, Jeng WL, Jeng MS, Kao LT, Meng PJ, Huang YL (1997) Rock-shells (Thais clavigera) as an indicator of As, Cu, and Zn contamination on the Putai coast of the black-foot disease area in Taiwan. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 32:456–461
Hernandez-Zavala A, Cordova E, Del Razo LM, Cebrian ME, Garrido E (2005) Effects of arsenite on cell cycle progression in a human bladder cancer cell line. Toxicology 207:49–57
Garrison FH (1921) An introduction to the history of medicine c, 2nd edn. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia
Frith J (2013) Arsenic—the “Poison of Kings” and the “Saviour of Syphilis”. J Milit Vet Health 21:11–17
Zhu Q, Deng Z, Zhu S, Zhao P, Wang M, Hu X (2017) Study on the clinical safe and effective methods of arsenic-containing compound-Qinghuang powder in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017:1–6 (Article ID 2095682)
Ding W, Zhang L, Kim S, Tian W, Tong Y, Liu J, Ma Y, Chen S (2015) Arsenic sulfide as a potential anti-cancer drug. Mol Med Rep 11:968–974
Chen B, Liu Q, Popowich A, Shen S, Yan X, Zhang Q, Li XF, Weinfeld M, Cullen WR, Le XC (2015) Therapeutic and analytical applications of arsenic binding to proteins. Metallomics 7:39–55
Hsu E (2001) Innovation in Chinese medicine. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Treleaven J, Meller S, Farmer P, Birchall D, Goldman J, Piller G (1993) Arsenic and ayurveda. Leukemia Lymphoma 10:343–345
Panda AK, Hazra J (2012) Arsenical compounds in ayurveda medicine: a prospective analysis. Int J Res Ayurveda Pharm 3:772–776
Haller JS (1975) Therapeutic mule: the use of arsenic in the nineteenth century material medica. Pharm Hist 17:87–100
Hughes MF, Beck BD, Chen Y, Lewis AS, Thomas DJ (2011) Arsenic exposure and toxicology: a historical perspective. Toxicol Sci 123:305–332
Forkner CE, Scott TFM (1931) Arsenic as a therapeutic agent in CML. JAMA 97:3–5
Doyle D (2009) Notoriety to respectability: a short history of arsenic prior to its present day use in haematology. Br J Haematol 145:309–317
Hu J, Fang J, Dong Y, Chen SJ, Chen Z (2005) Arsenic in cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 16:119–127
Gharde SR, Suryawanshi SS (2014) Physico-chemical study of arsenic trioxide (somal) before and after detoxification (shodhan). World J Pharm Pharm Sci 3:1711–1716
Kwong YL, Todd D (1997) Delicious poison: arsenic trioxide for the treatment of leukemia. Blood 89(9):3487–3488
Au WY, Kumana CR, Kou M, Mak R, Chan GC, Lam CW et al (2003) Oral arsenic trioxide in the treatment of relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood 102:407–408
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM, Qiu QY et al (1997) Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): II. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood 89:3354–3360
Kumana C, Au W, Lee N, Kou M, Mak R, Lam C et al (2002) Systemic availability of arsenic from oral arsenic-trioxide used to treat patients with hematological malignancies. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 58:521–526
Kwong YL (2004) Arsenic trioxide in the treatment of haematological malignancies. Expert Opin Drug Saf 3:589–597
Huang C, Ke Q, Costa M, Shi X (2004) Molecular mechanisms of arsenic carcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 255:57–66
Shi H, Shi X, Liu KJ (2004) Oxidative mechanism of arsenic toxicity and carcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 255:67–78
Corsini E, Asti L, Viviani B, Marinovich M, Galli CL (1999) Sodium arsenate induces overproduction of interleukin-1α in murine keratinocytes: role of mitochondria. J Invest Dermatol 113:760–765
Kondoh K, Torii S, Nishida E (2005) Control of MAP kinase signaling to the nucleus. Chromosoma 114:86–91
Rossman TG (2003) Mechanism of arsenic carcinogenesis: an integrated approach. Mutat Res Mol Mech Mutagen 533:37–65
Huang C, Ma WY, Li J, Goranson A, Dong Z (1999) Requirement of Erk, but not JNK, for arsenite-induced cell transformation. J Biol Chem 274:14595–14601
Yih LH, Lee TC (2003) Induction of C-anaphase and diplochromosome through dysregulation of spindle assembly checkpoint by sodium arsenite in human fibroblasts. Cancer Res 63:6680–6688
