Abstract
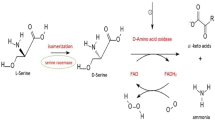
Since d-amino acids were identified in mammals, d-serine has been one of the most extensively studied “unnatural amino acids”. This brain-enriched transmitter-like molecule plays a pivotal role in the human central nervous system by modulating the activity of NMDA receptors. Physiological levels of d-serine are required for normal brain development and function; thus, any alterations in neuromodulator concentrations might result in NMDA receptor dysfunction, which is known to be involved in several pathological conditions, including neurodegeneration(s), epilepsy, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder. In the brain, the concentration of d-serine stored in cells is defined by the activity of two enzymes: serine racemase (responsible for both the synthesis and degradation) and d-amino acid oxidase (which catalyzes d-serine degradation). Both enzymes emerged recently as new potential therapeutic targets for NMDA receptor-related diseases. In this review we have focused on human d-amino acid oxidase and provide an extensive overview of the biochemical and structural properties of this flavoprotein and their functional significance. Furthermore, we discuss the mechanisms involved in modulating enzyme activity and stability with the aim to substantiate the pivotal role of d-amino acid oxidase in brain d-serine metabolism in physiological and pathological conditions and to highlight its great significance for novel drug design/development.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- BSN:
-
Bassoon protein
- CP:
-
Choroid plexus
- CPZ:
-
Chlorpromazine
- CBIO:
-
6-Chlorobenzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- DAAO:
-
d-Amino acid oxidase
- d-KYN:
-
d-Kynurenine
- DOPA:
-
3,4-Dihydroxy-phenylalanine
- ECFP:
-
Enhanced cyan fluorescent protein
- EYFP:
-
Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein
- FRET:
-
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- hDAAO:
-
Human d-amino acid oxidase
- KYNA:
-
Kynurenic acid
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate
- NMDAR:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate type glutamate receptor
- pkDAAO:
-
Porcine kidney d-amino acid oxidase
- PTS1:
-
Peroxisomal targeting signal 1
- RMSD:
-
Root-mean-square deviation
- SAP:
-
Structurally ambivalent peptide
- SPR:
-
Surface plasmon resonance
- SR:
-
Serine racemase
- T m :
-
Melting temperature
References
Adage T, Trillat AC, Quattropani A, Perrin D, Cavarec L, Shaw J, Guerassimenko O, Giachetti C, Greco B, Chumakov I, Halazy J, Roach A, Zaratin P (2008) In vitro and in vivo pharmacological profile of AS057278, a selective D-amino acid oxidase inhibitor with potential antipsychotic properties. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18:200–214
Almond SL, Fradley RL, Armstrong EJ, Heavens RB, Rutter AR, Newman RJ, Chiu CS, Konno R, Huston PH, Brandon NJ (2006) Behavioral and biochemical characterization of a mutant mouse strain lacking D-amino acid oxidase activity and its implications for schizophrenia. Mol Cell Neurosci 32:324–334
Arnold G, Liscum L, Holtzman E (1979) Ultrastructural localization of D-amino acid oxidase in microperoxisomes of the rat nervous system. J Histochem Cytochem 27:735–745
Banks WA, Kastin AJ (1991) Leucine modulates peptide transport system-1 across the blood-brain barrier at the stereospecific site within the central nervous system. J Pharm Pharmacol 43:252–254
Bendikov I, Nadri C, Amar S, Panizzutti R, De Miranda J, Wolosker H, Agam G (2007) A CSF and postmortem brain study of d-serine metabolic parameters in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 90:41–51
