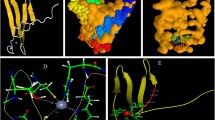
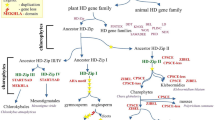
Abstract
The recent advancements in sequencing technologies and informatic tools promoted a paradigm shift to decipher the hidden biological mysteries and transformed the biological issues into digital data to express both qualitative and quantitative forms. The transcriptomic approach, in particular, has added new dimensions to the versatile essence of plant genomics through the large and deep transcripts generated in the process. This has enabled the mining of super families from the sequenced plants, both model and non-model, understanding their ancestry, diversity, and evolution. The elucidation of the crystal structure of the WRKY proteins and recent advancement in computational prediction through homology modeling and molecular dynamic simulation has provided an insight into the DNA–protein complex formation, stability, and interaction, thereby giving a new dimension in understanding the WRKY regulation. The present review summarizes the functional aspects of the high volume of sequence data of WRKY transcription factors studied from different species, till date. The review focuses on the dynamics of structural classification and lineage in light of the recent information. Additionally, a comparative analysis approach was incorporated to understand the functions of the identified WRKY transcription factors subjected to abiotic (heat, cold, salinity, senescence, dark, wounding, UV, and carbon starvation) stresses as revealed through various sets of studies on different plant species. The review will be instrumental in understanding the events of evolution and the importance of WRKY TFs under the threat of climate change, considering the new scientific evidences to propose a fresh perspective.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aamir M, Singh VK, Meena M, Upadhyay RS, Gupta VK, Singh S (2017) Structural and functional insights into WRKY3 and WRKY4 transcription factors to unravel the WRKY-DNA (W-Box) complex interaction in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). A computational approach. Front Plant Sci 8:819. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00819
Aguayo P, Lagos C, Conejera D, Medina D, Fernandez M, Valenzuela S (2019) Transcriptome-wide identification of WRKY family genes and their expression under cold acclimation in Eucalyptus globulus. Trees 33:1313–1327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-019-01860-3
Asseng S, Ewert F, Martre P et al (2015) Rising temperatures reduce global wheat production. Nature Clim Change 5:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2470
Ayadi M, Rim M, Ayed RB, Kharrat N, Merchaoui H, Rebai A, Hanana M (2019) Genome-wide identification and molecular characterization of Citrus unshiu WRKY transcription factors in Satsuma mandarin: clues for putative involvement in cell growth, fruit ripening, and stress response.Turk J Agric For 43:209–231. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1803-36
Baillo EH, Kimotho RN, Zhang Z, Xu P (2019) Transcription factors associated with abiotic and biotic stress tolerance and their potential for crops improvement. Genes 10:771. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100771
Baillo EH, Hanif MS, Guo Y, Zhang Z, Xu P, Algam SA (2020) Genome-wide Identification of WRKY transcription factor family members in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) moench). PloS One 15:e0236651. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0236651
Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2015) WRKY proteins: signaling and regulation of expression during abiotic stress responses. Sci World J 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/807560
Bankaji I, Sleimi N, Vives-Peris V, Gomez-Cadenas A, Perez-Clemente RM (2019) Identification and expression of the Cucurbita WRKY transcription factors in response to water deficit and salt stress. Sci Hortic 256:108562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108562
Bao W, Wang X, Chen M, Chai T, Wang H (2018) A WRKY transcription factor, PcWRKY33, from Polygonum cuspidatum reduces salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 37:1033–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2289-2
Bao F, Ding A, Cheng T, Wang J, Zhang Q (2019) Genome-wide analysis of members of the WRKY gene family and their cold stress response in Prunus mume. Genes 10:911. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110911
Baranwal VK, Negi N, Khurana P (2016) Genome-wide identification and structural, functional and evolutionary analysis of WRKY components of mulberry. Sci Rep 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30794
Besseau S, Li J, Palva ET (2012) WRKY54 and WRKY70 co-operate as negative regulators of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 63:2667–2679. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err450
Bi C, Xu Y, Ye Q, Yin T, Ye N (2016) Genome-wide identification and characterization of WRKY gene family in Salix suchowensis. PeerJ 4:e2437. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2437
Birkenbihl RP, Kracher B, Roccaro M, Somssich IE (2017) Induced genome-wide binding of three Arabidopsis WRKY transcription factors during early MAMP-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 29:20–38. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00681