Lai YL, Chang HH, Huang MJ, Chang KH, Su WH, Chen HW et al (2003) Combined effect of topical arsenic trioxide and radiation therapy on skin-infiltrating lesions of breast cancer—a pilot study. Anticancer Drugs 14:825–828
Emadi A, Gore SD (2010) Arsenic trioxide—an old drug rediscovered. Blood Rev 24:191–199
Chen W, Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ, Liu Y (1998) Tumor promoter arsenite activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase through a signaling pathway mediated by epidermal growth factor receptor and Shc. Mol Cell Biol 18:5178–5188
Gupta S, Yel L, Kim D, Kim C, Chiplunkar S, Gollapudi S (2003) Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets by inducing oxidative stress: a role of Bcl-2. Mol CancerTher 2:711–719
Chen GQ, Zhu J, Shi XG, Ni JH, Zhong HJ, Si GY et al (1996) In vitro studies on cellular and molecular mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia: As2O3 induces NB4 cell apoptosis with downregulation of Bcl-2 expression and modulation of PML–RAR alpha/PML proteins. Blood 88:1052–1061
Zhu J, Lallemand-Breitenbach V, de Thé H (2001) Pathways of retinoic acid- or arsenic trioxide-induced PML/RARalpha catabolism, role of oncogene degradation in disease remission. Oncogene 20:7257–7265
Zhu J, Koken MH, Quignon F, Chelbi-Alix MK, Degos L, Wang ZY et al (1997) Arsenic-induced PML targeting onto nuclear bodies: implications for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94:3978–3983
Cheng HY, Li P, David M, Smithgall TE, Feng L, Lieberman MW (2004) Arsenic inhibition of the JAK–STAT pathway. Oncogene 23:3603–3612
Seol JG, Park WH, Kim ES, Jung CW, Hyun JM, Kim BK et al (1999) Effect of arsenic trioxide on cell cycle arrest in head and neck cancer cell line PCI-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265:400–404
Lew YS, Brown SL, Griffin RJ, Song CW, Kim JH (1999) Arsenic trioxide causes selective necrosis in solid murine tumors by vascular shutdown. Cancer Res 59:6033–6037
Soignet SL, Maslak P, Wang ZG, Jhanwar S, Calleja E, Dardashti LJ et al (1998) Complete remission after treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide. N Engl J Med 339:1341–1348
Chiu HW, Chen YA, Ho SY, Wang YJ (2012) Arsenic trioxide enhances the radiation sensitivity of androgen-dependent and-independent human prostate cancer cells. PLoS One 7:e31579
AkaoY Nakagawa Y, Akiyama K (1999) Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cell lines through the activation of caspase 3 in vitro. FEBS Lett 455:59–62
Maeda H, Hori S, Nishitoh H, Ichijo H, Ogawa O, Kakehi Y et al (2001) Tumor growth inhibition by arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the orthotopic metastasis model of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res 61:5432–5440
Chow SK, Chan JY, Fung KP (2004) Inhibition of cell proliferation and the action mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) on human breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 93:173–187
Degos L (2003) The history of acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 122:539–553
Hillestad LK (1957) Acute promyelocytc leukemia. Acta Med Scand 159:189–194
Rowley JD, Golomb HM, Dougherty C (1997) The 15–17 translocation: a consistent chromosomal change in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Lancet 1:549–550
Lo-Coco F, Cicconi L (2011) History of acute promyelocytic leukemia: a tale of endless revolution. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis 3:2011067
Castaigne S, Chomienne C, Daniel MT, Ballerini P, Berger R, Fenaux P et al (1990) All-trans retinoic acid as a differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. I. Clinical results. Blood 76:1704–1709
Warrell RP Jr, Frankel SR, Miller WH Jr, Scheinberg DA, Itri LM, Hittelman WN et al (1991) Differentiation therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia with tretinoin (all-trans-retinoic acid). N Engl J Med 324:1385–1393
de Thé H, Lavau C, Marchio A, Chomienne C, Degos L, Dejean A (1991) The PML–RARα fusion mRNA generated by the t(15;17) translocation in acute promyelocytic leukemia encodes a functionally altered RAR. Cell 66:675–684