Benzel I, Kew JN, Viknaraja R, Kelly F, de Belleroche J, Hirsch S, Sanderson TH, Maycox PR (2008) Investigation of G72 (DAOA) expression in the human brain. BMC Psychiatry 11:8–94
Billard JM (2008) d-serine signalling as a prominent determinant of neuronal-glial dialogue in the healthy and diseased brain. J Cell Mol Med 12:1872–1884
Burnet PW, Eastwood SL, Bristow GC, Godlewska BR, Sikka P, Walker M, Harrison PJ (2008) D-amino acid oxidase activity and expression are increased in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatr 13:658–660
Caldinelli L, Molla G, Sacchi S, Pilone MS, Pollegioni L (2009) Relevance of weak flavin binding in human D-amino acid oxidase. Protein Sci 18:801–810
Caldinelli L, Molla G, Bracci L, Lelli B, Pileri S, Cappelletti P, Sacchi S, Pollegioni L (2010) Effect of ligand binding on human D-amino acid oxidase: implications for the development of new drugs for schizophrenia treatment. Protein Sci 19:1500–1512
Chatterton JE, Awobuluyi M, Premkumar LS, Takahashi H, Talantova M, Shin Y, Cui J, Tu S, Sevarino KA, Nakanishi N, Tong G, Lipton SA, Zhang D (2002) Excitatory glycine receptors containing the NR3 family of NMDA receptor subunits. Nature 415:793–798
Chen FC, Li WH (2001) Genomic divergences between humans and other hominoids and the effective population size on the common ancestor of humans and chimpanzee. Am J Hum Genet 68:444–456
Chumakov I, Blumenfeld M, Guerassimenko O, Cavarec L, Palicio M, Abderrahim H, Bougueleret L, Barry C, Tanaka H, La Rosa P, Puech A, Tahri N, Cohen-Akenine A, Delabrosse S, Lissarrague S, Picard FP, Maurice K, Essioux L, Millasseau P, Grel P, Debailleul V, Simon AM, Caterina D, Dufaure I, Malekzadeh K, Belova M, Luan JJ, Bouillot M, Sambucy JL, Primas G, Saumier M, Boubkiri N, Martin-Saumier S, Nasroune M, Peixoto H, Delaye A, Pinchot V, Bastucci M, Guillou S, Chevillon M, Sainz-Fuertes R, Meguenni S, Aurich-Costa J, Cherif D, Gimalac A, Van Duijn C, Gauvreau D, Ouellette G, Fortier I, Raelson J, Sherbatich T, Riazanskaia N, Rogaev E, Raeymaekers P, Aerssens J, Konings F, Luyten W, Macciardi F, Sham PC, Straub RE, Weinberger DR, Cohen N, Cohen D (2002) Genetic and physiological data implicating the new human gene G72 and the gene for D-amino acid oxidase in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13675–13680
Coyle JT (2006) Glutamate and schizophrenia: beyond the dopamine hypothesis. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:365–384
Conti P, Tamborini L, Pinto A, Blondel A, Minoprio P, Mozzarelli A, De Micheli C (2011) Drug discovery targeting amino acid racemase. Chem Rev 111:6919–6946
Curti B, Ronchi S, Simonetta PM (1992) In: Muller F (ed) Chemistry and Biochemistry of Flavoenzyme. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 69–94
Ding X, Ma N, Nagahama M, Yamada K, Semba R (2011) Localization of d-serine and serine racemase in neurons and neuroglias in mouse brain. Neurol Sci 32:263–267
Duplantier AJ, Becker SL, Bohanon MJ, Borzilleri KA, Chrunyk BA, Downs JT, Hu LY, El-Kattan A, James LC, Liu S, Lu J, Maklad N, Mansour MN, Mente S, Piotrowski MA, Sakya SM, Sheehan S, Steyn SJ, Strick CA, Williams VA, Zhang L (2009) Discovery, SAR, and pharmacokinetics of a novel 3-hydroxyquinolin-2(1H)-one series of potent D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitors. J Med Chem 52:3576–3585
Fernandez HH, Odin P (2011) Levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel for treatment of advanced Parkinson’s disease. Curr Med Res Opin 27:907–919
Ferraris D, Duvall B, Ko YS, Thomas AG, Rojas C, Majer P, Hashimoto K, Tsukamoto T (2008) Synthesis and biological evaluation of D-amino acid oxidase inhibitors. J Med Chem 51:3357–3359