Brand LH, Fischer NM, Harter K, Kohlbacher O, Wanke D (2013) Elucidating the evolutionary conserved DNA-binding specificities of WRKY transcription factors by molecular dynamics and in vitro binding assays. Nucleic Acids Res 41:9764–9778. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt732
Cai H, Yang S, Yan Y, Xiao Z, Cheng J, Wu J, Qiu A, Lai Y, Mou S, Guan D (2015) CaWRKY6 transcriptionally activates CaWRKY40, regulates Ralstonia solanacearum resistance, and confers high-temperature and high-humidity tolerance in pepper. J Exp Bot 66:3163–3174. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv125
Chanwala J, Satpati S, Dixit A, Parida A, Giri MK, Dey N (2020) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factors in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) under dehydration and salinity stress. BMC Genomics 21:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-6622-0
Chen C, Chen Z (2002) Potentiation of developmentally regulated plant defense response by AtWRKY18, a pathogen-induced Arabidopsis transcription factor. Plant Physiol 129:706–716. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.001057
Chen YF, Li LQ, Xu Q, Kong YH, Wang H, Wu WH (2009) The WRKY6 transcription factor modulates PHOSPHATE1 expression in response to low Pi stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:3554–3566. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.064980
Chen L, Song Y, Li S, Zhang L, Zou C, Yu D (2012) The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant abiotic stresses. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1819:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.09.002
Chen F, Hu Y, Vannozzi A, Wu K, Cai H, Qin Y, Mullis A, Lin Z, Zhang L (2017a) The WRKY transcription factor family in model plants and crops. Crit Rev Plant Sci 36:311–335. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2018.1441103
Chen J, Nolan TM, Ye H, Zhang M, Tong H, Xin P, Chu J, Chu C, Li Z, Yin Y (2017b) Arabidopsis WRKY46, WRKY54, and WRKY70 transcription factors are involved in brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and drought responses. Plant Cell 29:1425–1439. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00364
Chen L, Zhao Y, Xu S, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Zhang J, Chong K (2018a) OsMADS57 together with OsTB1 coordinates transcription of its target OsWRKY94 and D14 to switch its organogenesis to defense for cold adaptation in rice. New Phytol 218:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph14977
Chen Q, Lu X, Guo X, Liu J, Liu Y, Guo Q, Tang Z (2018b) The specific responses to mechanical wound in leaves and roots of Catharanthus roseus seedlings by metabolomics. J Plant Interact 13:450–460. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2018.1499970
Chen X, Li C, Wang H, Guo Z (2019) WRKY transcription factors: evolution, binding, and action. Phytopathol Res 1:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42483-019-0022-x
Chen C, Chen X, Han J, Lu W, Ren Z (2020) Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY gene family in the cucumber genome and transcriptome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factors that respond to biotic and abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02625-8
Cheng Y, Yao ZP, Ruan MY, Ye QJ, Wang RQ, Zhou GZ, Luo J, Li ZM, Yang YJ, Wan HJ (2016) In silico identification and characterization of the WRKY gene superfamily in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Genet Mol Res 15:1–12. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15038675
Cheng X, Zhao Y, Jiang Q, Yang J, Zhao W, Taylor IA, Peng Y-L, Wang D, Liu J (2019b) Structural basis of dimerization and dual W-box DNA recognition by rice WRKY domain. Nucleic Acids Res 47:4308–4318. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz113
Cheng Z, Luan Y, Meng J, Sun J, Tao J, Zhao D (2021) WRKY transcription factor response to high-temperature stress. Plants 10:2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102211
Cheng S, Xiaomeng L, Yongling L, Zhang W, Jiabao Y, Shen R, Feng XU (2019a) Genome-wide identification of WRKY family genes and analysis of their expression in response to abiotic stress in Ginkgo biloba L. Not Bot Horti Agrobot Cluj-Napoca 47:1100–1115. https://doi.org/10.15835/nbha47411651
Cheong YH, Chang HS, Gupta R, Wang X, Zhu T, Luan S (2002) Transcriptional profiling reveals novel interactions between wounding, pathogen, abiotic stress, and hormonal responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129:661–677. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.002857
Chu X, Wang C, Chen X, Lu W, Li H, Wang X, Hao L, Guo X (2016) The cotton WRKY gene GhWRKY41 positively regulates salt and drought stress tolerance in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. PLoS ONE 11:e0157026. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0157026
Contento AL, Kim SJ, Bassham DC (2004) Transcriptome profiling of the response of Arabidopsis suspension culture cells to Suc starvation. Plant Physiol 135:2330–2347. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.044362
Dai X, Wang Y, Zhang WH (2016) OsWRKY74, a WRKY transcription factor, modulates tolerance to phosphate starvation in rice. J Exp Bot 67:947–960. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv515