Kakizuka A, Miller WH, Umesono K, Warrell RP, Frankel SR, Murty VVVS et al (1991) Chromosomal translocation t(15;17) in human acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses RARα with a novel putative transcription factor, PML. Cell 66:663–674
Lufkin T, Lohnes D, Mark M, Dierich A, Gorry P, Gaub MP et al (1993) High postnatal lethality and testis degeneration in retinoic acid receptor alpha mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:7225–7229
Koken MH, Puvion-Dutilleul F, Guillemin MC, Viron A, Linares-Cruz G, Stuurman N et al (1994) The t(15;17) translocation alters a nuclear body in a retinoic acid-reversible fashion. EMBO J 13:1073–1083
Wang ZY, Chen Z (2008) Acute promyelocytic leukemia: from highly fatal to highly curable. Blood 111:2505–2515
Sanz MA, Lo-Coco F (2011) Modern approaches to treating acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 29:495–503
Antman KH (2001) Introduction: the history of arsenic trioxide in cancer therapy. Oncologist 6:1–2
Munshi NC (2001) Arsenic trioxide: an emerging therapy for multiple myeloma. Oncologist 6:17–21
Dilda PJ, Hogg PJ (2007) Arsenical-based cancer drugs. Cancer Treat Rev 33:542–564
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M et al (2014) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136:E359–E386
Walker AM, Stevens JJ, Ndebele K, Tchounwou PB (2016) Evaluation of arsenic trioxide potential for lung cancer treatment: assessment of apoptotic mechanisms and oxidative damage. J Cancer Sci Ther 8:1
Ge-ping Q, Qing-Yu X, Bing L, Yong-an L, Ling-Zhen Z (2009) Arsenic trioxide inhibits the growth of human lung cancer cell lines via cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis at both normoxia and hypoxia. Toxicol Ind Health 25:505–515
Zheng CY, Lam SK, Li YY, Fong BMW, Mak JCW, Ho JCM (2013) Combination of arsenic trioxide and chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 82:222–230
Speiser J, Foreman K, Drinka E, Godellas C, Perez C, Salhadar A et al (2012) Notch-1 and Notch-4 biomarker expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Surg Pathol 20:137–143
Yao K, Rizzo P, Rajan P, Albain K, Rychlik K, Shah S (2011) Notch-1 and notch-4 receptors as prognostic markers in breast cancer. Int J Surg Pathol 19:607–613
Xia J, Li Y, Yang Q, Mei C, Chen Z, Bao B et al (2012) Arsenic trioxide inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis through inactivation of notch signaling pathway in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci 13:9627–9641
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Yang L, Cai B, Li J, Zhou Y et al (2011) Arsenic trioxide induces the apoptosis of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells through activation of caspase-3 and inhibition of HERG channels. Exp Ther Med 2:481–486
Sun RC, Board PG, Blackburn AC (2011) Targeting metabolism with arsenic trioxide and dichloroacetate in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer 10:1
Baj G, Arnulfo A, Deaglio S, Mallone R, Vigone A, De Cesaris MG et al (2002) Arsenic trioxide and breast cancer: analysis of the apoptotic, differentiative and immunomodulatory effects. Breast Cancer Res Treat 73:61–73
Uslu R, Sanli UA, Sezgin C, Karabulut B, Terzioglu E, Omay SB et al (2000) Arsenic trioxide-mediated cytotoxicity and apoptosis in prostate and ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 6:4957–4964
Zheng Y, Zhou M, Ye A, Li Q, Bai Y, Zhang Q (2010) The conformation change of Bcl-2 is involved in arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation in SGC7901 human gastric cancer cells. World J Surg Oncol 8(1):1
Xiao YF, Liu SX, Wu DD, Chen X, Ren LF (2006) Inhibitory effect of arsenic trioxide on angiogenesis and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 12:5780
Wen X, Li D, Zhang Y, Liu S, Ghali L, Iles RK (2012) Arsenic trioxide induces cervical cancer apoptosis, but specifically targets human papillomavirus-infected cell populations. Anticancer Drugs 23:280–287
Yu J, Qian H, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Liang X et al (2007) Therapeutic effect of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) on cervical cancer in vitro and in vivo through apoptosis induction. Cancer Biol Ther 6:580–586