Foltyn VN, Bendikov I, De Miranda J, Panizzutti R, Dumin E, Shleper M, Li P, Toney MD, Kartvelishvily E, Wolosker H (2005) Serine racemase modulates intracellular d-serine levels through an alpha, beta-elimination activity. J Biol Chem 280:1754–1763
Fonda ML, Anderson BM (1968) D-Amino acid oxidase-II Studies of substrate-competitive inhibitors. J Biol Chem 243:1931–1935
Frattini LF, Piubelli L, Sacchi S, Molla G, Pollegioni L (2011) Is rat an appropriate animal model to study the involvement of d-serine catabolism in schizophrenia? Insights from characterization of D-amino acid oxidase. FEBS J 278:4362–4373
Fuchs SA, Berger R, de Koning TJ (2011) d-serine: the right or wrong isoform? Brain Res 1401:104–117
Fukushima T, Sone Y, Mitsuhashi S, Tomiya M, Toyo’oka T (2009) Alteration of kynurenic acid concentration in rat plasma following optically pure kynurenine administration: a comparative study between enantiomers. Chirality 21:468–472
Ganong AH, Lanthorn TH, Cotman CW (1983) Kynurenic acid inhibits synaptic and acidic amino acid-induced responses in the rat hippocampus and spinal cord. Brain Res 273:170–174
Gao J, Kelly JW (2008) Toward quantification of protein backbone–backbone hydrogen bonding energies: an energetic analysis of an amide-to-ester mutation in an alpha-helix within a protein. Protein Sci 17:1096–1101
Garner CC, Kindler S, Gundelfinger ED (2000) Molecular determinants of presynaptic active zones. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10:321–327
Gong XQ, Zabek RL, Bai D (2007) d-Serine inhibits AMPA receptor-mediated current in rat hippocampal neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 85:546–555
Hamase K, Homma H, Takigawa Y, Fukushima T, Santa T, Imai K (1997) Regional distribution and postnatal changes of D-amino acids in rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1334:214–222
Hamasu K, Shigemi K, Tsuneyoshi Y, Yamane H, Sato H, Denbow DM, Furuse M (2008) Intracerebroventricular injection of l-proline and d-proline induces sedative and hypnotic effects by different mechanisms under an acute stressful condition in chicks. Amino Acids 38:57–64
Harris CM, Molla G, Pilone MS, Pollegioni L (1999) Studies on the reaction mechanism of Rhodotorula gracilis D-amino-acid oxidase. Role of the highly conserved Tyr-223 on substrate binding and catalysis. J Biol Chem 274:36233–36240
Harris CM, Pollegioni L, Ghisla S (2001) pH and kinetic isotope effects in D-amino acid oxidase catalysis. Eur J Biochem 268:5504–5520
Hansen KB, Naur P, Kurtkaya NL, Kristensen AS, Gajhede M, Kastrup JS, Gajhede M, Kastrup JS, Traynelis SF (2009) Modulation of the dimer interface at ionotropic glutamate-like receptor δ2 by d-serine and extracellular calcium. J Neurosci 29:907–917
Hashimoto A, Kumashiro S, Nishikawa T, Oka T, Takahashi K, Mito T, Takashima S, Doi N, Mizutani Y, Yamazaki T, Kaneko T, Ootomo E (1993) Embryonic development and postnatal changes in free D-aspartate and d-serine in the human prefrontal cortex. J Neurochem 61:348–351
Hashimoto A, Oka T, Nishikawa T (1995) Anatomical distribution and postnatal changes in endogenous free D-aspartate and d-serine in rat brain and periphery. Eur J Neurosci 7:1657–1663
Hashimoto K, Fukushima T, Shimizu E, Komatsu N, Watanabe H, Shinoda N, Nakazato M, Kumakiri C, Okada S, Hasegawa H, Imai K, Iyo M (2003) Decreased serum levels of d-serine in patients with schizophrenia: evidence in support of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor hypofunction hypothesis of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:572–576