Ding W, Ouyang Q, Li Y, Shi T, Li L, Yang X, Ji K, Wang L, Yue Y (2020) Genome-wide investigation of WRKY transcription factors in sweet osmanthus and their potential regulation of aroma synthesis. Tree Physiol 40:557–572. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpz129
Ding ZJ, Yan JY, Li CX, Li GX, Wu YR, Zheng SJ (2015) Transcription factor WRKY46 modulates the development of Arabidopsis lateral roots in osmotic/salt stress conditions via regulation of ABA signaling and auxin homeostasis. Plant J 84:56–69.101111/tpj12958
Doll J, Muth M, Riester L, Nebel S, Bresson J, Lee H-C, Zentgraf U (2020) Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY25 transcription factor mediates oxidative stress tolerance and regulates senescence in a redox-dependent manner. Front Plant Sci 10:1734. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01734
Duan M-R, Nan J, Liang Y-H, Mao P, Lu L, Li L, Wei C, Lai L, Li Y, Su X-D (2007) DNA binding mechanism revealed by high resolution crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res 35:1145–1154. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm001
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:366–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.020
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2000) The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 5:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(00)01600-9
Fan Z-Q, Tan X-L, Shan W, Kuang J-F, Lu W-J, Chen J-Y (2017) BrWRKY65, a WRKY transcription factor, is involved in regulating three leaf senescence-associated genes in Chinese flowering cabbage. Int J Mol Sci 18:1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061228
Fan C, Yao H, Qiu Z, Ma H, Zeng B (2018) Genome-wide analysis of Eucalyptus grandis WRKY genes family and their expression profiling in response to hormone and abiotic stress treatment. Gene 678:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.08.003
Fan F, Wang Q, Li H, Ding G, Wen X (2020) Transcriptome-wide identification and expression profiles of Masson pine WRKY transcription factors in response to low phosphorus stress. Plant Mol Biol Rep 39:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-020-01222-1
Finatto T, Viana VE, Woyann LG, Busanello C, Maia LCd, Oliveira ACd (2018) Can WRKY transcription factors help plants to overcome environmental challenges? Genet Mol Biol 41:533–544. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2017-0232
Fu S, Lei M, Zhang Y, Deng Z, Shi J, Hao D (2019) De novo transcriptome analysis of Tibetan medicinal plant Dysphania schraderiana. Genet Mol Biol 42:480–487. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2018-0033
Fu QT, Yu DQ (2010) Expression profiles of AtWRKY25, AtWRKY26 and AtWRKY33 under abiotic stresses. 32:848–856. https://doi.org/10.3724/spj1005201000848
Gao H, Wang Y, Xu P, Zhang Z (2018) Overexpression of a WRKY transcription factor TaWRKY2 enhances drought stress tolerance in transgenic wheat. Front Plant Sci 9:997. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00997
Goel R, Pandey A, Trivedi PK, Asif MH (2016) Genome-wide analysis of the Musa WRKY gene family: evolution and differential expression during development and stress. Front Plant Sci 7:299. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00299
Gong X, Zhang J, Hu J, Wang W, Wu H, Zhang Q, Liu JH (2015) FcWRKY 70, a WRKY protein of Fortunella crassifolia, functions in drought tolerance and modulates putrescine synthesis by regulating arginine decarboxylase gene. Plant Cell Environ 38:2248–2262. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12539
Govardhana M, Kumudini BS (2020) In-silico analysis of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Genome for WRKY transcription factors and cis-acting elements. Comput Biol Chem 85:107212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107212
Goyal P, Manzoor MM, Vishwakarma RA, Sharma D, Dhar MK, Gupta S (2020) A comprehensive transcriptome-wide identification and screening of WRKY gene family engaged in abiotic stress in Glycyrrhiza glabra. Sci Rep 10:373. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57232-x
Grzechowiak M, Ruszkowska A, Sliwiak J, Urbanowicz A, Jaskolski M, Ruszkowski M (2022) New aspects of DNA recognition by group II WRKY transcription factor revealed by structural and functional study of AtWRKY18 DNA binding domain. Int J Biol Macromol 213:589–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.05.186
Gu Y, Ji Z, Chi F, Qiao Z, Xu C, Zhang J, Zhou Z, Dong Q (2016) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in peach. Yi Chuan= Hered 38:254–270. https://doi.org/10.16288/j.yczz.15-235
Gu L, Dou L, Guo Y, Wang H, Li L, Wang C, Ma L, Wei H, Yu S (2019) The WRKY transcription factor GhWRKY27 coordinates the senescence regulatory pathway in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) BMC Plant Biol 19:116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1688-z
Guo Y, Cai Z, Gan S (2004) Transcriptome of Arabidopsis leaf senescence. Plant Cell Environ 27:521–549. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2003.01158.x
Haider S, Raza A, Iqbal J, Shaukat M, Mahmood T (2022) Analyzing the regulatory role of heat shock transcription factors in plant heat stress tolerance: a brief appraisal. Mol Biol Rep 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07190-x