Yu J, Qian H, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Liang X et al (2007) Arsenic trioxide (As2O3) reduces the invasive and metastatic properties of cervical cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Gynecol Oncol 106:400–406
Tong Q, Zeng F, Zheng L, Zhao J, Lu G (2001) Apoptosis inducing effects of arsenic trioxide on human bladder cancer cell line BIU-87. Chin Med J114:402–406
Cao Y, Yu SL, Wang Y, Guo GY, Ding Q, An RH (2011) MicroRNA-dependent regulation of PTEN after arsenic trioxide treatment in bladder cancer cell line T24. Tumor Biol 32:179–188
Li X, Ding X, Adrian TE (2003) Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells via changes in cell cycle, caspase activation, and GADD expression. Pancreas 27:174–179
Wang W, Adachi M, Zhang R, Zhou J, Zhu D (2009) A novel combination therapy with arsenic trioxide and parthenolide against pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas 38:e114–e123
Du CW, Wen BG, Li DR, Peng X, Hong CQ, Chen JY et al (2006) Arsenic trioxide reduces the invasive and metastatic properties of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in vitro. Braz J Med Biol Res 39:677–685
Zheng Y, Caiwen DU, Derui LI, Yingcheng LIN, Mingyao WU (2004) Arsenic trioxide induced differentiation and apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts in BALB/C nude mice. Chin German J Clin Oncol 3:151–155
Li DR, Lin YC, Xie LX, Du CW, Wu MY (2003) Arsenic trioxide enhances radiosensitivity in vitro of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Exp Oncol 25:248–251
Helm CW, States CJ (2009) Enhancing the efficacy of cisplatin in ovarian cancer treatment—could arsenic have a role. J Ovarian Res 2:1
Kong B, Huang S, Wang W, Ma D, Qu X, Jiang J et al (2005) Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Int J Gynecol Cancer 15:872–877
Zhang N, Wu ZM, McGowan E, Shi J, Hong ZB, Ding CW et al (2009) Arsenic trioxide and cisplatin synergism increase cytotoxicity in human ovarian cancer cells: therapeutic potential for ovarian cancer. Cancer Sci 100:2459–2464
Hirano S, Kobayashi Y, Cui X, Kanno S, Hayakawa T, Shraim A (2004) The accumulation and toxicity of methylated arsenicals in endothelial cells: important roles of thiol compounds. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:458–467
Sattar A, Xie S, Hafeez MA, Wang X, Hussain HI, Iqbal Z et al (2016) Metabolism and toxicity of arsenicals in mammals. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 48:214–224
Naranmandura H, Suzuki N, Suzuki KT (2006) Trivalent arsenicals are bound to proteins during reductive methylation. Chem Res Toxicol 19:1010–1018
Khairul I, Wang QQ, Jiang YH, Wang C, Naranmandura H (2017) Metabolism, toxicity and anticancer activities of arsenic compounds. Oncotarget 8:23905–23926
Wang Z, Zhou J, Lu X, Gong Z, Le XC (2004) Arsenic speciation in urine from acute promyelocytic leukemia patients undergoing arsenic trioxide treatment. Chem Res Toxicol 17:95–103
Chendamarai E, Ganesan S, Alex AA, Kamath V, Nair SC, Nellickal AJ et al (2015) Comparison of newly diagnosed and relapsed patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with arsenic trioxide: insight into mechanisms of resistance. PLoS One 10:e0121912
Mathews V, George B, Lakshmi KM, Viswabandya A, Bajel A, Balasubramanian P et al (2006) Single-agent arsenic trioxide in the treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia: durable remissions with minimal toxicity. Blood 107:2627–2632
Murgo AJ (2001) Clinical trials of arsenic trioxide in hematologic and solid tumors: overview of the National Cancer Institute Cooperative Research and Development Studies. Oncologist 6:22–28
Owonikoko TK, Zhang G, Kim HS, Stinson RM, Bechara R, Zhang C et al (2016) Patient-derived xenografts faithfully replicated clinical outcome in a phase II co-clinical trial of arsenic trioxide in relapsed small cell lung cancer. J Trans Med 14:111 [Clinical study no: NCT01470248 (Study of Arsenic Trioxide in Small Cell Lung Cancer)]