Hashimoto A, Yoshikawa M, Niwa A, Konno R (2005) Mice lacking D-amino acid oxidase activity display marked attenuation of stereotypy and ataxia induced by MK-801. Brain Res 1033:210–215
Heresco-Levy U, Javitt DC, Ebstein R, Vass A, Lichtenberg P, Bar G, Catinari S, Ermilov M (2005) d-serine efficacy as add-on pharmacotherapy to risperidone and olanzapine for treatment-refractory schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 57:577–585
Holtze M, Asp L, Schwieler L, Engberg G, Karlsson H (2008) Induction of the kynurenine pathway by neurotropic influenza A virus infection. J Neurosci Res 86:3674–3683
Horiike K, Tojo H, Arai R, Nozaki M, Maeda T (1994) D-amino-acid oxidase is confined to the lower brain stem and cerebellum in rat brain: regional differentiation of astrocytes. Brain Res 652:297–303
Inoue T, Hamase K, Morikawa A, Zaitsu K (2000) Determination of minute amounts of d-leucine in various brain regions of rat and mouse using column-switching high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 744:213–219
Ishii K, Ogaya T, Song Z, Iizuka H, Fukushima T (2010) Changes in the plasma concentrations of D-kynurenine and kynurenic acid in rats after intraperitoneal administration of tryptophan enantiomers. Chirality 22:901–906
Iwana S, Kawazoe T, Park HK, Tsuchiya K, Ono K, Yorita K, Sakai T, Kusumi T, Fukui K (2008) Chlorpromazine oligomer is a potentially active substance that inhibits human D-amino acid oxidase, product of a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 23:901–911
Kapoor R, Lim KS, Cheng A, Garrick T, Kapoor V (2006) Preliminary evidence for a link between schizophrenia and NMDA-glycine site receptor ligand metabolic enzymes, d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) and kynurenine aminotransferase-1 (KAT-1). Brain Res 1106:205–210
Kartvelishvily E, Shleper M, Balan L, Dumin E, Wolosker H (2006) Neuron-derived d-serine release provides a novel means to activate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Biol Chem 281:14151–14162
Kawazoe T, Tsuge H, Pilone MS, Fukui K (2006) Crystal structure of human D-amino acid oxidase: context-dependent variability of the backbone conformation of the VAAGL hydrophobic stretch located at the si-face of the flavin ring. Protein Sci 15:2708–2717
Kawazoe T, Tsuge H, Imagawa T, Aki K, Kuramitsu S, Fukui K (2007) Structural basis of D-DOPA oxidation by D-amino acid oxidase: alternative pathway for dopamine biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 355:385–391
Kvajo M, Dhilla A, Swor DE, Karayiorgou M, Gogos JA (2008) Evidence implicating the candidate schizophrenia/bipolar disorder susceptibility gene G72 in mitochondrial function. Mol Psychiatry 13:685–696
Kessler M, Terramani T, Lynch G, Baudry M (1989) A glycine site associated with N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptors: characterization and identification of a new class of antagonists. J Neurochem 52:1319–1328
Konno R, Yasumura Y (1983) Mouse mutant deficient in D-amino acid oxidase activity. Genetics 103:277–285
Konno R, Sasaki M, Asakura S, Fukui K, Enami J, Niwa A (1997) D-amino-acid oxidase is not present in the mouse liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 1335:173–181
Korostishevsky M, Kaganovich M, Cholostoy S, Ashkenazy M, Ratner Y, Dahary D, Bernstein J, Bening-Abu-Shach U, Ben-Asher E, Lancet D, Ritsner M, Navon R (2004) Is the G72/G30 locus associated with schizophrenia? Single nucleotide polymorphism, haplotypes, and gene expression analysis. Biol Psychiatry 56:169–176
Krebs HA (1935) Metabolism of amino-acids: deamination of amino acids. Biochem J 29:1620–1644