Hammargren J, Rosenquist S, Jansson C, Knorpp C (2008) A novel connection between nucleotide and carbohydrate metabolism in mitochondria: sugar regulation of the Arabidopsis nucleoside diphosphate kinase 3a gene. Plant Cell Rep 27:529–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0486-5
Han R, Rai A, Nakamura M, Suzuki H, Takahashi H, Yamazaki M, Saito K (2016) De novo deep transcriptome analysis of medicinal plants for gene discovery in biosynthesis of plant natural products. Methods Enzymol 576:19–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/bsmie201603001
Han M, Kim C-Y, Lee J, Lee S-K, Jeon J-S (2014) OsWRKY42 represses OsMT1d and induces reactive oxygen species and leaf senescence in rice. Mol Cells 37:532. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2014.0128
Hara K, Yagi M, Kusano T, Sano H (2000) Rapid systemic accumulation of transcripts encoding a tobacco WRKY transcription factor upon wounding. Mol Gen Genet 263:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008673
He Y, Fukushige H, Hildebrand DF, Gan S (2002) Evidence supporting a role of jasmonic acid in Arabidopsis leaf senescence. Plant Physiol 128:876–884. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010843
He G-H, Xu JY, Wang YX, Liu JM, Li PS, Chen M, Ma YZ, Xu ZS (2016a) Drought-responsive WRKY transcription factor genes TaWRKY1 and TaWRKY33 from wheat confer drought and/or heat resistance in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 16:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0806-4
He Y, Mao S, Gao Y, Zhu L, Wu D, Cui Y, Li J, Qian W (2016b) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factors under multiple stresses in Brassica napus. PLoS ONE 11:e0157558. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0157558
He C, da Silva JAT, Tan J, Zhang J, Pan X, Li M, Luo J, Duan J (2017) A genome-wide identification of the WRKY family genes and a survey of potential WRKY target genes in Dendrobium officinale. Sci Rep 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07872-8
He X, Li J-j, Chen Y, Yang J-q, Chen X-y (2019) Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY gene family and its response to abiotic stress in buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). Open Life Sci 14:80–96. https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2019-0010
Huang Y, Li MY, Wu P, Xu ZS, Que F, Wang F, Xiong AS (2016) Members of WRKY Group III transcription factors are important in TYLCV defense signaling pathway in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). BMC Genomics 17:788. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-3123-2
Hussain RMF, Sheikh AH, Haider I, Quareshy M, Linthorst HJM (2018) Arabidopsis WRKY50 and TGA transcription factors synergistically activate expression of PR1. Front Plant Sci 9:930–930. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00930
Jain M, Nagar P, Goel P, Singh AK, Kumari S, Mustafiz A (2018) Second messengers: central regulators in plant abiotic stress response. In: Abiotic stress-mediated sensing and signaling in plants: an omics perspective. Springer, pp 47–94
Jiang J, Ma S, Ye N, Jiang M, Cao J, Zhang J (2017b) WRKY transcription factors in plant responses to stresses. J Integr Plant Biol 59:86–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12513
Jiang C, Shen QJ, Wang B, He B, Xiao S, Chen L, Yu T, Ke X, Zhong Q, Fu J (2017a) Transcriptome analysis of WRKY gene family in Oryza officinalis Wall ex Watt and WRKY genes involved in responses to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae stress. PloS One 12:e0188742. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188742
Jimmy JL, Babu S (2019) Variations in the structure and evolution of rice WRKY genes in Indica and Japonica genotypes and their co-expression network in mediating disease resistance. Evol Bioinform Online. https://doi.org/10.1177/1176934319857720
Jing Z, Liu Z (2018) Genome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factors in kiwifruit (Actinidia spp.) and analysis of WRKY expression in responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Genes Genom 40:429–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-017-0645-1
Joshi R, Wani SH, Singh B, Bohra A, Dar ZA, Lone AA, Pareek A, Singla-Pareek SL (2016) Transcription factors and plants response to drought stress: current understanding and future directions. Front Plant Sci 7:1029. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01029
Jue D, Sang X, Liu L, Shu B, Wang Y, Liu C, Xie J, Shi S (2018) Identification of WRKY gene family from Dimocarpus longan and its expression analysis during flower induction and abiotic stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 19:2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082169
Kang SG, Price J, Lin P-C, Hong JC, Jang J-C (2010) The Arabidopsis bZIP1 transcription factor is involved in sugar signaling, protein networking, and DNA binding. Mol Plant 3:361–373. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssp115
Karanja BK, Fan L, Xu L, Wang Y, Zhu X, Tang M, Wang R, Zhang F, Muleke EMm, Liu L (2017) Genome-wide characterization of the WRKY gene family in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) reveals its critical functions under different abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep 36:1757–1773.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2190-4