Qazilbash MH, Saliba RM, Nieto Y, Parikh G, Pelosini M, Khan FB et al (2008) Arsenic trioxide with ascorbic acid and high-dose melphalan: results of a phase II randomized trial. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 14:1401–1407 [Clinical study no: NCT00661544 (Arsenic Trioxide with Ascorbic Acid and Melphalan for Myeloma)]
Ehrlich P (1906) Collected studies on immunity. Wiley, Oxford
Pfizenmaier K, Nagel GA (1985) Monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 110:615–617
Nadler LM, Stashenko P, Hardy R, Kaplan WD, Button LN, Kufe DW et al (1980) Serotherapy of a patient with a monoclonal antibody directed against a human lymphoma-associated antigen. Cancer Res 40:3147–3154
Rosenberg SA, Terry WD (1977) Passive immunotherapy of cancer in animals and man. Adv Cancer Res 25:323–388
Dillman RO, Beauregard JC, Halpern SE, Clutter M (1986) Toxicities and side effects associated with intravenous infusions of murine monoclonal antibodies. J Immunother 5:73–84
Senter PD, Springer CJ (2001) Selective activation of anticancer prodrugs by monoclonal antibody–enzyme conjugates. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 53:247–264
Reubi JC, Schaer JC, Markwalder R, Waser B, Horisberger U, Laissue J (1997) Distribution of somatostatin receptors in normal and neoplastic human tissues: recent advances and potential relevance. Yale J Biol Med 70:471–479
Boerman OC, Oyen WJ, Corstens FH (2000) Radio-labeled receptor-binding peptides: a new class of radiopharmaceuticals. Semin Nucl Med 30:195–208
Katsuno T, Pradhan TK, Ryan RR, Mantey SA, Hou W, Donohue PJ et al (1999) Pharmacology and cell biology of the bombesin receptor subtype 4 (BB4-R). Biochemistry 38:7307–7320
Jensen RT, Moody T, Pert C, Rivier JE, Gardner JD (1978) Interaction of bombesin and litorin with specific membrane receptors on pancreatic acinar cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 75:6139–6143
Nanda PK, Lane SR, Retzloff LB, Pandey US, Smith CJ (2010) Radiolabeled regulatory peptides for imaging and therapy. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 17:69
McNeil SE (2005) Nanotechnology for the biologist. J Leukoc Biol 78:585–594
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mater 4:435–446
Åkerman ME, Chan WC, Laakkonen P, Bhatia SN, Ruoslahti E (2002) Nanocrystal targeting in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:12617–12621
Xiang SD, Selomulya C, Ho J, Apostolopoulos V, Plebanski M (2010) Delivery of DNA vaccines: an overview on the use of biodegradable polymeric and magnetic nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2:205–218
Plank C, Schillinger U, Scherer F, Bergemann C, Rémy JS, Krötz F et al (2003) The magnetofection method: using magnetic force to enhance gene delivery. Biol. Chem 384:737–747
Sun C, Lee JS, Zhang M (2008) Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1252–1265
Kaasgaard T, Andresen TL (2010) Liposomal cancer therapy: exploiting tumor characteristics. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7:225–243
Cho K, Wang XU, Nie S, Shin DM (2008) Therapeutic nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:1310–1316
Nie S, Xing Y, Kim GJ, Simons JW (2007) Nanotechnology applications in cancer. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 9:257–288
Mahmoud W, Sukhanova A, Oleinikov V, Rakovich YP, Donegan JF, Pluot M et al (2010) Emerging applications of fluorescent nanocrystals quantum dots for micrometastases detection. Proteomics 10:700–716
Batist G, Barton J, Chaikin P, Swenson C, Welles L (2002) Myocet (liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin citrate): a new approach in breast cancer therapy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 3:1739–1751
Cherukuri P, Curley SA (2010) Use of nanoparticles for targeted, noninvasive thermal destruction of malignant cells. Cancer nanotechnology: methods and protocols. Springer, Berlin, pp 359–373
Samia AC, Chen X, Burda C (2003) Semiconductor quantum dots for photodynamic therapy. J Am Chem Soc 125:15736–15737
Bakalova R, Ohba H, Zhelev Z, Ishikawa M, Baba Y (2004) Quantum dots as photosensitizers? Nat Biotechnol 22:1360–1361