Labrie V, Roder JC (2010) The involvement of the NMDA receptor d-serine/glycine site in the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34:351–372
Lange JH, Venhorst J, van Dongen MJ, Frankena J, Bassissi F, de Bruin NM, den Besten C, de Beer SB, Oostenbrink C, Markova N, Kruse CG (2011) Biophysical and physicochemical methods differentiate highly ligand-efficient human D-amino acid oxidase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 46:4808–4819
Lu M, Fan Y, Tang M, Qian X, Ding J, Hu G (2011) Potentiation of d-serine involves degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in MPTP/p mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 17:796–798
Lugo-Huitrón R, Blanco-Ayala T, Ugalde-Muñiz P, Carrillo-Mora P, Pedraza-Chaverrí J, Silva-Adaya D, Maldonado PD, Torres I, Pinzón E, Ortiz-Islas E, López T, García E, Pineda B, Torres-Ramos M, Santamaría A, La Cruz VP (2011) On the antioxidant properties of kynurenic acid: free radical scavenging activity and inhibition of oxidative stress. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:538–547
Madeira C, Freitas ME, Vargas-Lopes C, Wolosker H, Panizzutti R (2008) Increased brain D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) activity in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 101:76–83
Maekawa M, Watanabe M, Yamaguchi S, Konno R, Hori Y (2005) Spatial learning and long-term potentiation of mutant mice lacking D-amino-acid oxidase. Neurosci Res 53:34–38
Martineau M, Baux G, Mothet JP (2006) d-serine signalling in the brain: friend and foe. Trends Neurosci 29:481–491
Mattevi A, Vanoni MA, Todone F, Rizzi M, Teplyakov A, Coda A, Bolognesi M, Curti B (1996) Crystal structure of D-amino acid oxidase: a case of active site mirror-image convergent evolution with flavocytochrome b2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7496–7501
Mitchell J, Paul P, Chen HJ, Morris A, Payling M, Falchi M, Habgood J, Panoutsou S, Winkler S, Tisato V, Hajitou A, Smith B, Vance C, Shaw C, Mazarakis ND, de Belleroche J (2010) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is associated with a mutation in D-amino acid oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:7556–7561
Molla G, Porrini D, Job V, Motteran L, Vegezzi C, Campaner S, Pilone MS, Pollegioni L (2000) Role of arginine 285 in the active site of Rhodotorula gracilis D-amino acid oxidase. A site-directed mutagenesis study. J Biol Chem 275:24715–24721
Molla G, Sacchi S, Bernasconi M, Pilone MS, Fukui K, Pollegioni L (2006a) Characterization of human D-amino acid oxidase. FEBS Lett 580:2358–2364
Molla G, Bernasconi M, Sacchi S, Pilone MS, Pollegioni L (2006b) Expression in Escherichia coli and in vitro refolding of the human protein pLG72. Protein Expr Purif 46:150–155
Moreno S, Nardacci R, Cimini A, Cerù MP (1999) Immunocytochemical localization of D-amino acid oxidase in rat brain. J Neurocytol 28:169–185
Morikawa A, Hamase K, Zaitsu K (2003) Determination of d-alanine in the rat central nervous system and periphery using column-switching high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 312:66–72
Mothet JP, Parent AT, Wolosker H, Brady RO Jr, Linden DJ, Ferris CD, Rogawsky MA, Snyder SH (2000) d-serine is an endogenous ligand for the glycine site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4926–4931
Mustafa AK, Ahmad AS, Zeynalov E, Gazi SK, Sikka G, Ehmsen JT, Barrow RK, Coyle JT, Snyder SH, Doré S (2010) Serine racemase deletion protects against cerebral ischemia and excitotoxicity. J Neurosci 30:1413–1416
Nagata Y, Yamamoto K, Shimojo T, Konno R, Yasumura Y, Akino T (1992) The presence of free d-alanine, d-proline and d-serine in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1115:208–211