Karkute SG, Gujjar RS, Rai A, Akhtar M, Singh M, Singh B (2018) Genome wide expression analysis of WRKY genes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) under drought stress. Plant Gene 13:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2017.11.002
Khuman A, Arora S, Makkar H, Patel A, Chaudhary B (2021) Extensive intragenic divergences amongst ancient WRKY transcription factor gene family is largely associated with their functional diversity in plants. Plant Gene 22:100222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2020.100222
Kidokoro S, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2022) Transcriptional regulatory network of plant cold-stress responses. Trends Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2022.01.008
Kilian J, Whitehead D, Horak J et al (2007) The AtGen Express global stress expression data set: protocols, evaluation and model data analysis of UV-B light, drought and cold stress responses. The Plant J 50:347–363. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03052.x
Kim CY, Vo KTX, Nguyen CD, Jeong DH, Lee SK, Kumar M, Kim SR, Park SH, Kim JK, Jeon JS (2016) Functional analysis of a cold-responsive rice WRKY gene, OsWRKY71. Plant Biotechnol Rep 10:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-015-0383-2
Kim J, Kim JH, Lyu JI, Woo HR, Lim PO (2018) New insights into the regulation of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 69:787–799. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx287
Kunz S, Gardestrom P, Pesquet E, Kleczkowski LA (2015) Hexokinase 1 is required for glucose-induced repression of bZIP63, At5g22920, and BT2 in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 6:525. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00525
Lai Z, Li Y, Wang F, Cheng Y, Fan B, Yu JQ, Chen Z (2011) Arabidopsis sigma factor binding proteins are activators of the WRKY33 transcription factor in plant defense. Plant Cell 23:3824–3841. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.090571
Li S, Zhou X, Chen L, Huang W, Yu D (2010) Functional characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY39 in heat stress. Mol Cells 29:475–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0059-2
Li C, Li D, Shao F, Lu S (2015a) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factor genes in Salvia miltiorrhiza. BMC Genom 16:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1411-x
Li J-b, Luan Y-s, Liu Z (2015b) SpWRKY1 mediates resistance to Phytophthora infestans and tolerance to salt and drought stress by modulating reactive oxygen species homeostasis and expression of defense-related genes in tomato. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 123:67–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0815-2
Li MY, Xu ZS, Tian C, Huang Y, Wang F, Xiong AS (2016) Genomic identification of WRKY transcription factors in carrot (Daucus carota) and analysis of evolution and homologous groups for plants. Sci Rep 6:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23101
Li D, Liu P, Yu J, Wang L, Dossa K, Zhang Y, Zhou R, Wei X, Zhang X (2017a) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY gene family in the sesame genome and identification of the WRKY genes involved in responses to abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol 17:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1099-y
Li L, Mu S, Cheng Z, Cheng Y, Zhang Y, Miao Y, Hou C, Li X, Gao J (2017b) Characterization and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in moso bamboo. Sci Rep 7:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06701-2
Li J, Xiong Y, Li Y, Ye S, Yin Q, Gao S, Yang D, Yang M, Palva ET, Deng X (2019a) Comprehensive analysis and functional studies of WRKY transcription factors in Nelumbo nucifera. Int J Mol Sci 20:5006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205006
Li Y, Zhang L, Zhu P, Cao Q, Sun J, Li Z, Xu T (2019b) Genome-wide identification, characterisation and functional evaluation of WRKY genes in the sweet potato wild ancestor Ipomoea trifida (HBK) G. Don under Abiotic Stresses. BMC Genet 20:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-019-0789-x
Li CX, Yan JY, Ren JY, Sun L, Xu C, Li GX, Ding ZJ, Zheng SJ (2020a) A WRKY transcription factor confers aluminum tolerance via regulation of cell wall modifying genes. J Integr Plant Biol 62:1176–1192. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12888
Li J, Zhao X, Dong Y, Li S, Yuan J, Li C, Zhang X, Li M (2020c) Transcriptome analysis reveals key pathways and hormone activities involved in early microtuber formation of Dioscorea opposita. BioMed Res Int 2020:8057929. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8057929
Li Z, Hua X, Zhong W, Yuan Y, Wang Y, Wang Z, Ming R, Zhang J (2020d) Genome-wide identification and expression profile analysis of WRKY family genes in the autopolyploid Saccharum spontaneum. Plant Cell Physiol 61:616–630. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcz227
Li YM, Zhu L, Zhu HY, Song PY, Guo LQ, Yang LM (2018) Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY family genes and their responses to cold stress in watermelon. Czech J Genet Plant Breed 54:168–176. https://doi.org/10.17221/72/2017-CJGPB
Li J, Islam F, Huang Q, Wang J, Zhou W, Xu L, Yang C (2020b) Genome-wide characterization of WRKY gene family in Helianthus annuus L. and their expression profiles under biotic and abiotic stresses. PloS One 15:e0241965. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241965