Vyshnava SS, Kanderi DK, Panjala SP, Pandian K, Bontha RR, Goukanapalle PKR, Banaganapalli B (2016) Effect of silver nanoparticles against the formation of biofilm by Pseudomonas aeruginosa an in silico approach. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 180:426–437
Kang SG, Zhou G, Yang P, Liu Y, Sun B, Huynh T et al (2012) Molecular mechanism of pancreatic tumor metastasis inhibition by Gd@ C82 (OH) 22 and its implication for de novo design of nanomedicine. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:15431–15436
Yin JJ, Sharma S, Shumyak SP, Wang ZX, Zhou ZW, Zhang Y et al (2013) Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel folic acid receptor-targeted, β-cyclodextrin-based drug complexes for cancer treatment. PLoS One 8:e62289
Al-Khodairy FM, Khan MKA, Kunhi M, Pulicat MS, Akhtar S, Arif JM (2013) In Silico prediction of mechanism of Erysolin-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines. Am J Bioinf Res 3:62–71
Silviya AE, Kavitha G, Kutty KN, PK KN (2015) Insilico modeling of chitosan as a drug delivery system. Int J Drug Deliv 7:27–31
Farokhzad OC, Langer R (2009) Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano 3:16–20
Jadhav V, Sachar S, Chandra S, Bahadur D, Bhatt P (2016) Synthesis and characterization of arsenic trioxide nanoparticles and their In vitro cytotoxicity studies on mouse fibroblast and prostate cancer cell lines. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 16:7599–7605
Jadhav V, Ray P, Sachdeva G, Bhatt P (2016) Biocompatible arsenic trioxide nanoparticles induce cell cycle arrest by p21 WAF1/CIP1 expression via epigenetic remodeling in LNCaP and PC3 cell lines. Life Sci 148:41–52
Ahn RW, Chen F, Chen H, Stern ST, Clogston JD, Patri AK et al (2010) A novel nanoparticulate formulation of arsenic trioxide with enhanced therapeutic efficacy in a murine model of breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:3607–3617
Chen H, Ahn R, Van den Bossche J, Thompson DH, O’Halloran TV (2009) Folate-mediated intracellular drug delivery increases the anticancer efficacy of nanoparticulate formulation of arsenic trioxide. Mol Cancer Ther 8:1955–1963
Gortzi O, Papadimitriou E, Kontoyannis CG, Antimisiaris SG, Ioannou PV (2002) Arsonoliposomes, a novel class of arsenic-containing liposomes: effect of palmitoyl-arsonolipid-containing liposomes on the viability of cancer and normal cells in culture. Pharm Res 19:79–86
Wu X, Han Z, Schur RM, Lu ZR (2016) Targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticles delivering arsenic trioxide with environment sensitive drug release for effective treatment of triple negative breast cancer. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2:501–507
Zeng L, Li J, Wang Y, Qian C, Chen Y, Zhang Q et al (2014) Combination of siRNA-directed Kras oncogene silencing and arsenic-induced apoptosis using a nanomedicine strategy for the effective treatment of pancreatic cancer. Nanomed Nanotechnol 10:463–472
Fei W, Zhang Y, Han S, Tao J, Zheng H, Wei Y et al (2017) RGD conjugated liposome-hollow silica hybrid nanovehicles for targeted and controlled delivery of arsenic trioxide against hepatic carcinoma. Int J Pharm 519:250–262
Zhang Q, Vakili MR, Li XF, Lavasanifar A, Le XC (2016) Terpolymer micelles for the delivery of arsenic to breast cancer cells: the effect of chain sequence on polymeric micellar characteristics and cancer cell uptake. Mol Pharm 13:4021–4033
Zhu J, Chen Z, Lallemand-Breitenbach V, de Thé H (2002) How acute promyelocytic leukaemia revived arsenic. Nat Rev Cancer 2:705–714
Acknowledgements
Ms. Maneka Hoonjan is a recipient of the Senior Research Fellowship from the University Grants Commission-Maulana Azad National Fellowship for Minority (UGC-MANF), India, under the sanction number: MANF-2014-15-SIK-MAH-37834. The authors would like to thank Mr. Mitesh Joshi, NMIMS Sunandan Divatia School of Science for providing help with figure artwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoonjan, M., Jadhav, V. & Bhatt, P. Arsenic trioxide: insights into its evolution to an anticancer agent. J Biol Inorg Chem 23, 313–329 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-018-1537-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-018-1537-9