Nagata Y, Horiike K, Maeda T (1994) Distribution of free d-serine in vertebrate brains. Brain Res 634:291–295
Neims AH, Zieverink WD, Smilack JD (1966) Distribution of D-amino acid oxidase in bovine and human nervous tissues. J Neurochem 13:163–168
Ono K, Shishido Y, Park HK, Kawazoe T, Iwana S, Chung SP, Abou El-Magd RM, Yorita K, Okano M, Watanabe T, Sano N, Bando Y, Arima K, Sakai T, Fukui K (2009) Potential pathophysiological role of D-amino acid oxidase in schizophrenia: immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization study of the expression in human and rat brain. J Neural Transm 116:1335–1347
Otte DM, Bilkei-Gorzo A, Filiou MD, Turck CW, Ylmaz O, Holst MI, Schilling K, Abou-Jamra R, Schumacher J, Benzel I, Kunz WS, Beck H, Zimmer A (2009) Behavioral changes in G72/G30 transgenic mice. Eur Neuropharmacol 19:339–348
Owald D, Sigrist SJ (2009) Assembling the presynaptic active zone. Curr Opin Neurobiol 19:311–318
Panatier A, Theodosis DT, Mothet JP, Touquet B, Pollegioni L, Poulain DA, Oliet SH (2006) Glia-derived d-serine controls NMDA receptor activity and synaptic memory. Cell 125:775–784
Pérez-de la Cruz V, Amori L, Sathyasaikumar KV, Wang XD, Notarangelo FM, Wu HQ, Schwarcz R (2012) Enzymatic transamination of D-kynurenine generates kynurenic acid in rat and human brain. J Neurochem (ahead of print)
Perkins MN, Stone TW (1982) An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res 247:184–187
Pilone MS, Pollegioni L, Casalin P, Curti B, Ronchi S (1989) Properties of D-amino-acid oxidase from Rhodotorula gracilis. Eur J Biochem 180:199–204
Pilone MS (2000) D-Amino acid oxidase: new findings. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:1732–1747
Pollegioni L, Butò S, Tischer W, Ghisla S, Pilone MS (1993) Characterization of D-amino acid oxidase from Trigonopsis variabilis. Biochem Mol Biol Int 31:709–717
Pollegioni L, Diederichs K, Molla G, Umhau S, Welte W, Ghisla S, Pilone MS (2002) Yeast D-amino acid oxidase: structural basis of its catalytic properties. J Mol Biol 324:535–546
Pollegioni L, Piubelli L, Sacchi S, Pilone MS, Molla G (2007a) Physiological functions of D-amino acid oxidases: from yeast to humans. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1373–1394
Pollegioni L, Sacchi S, Caldinelli L, Boselli A, Pilone MS, Piubelli L, Molla G (2007b) Engineering the properties of D-amino acid oxidases by a rational and a directed evolution approach. Curr Protein Pept Sci 8:600–618
Pollegioni L, Sacchi S (2010) Metabolism of the neuromodulator d-serine. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:2387–2404
Popiolek M, Ross JF, Charych E, Chanda P, Gundelfinger ED, Moss SJ, Brandon NJ, Pausch MH (2011) D-amino acid oxidase activity is inhibited by an interaction with bassoon protein at the presynaptic active zone. J Biol Chem 286:28867–28875
Porter DJ, Voet JG, Bright HJ (1977) Mechanistic features of the D-amino acid oxidase reaction studied by double stopped flow spectrophotometry. J Biol Chem 252:4464–4473
Puyal J, Martineau M, Mothet JP, Nicolas MT, Raymond J (2006) Changes in d-serine levels and localization during postnatal development of the rat vestibular nuclei. J Comp Neurol 497:610–621
Raibekas AA, Fukui K, Massey V (2000) Design and properties of human D-amino acid oxidase with covalently attached flavin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3089–3093
Redzic ZB, Segal MB (2004) The structure of the choroid plexus and the physiology of the choroid plexus epithelium. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56:1695–1716