Liang Q-y, Wu Y-h, Wang K, Bai Z-y, Liu Q-l, Pan Y-z, Zhang L, Jiang B-b (2017) Chrysanthemum WRKY gene DgWRKY5 enhances tolerance to salt stress in transgenic chrysanthemum. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05170-x
Liao YL, Shen YB, Chang J, Zhang WW, Cheng SY, Xu F (2015) Isolation, expression, and promoter analysis of GbWRKY2: a novel transcription factor gene from Ginkgo biloba. Int J Genomics 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/607185
Liu QN, Liu Y, Xin ZZ, Zhang DZ, Ge BM, Yang RP, Wang ZF, Yang L, Tang BP, Zhou CL (2017) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the WRKY gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum). Biochem Syst Ecol 71:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2017.02.010
Liu X, Li D, Zhang S, Xu Y, Zhang Z (2019) Genome-wide characterization of the rose (Rosa chinensis) WRKY family and role of RcWRKY41 in gray mold resistance. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2139-6
Liu Z, Chang Q, Cheng C, Zheng Z, Yu S (2020) Identification of yellowhorn (Xanthoceras sorbifolium) WRKY transcription factor family and analysis of abiotic stress response model. J for Res 32:987–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-020-01134-6
Liu ZQ, Shi LP, Yang S, Qiu SS, Ma XL, Cai JS, Guan DY, Wang ZH, He SL (2021) A conserved double W box in the promoter of CaWRKY40 mediates auto regulation during response to pathogen attack and heat stress in pepper. Mol Plant Pathol 22:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.13004
Lowe R, Shirley N, Bleackley M, Dolan S, Shafee T (2017) Transcriptomics technologies. PLoS Comput Biol 13:e1005457. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005457
Lui S, Luo C, Zhu L, Sha R, Qu S, Cai B, Wang S (2017) Identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factor genes in response to fungal pathogen and hormone treatments in apple (Malus domestica). J Plant Biol 60:215–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-016-0577-3
Luo D-l, Ba L-j, Shan W, Kuang J-f, Lu W-j, Chen J-y (2017) Involvement of WRKY transcription factors in abscisic-acid-induced cold tolerance of banana fruit. J Agric Food Chem 65:3627–3635. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00915
Lv B, Wu Q, Wang A, Li Q, Dong Q, Yang J, Zhao H, Wang X, Chen H, Li C (2020) A WRKY transcription factor, FtWRKY46, from tartary buckwheat improves salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 147:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.12.004
Ma J, Gao X, Liu Q, Shao Y, Zhang D, Jiang L, Li C (2017) Overexpression of TaWRKY146 increases drought tolerance through inducing stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 8:2036. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02036
Ma Q, Xia Z, Cai Z, Li L, Cheng Y, Liu J, Nian H (2019) GmWRKY16 Enhances drought and salt tolerance through an ABA-mediated pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 9:1979. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01979
Mangelsen E, Wanke D, Kilian J, Sundberg E, Harter K, Jansson C (2010) Significance of light, sugar, and amino acid supply for diurnal gene regulation in developing barley caryopses. Plant Physiol 153:14–33. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.154856
Mao P, Jin X, Bao Q, Mei C, Zhou Q, Min X, Liu Z (2020) WRKY Transcription factors in Medicago sativa L.: genome-wide identification and expression analysis under abiotic stress. DNA Cell Biol 39:2212–2225. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2020.5726
Mare C, Mazzucotelli E, Crosatti C, Francia E, Cattivelli L (2004) Hv-WRKY38: a new transcription factor involved in cold-and drought-response in barley. Plant Mol Biol 55:399–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-004-0906-7
Matiolli CC, Tomaz JP, Duarte GT et al (2011) The Arabidopsis bZIP gene AtbZIP63 is a sensitive integrator of transient abscisic acid and glucose signals. Plant Physiol 157:692–705. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.181743
Mishra S, Triptahi V, Singh S, Phukan UJ, Gupta MM, Shanker K, Shukla RK (2013) Wound induced tanscriptional regulation of benzylisoquinoline pathway and characterization of wound inducible PsWRKY transcription factor from Papaver somniferum. PLoS ONE 8:e52784. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052784
Mohanty B, Takahashi H, de Los Reyes BG, Wijaya E, Nakazono M, Lee DY (2016) Transcriptional regulatory mechanism of alcohol dehydrogenase 1-deficient mutant of rice for cell survival under complete submergence. Rice 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-016-0124-3
Nan H, Gao L-z (2019) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY genes and their response to hormone and mechanic stresses in carrot. Front Genet 10:363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00363
Ning P, Liu C, Kang J, Lv J (2017) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and differential expression under water deficit condition. PeerJ 5:e3232. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3232
Niu CF, Wei WEI, Zhou QY, Tian AG, Hao YJ, Zhang WK, Ma B, Lin Q, Zhang ZB, Zhang JS (2012) Wheat WRKY genes TaWRKY2 and TaWRKY19 regulate abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell Environ 35:1156–1170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02480.x
Nuruzzaman M, Cao H, Xiu H, Luo T, Li J, Chen X, Luo J, Luo Z (2016) Transcriptomics-based identification of WRKY genes and characterization of a salt and hormone-responsive PgWRKY1 gene in Panax ginseng. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 48:117–131. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmv122
Pandey B, Grover A, Sharma P (2018) Molecular dynamics simulations revealed structural differences among WRKY domain-DNA interaction in barley (Hordeum vulgare). BMC Genom 19:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4506-3
Phukan UJ, Jeena GS, Shukla RK (2016) WRKY transcription factors: molecular regulation and stress responses in plants. Front Plant Sci 7:760. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00760
Rensing SA, Lang D, Zimmer AD et al (2008) The Physcomitrella genome reveals evolutionary insights into the conquest of land by plants. Sci 319:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1126/science1150646
Rice WWG (2012) Nomenclature report on rice WRKY’s-conflict regarding gene names and its solution. Rice 5:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1939-8433-5-3
Rinerson CI, Rabara RC, Tripathi P, Shen QJ, Rushton PJ (2015) The evolution of WRKY transcription factors. BMC Plant Biol 15:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0456-y
Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2001) A new member of the Arabidopsis WRKY transcription factor family, AtWRKY6, is associated with both senescence- and defence-related processes. Plant J 28:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2001.01131.x
Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2002) Targets of AtWRKY6 regulation during plant senescence and pathogen defense. Genes Dev 16:1139–1149. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.222702
Rushton PJ, Somssich IE, Ringler P, Shen QJ (2010) WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 15:247–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/jtplants201002006
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J et al (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08670
Schwechheimer C, Schroder PM, Blaby-Haas CE (2022) Plant GATA factors: their biology, phylogeny, and phylogenomics. Annu Rev Plant Biol 73:123–148. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-072221-092913
Seki M, Narusaka M, Ishida J, Nanjo T, Fujita M, Oono Y, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Sakurai T (2002) Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J 31:279–292. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01359.x
da Silva EG, Ito TM, de Souza SGH (2017) In silico genome-wide identification and phylogenetic analysis of the WRKY transcription factor family in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis). Aust J Crop Sci 11: 716–726.https://doi.org/10.21475/ajcs.17.11.06.p471
Singh A, Singh PK, Sharma AK, Singh NK, Sonah H, Deshmukh R, Sharma TR (2019) Understanding the role of the WRKY gene family under stress conditions in pigeonpea (Cajanus Cajan L.). Plants 8:214. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8070214
Skibbe M, Qu N, Galis I, Baldwin IT (2008) Induced plant defenses in the natural environment: Nicotiana attenuata WRKY3 and WRKY6 coordinate responses to herbivory. Plant Cell 20:1984–2000. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.058594
Snyder RL, Jpd MA (2005) Frost damage: physiology and critical temperatures. Frost Protect 1:87–88
Song Y, Gao J (2014) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY gene family in Arabidopsis lyrata and comparison with Arabidopsis thaliana and Populus trichocarpa. Chin Sci Bull 59:754–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-0057-9
Song H, Wang P, Hou L, Zhao S, Zhao C, Xia H, Li P, Zhang Y, Bian X, Wang X (2016) Global analysis of WRKY genes and their response to dehydration and salt stress in soybean. Front Plant Sci 7:9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00009
Song H, Sun W, Yang G, Sun J (2018) WRKY transcription factors in legumes. BMC Plant Biol 18:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1467-2
Song Y, Cui H, Shi Y, Xue J, Ji C, Zhang C, Yuan L, Li R (2020) Genome-wide identification and functional characterization of the Camelina sativa WRKY gene family in response to abiotic stress. BMC Genom 21:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-07189-3
Song H, Nan Z (2014) Genome-wide identification and analysis of WRKY transcription factors in Medicago truncatula. Yi Chuan= Hered 36:152–168. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.1005.2014.00152
Srivastava R, Kumar S, Kobayashi Y, Kusunoki K, Tripathi P, Kobayashi Y, Koyama H, Sahoo L (2018) Comparative genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors in two Asian legume crops: Adzuki bean and Mung bean. Sci Rep 8:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34920-8
Strader L, Weijers D, Wagner D (2022) Plant transcription factors-being in the right place with the right company. Curr Opin Plant Biol 65:102136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2021.102136