Romano D, Molla G, Pollegioni L, Marinelli F (2009) Optimization of human D-amino acid oxidase expression in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 68:72–78
Rosenberg D, Kartvelishvily E, Shleper M, Klinker CM, Bowser MT, Wolosker H (2010) Neuronal release of d-serine: a physiological pathway controlling extracellular d-serine concentration. FASEB J 24:2951–2961
Ross CA, Margolis RL, Reading SA, Pletnikov M, Coyle JT (2006) Neurobiology of schizophrenia. Neuron 52:139–153
Rossi DJ, Brady JD, Mohr C (2007) Astrocyte metabolism and signaling during brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci 10:1377–1386
Sacchi S, Lorenzi S, Molla G, Pilone MS, Rossetti C, Pollegioni L (2002) Engineering the substrate specificity of D-amino-acid oxidase. J Biol Chem 277:27510–27516
Sacchi S, Bernasconi M, Martineau M, Mothet JP, Ruzzene M, Pilone MS, Pollegioni L, Molla G (2008) pLG72 modulates intracellular d-serine levels through its interaction with D-amino acid oxidase: effect on schizophrenia susceptibility. J Biol Chem 283:22244–22256
Sacchi S, Cappelletti P, Giovannardi S, Pollegioni L (2011) Evidence for the interaction of D-amino acid oxidase with pLG72 in a glial cell line. Mol Cell Neurosci 48:20–28
Sacchi S, Rosini E, Pollegioni L, Molla G (2012) D-amino acid oxidase as a novel class of drug for schizophrenia therapy. Curr Pharm Design (ahead of print)
Saitoh Y, Katane M, Kawata T, Maeda K, Sekine M, Furuchi T, Kobuna H, Sakamoto T, Inoue T, Arai H, Nakagawa Y, Homma H (2012) Spatiotemporal localization of D-amino acid oxidase and D-aspartate oxidases during development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol 32:1967–1983
Sasabe J, Chiba T, Yamada M, Okamoto K, Nishimoto I, Matsuoka M, Aiso S (2007) d-serine is a key determinant of glutamate toxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EMBO J 26:4149–4159
Sasabe J, Miyoshi Y, Suzuki M, Mita M, Konno R, Matsuoka M, Hamase K, Aiso S (2012) D-amino acid oxidase controls motoneuron degeneration through d-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:627–632
Sasaki M, Konno R, Nishio M, Niwa A, Yasumura Y, Enami J (1992) A single-base-pair substitution abolishes D-amino-acid oxidase activity in the mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta 1139:315–318
Schell MJ, Brady RO Jr, Molliver ME, Snyder SH (1997) d-serine as a neuromodulator: regional and developmental localizations in rat brain glia resemble NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 17:1604–1615
Sinnokrot MO, Valeev EF, Sherrill CD (2002) Estimates of the ab initio limit for pi–pi interactions: the benzene dimer. J Am Chem Soc 124:10887–10893
Smith SM, Uslaner JM, Yao L, Mullins CM, Surles NO, Huszar SL, McNaughton CH, Pascarella DM, Kandebo M, Hinchliffe RM, Sparey T, Brandon NJ, Jones B, Venkatraman S, Young MB, Sachs N, Jacobson MA, Hutson PH (2009) The behavioral and neurochemical effects of a novel D-amino acid oxidase inhibitor compound 8 [4H-thieno [3,2-b]pyrrole-5-carboxylic acid] and d-serine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:921–930
Snyder SH, Kim PM (2000) D-amino acids as putative neurotransmitters: focus on d-serine. Neurochem Res 25:553–560
Song Y, Feng Y, Lu X, Zhao S, Liu CW, Liu YM (2008) D-Amino acids in rat brain measured by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Neurosci Lett 445:53–57
Sparey T, Abeywickrema P, Almond S, Brandon N, Byrne N, Campbell A, Hutson PH, Jacobson M, Jones B, Munshi S, Pascarella D, Pike A, Prasad GS, Sachs N, Sakatis M, Sardana V, Venkatraman S, Young MB (2008) The discovery of fused pyrrole carboxylic acids as novel, potent D-amino acid oxidase (DAO) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:3386–3391
Stevens ER, Esguerra M, Kim PM, Newman EA, Snyder SH, Zahs KR, Miller RF (2003) d-serine and serine racemase are present in the vertebrate retina and contribute to the physiological activation of NMDA receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6789–6794
Strohmaier J, Georgi A, Schirmbeck F, Schmael C, Jamra RA, Schumacher J, Becker T, Hofels S, Klopp N, Illig T, Propping P, Cichon S, Nothen MM, Rietschell M, Shulze TG (2007) No association between the serine racemase gene (SRR) and schizophrenia in a German case-control sample. Psychiatr Genet 17:125
Takarada T, Takahata Y, Iemata M, Hinoi E, Uno K, Hirai T, Yamamoto T, Yoneda Y (2009) Interference with cellular differentiation by d-serine through antagonism at N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors composed of NR1and NR3A subunits in chondrocytes. J Cell Physiol 22:756–764
Tsai G, Yang P, Chung LC, Lange N, Coyle JT (1998) d-serine added to antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 44:1081–1089
Umhau S, Pollegioni L, Molla G, Diederichs K, Welte W, Pilone MS, Ghisla S (2000) The x-ray structure of D-amino acid oxidase at very high resolution identifies the chemical mechanism of flavin-dependent substrate dehydrogenation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12463–12468
Verrall L, Walker M, Rawlings N, Benzel I, Kew JN, Harrison PJ, Burnet PW (2007) D-Amino acid oxidase and serine racemase in human brain: normal distribution and altered expression in schizophrenia. Eur J Neurosci 26:1657–1669
Verrall L, Burnet PW, Betts JF, Harrison PJ (2010) The neurobiology of D-amino acid oxidase and its involvement in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 15:122–137
Weimar WR, Neims AH (1977) The development of D-amino acid oxidase in rat cerebellum. J Neurochem 29:649–656
Williams SM, Diaz CM, Macnab LT, Sullivan RK, Pow DV (2006) Immunocytochemical analysis of d-serine distribution in the mammalian brain reveals novel anatomical compartmentalizations in glia and neurons. Glia 53:401–411
Wolosker H, Sheth KN, Takahashi M, Mothet JP, Brady RO Jr, Ferris CD, Snyder SH (1999a) Purification of serine racemase: biosynthesis of the neuromodulator d-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:721–725
Wolosker H, Blackshaw S, Snyder SH (1999b) Serine racemase: a glial enzyme synthesizing d-serine to regulate glutamate-N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotransmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13409–13414
Wolosker H, Dumin E, Balan L, Foltyn VN (2008) D-amino acids in the brain: d-serine in neurotransmission and neurodegeneration. FEBS J 275:3514–3526
Yamada K, Ohnishi T, Hashimoto K, Ohba A, Iwayama-Shigeno Y, Toyoshima M, Okuno A, Takao H, Toyota T, Minabe Y, Nakamura K, Shimizu E, Itokawa M, Mori N, Iyo M, Yoshikawa T (2005) Identification of multiple serine racemase (SRR) mRNA isoforms and genetic analyses of SRR and DAO in schizophrenia and d-serine levels. Biol Psychiatry 57:1493–1503
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Fondo di Ateneo per la Ricerca to L. Pollegioni, S. Sacchi and G. Molla. We are grateful for the support from Consorzio Interuniversitario per le Biotecnologie and Centro Grandi Attrezzature, Università degli studi dell’Insubria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sacchi, S., Caldinelli, L., Cappelletti, P. et al. Structure–function relationships in human d-amino acid oxidase. Amino Acids 43, 1833–1850 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1345-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1345-4