Sun C, Palmqvist S, Olsson H, Boren M, Ahlandsberg S, Jansson C (2003) A novel WRKY transcription factor, SUSIBA2, participates in sugar signaling in barley by binding to the sugar-responsive elements of the iso1 promoter. Plant Cell 15:2076–2092. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.014597
Sun C, Hoglund AS, Olsson H, Mangelsen E, Jansson C (2005) Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibition as a potent strategy in plant biology: identification of SUSIBA2 as a transcriptional activator in plant sugar signalling. Plant J 44:128–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02515.x
Sun J, Hu W, Zhou R, Wang L, Wang X, Wang Q, Feng Z, Li Y, Qiu D, He G, Yang G (2015a) The Brachypodium distachyon BdWRKY36 gene confers tolerance to drought stress in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Cell Rep 34:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1684-6
Sun X-c, Gao Y-f, Li H-r, Yang S-z, Liu Y-s (2015b) Over-expression of SlWRKY39 leads to enhanced resistance to multiple stress factors in tomato. J Plant Biol 58:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-014-0407-4
Tang L, Cai H, Zhai H, Luo X, Wang Z, Cui L, Bai X (2014) Overexpression of Glycine soja WRKY20 enhances both drought and salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 118:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0463-y
Ueda J, Kato J (1980) Isolation and identification of a senescence-promoting substance from wormwood (Artemisia absinthium L.). Plant Physiol 66:246–249. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.66.2.246
van Verk MC, Pappaioannou D, Neeleman L, Bol JF, Linthorst HJM (2008) A novel WRKY transcription factor is required for induction of PR-1a gene expression by salicylic acid and bacterial elicitors. Plant Physiol 146:1983–1995. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.112789
Villacastin AJ, Adams KS, Boonjue R, Rushton PJ, Han M, Shen JQ (2021) Dynamic differential evolution schemes of WRKY transcription factors in domesticated and wild rice. Sci Rep 11:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-94109-4
Villano C, Esposito S, D’Amelia V, Garramone R, Alioto D, Zoina A, Aversano R, Carputo D (2020) WRKY genes family study reveals tissue-specific and stress-responsive TFs in wild potato species. Sci Rep 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63823-w
Wan Y, Mao M, Wan D, Yang Q, Yang F, Li G, Wang R (2018) Identification of the WRKY gene family and functional analysis of two genes in Caragana intermedia. BMC Plant Biol 18:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1235-3
Wang H-J, Wan A-R, Hsu C-M, Lee K-W, Yu S-M, Jauh G-Y (2007a) Transcriptomic adaptations in rice suspension cells under sucrose starvation. Plant Mol Biol 63:441–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-9100-4
Wang H, Hao J, Chen X, Hao Z, Wang X, Lou Y, Peng Y, Guo Z (2007b) Overexpression of rice WRKY89 enhances ultraviolet B tolerance and disease resistance in rice plants. Plant Mol Biol 65:799–815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9244-x
Wang L, Zhu W, Fang L, Sun X, Su L, Liang Z, Wang N, Londo JP, Li S, Xin H (2014) Genome-wide identification of WRKY family genes and their response to cold stress in Vitis vinifera. BMC Plant Biol 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-103
Wang F, Chen HW, Li QT, Wei W, Li W, Zhang WK, Ma B, Bi YD, Lai YC, Liu XL (2015) Gm WRKY 27 interacts with Gm MYB 174 to reduce expression of Gm NAC 29 for stress tolerance in soybean plants. Plant J 83:224–236. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12879
Wang N, Xia EH, Gao LZ (2016) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY family of transcription factors in common bean, Phaseolus vulgaris: chromosomal localization, structure, evolution and expression divergence. Plant Gene 5:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2015.11.003
Wang CT, Ru JN, Liu YW, Li M, Zhao D, Yang JF, Fu JD, Xu ZS (2018) Maize WRKY transcription factor ZmWRKY106 confers drought and heat tolerance in transgenic plants. Int J Mol Sci 19:3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103046
Wang C, Peng D, Zhu J, Zhao D, Shi Y, Zhang S, Ma K, Wu J, Huang L (2019a) Transcriptome analysis of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua: identification of genes involved in polysaccharide biosynthesis. Plant Methods 15:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-019-0441-9
Wang P, Yue C, Chen D, Zheng Y, Zhang Q, Yang J, Ye N (2019b) Genome-wide identification of WRKY family genes and their response to abiotic stresses in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Genes Genom 41:17–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0734-9
Wang Z, Feng R, Zhang X, Su Z, Wei J, Liu J (2019c) Characterization of the Hippophae rhamnoides WRKY gene family and functional analysis of the role of the HrWRKY21 gene in resistance to abiotic stresses. Genome 62:689–703. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2019-002
Wang M-q, Huang Q-x, Lin P, Zeng Q-h, Li Y, Liu Q-l, Zhang L, Pan Y-z, Jiang B-b, Zhang F (2020a) The overexpression of a transcription factor gene VbWRKY32 Enhances the cold tolerance in Verbena bonariensis. Front Plant Sci 10:1746. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01746
Wang Z, Ni L, Guo J, Liu L, Li H, Yin Y, Gu C (2020b) Phylogenetic and transcription analysis of Hibiscus hamabo Sieb. et Zucc. WRKY transcription factors. DNA Cell Biol 39:1141–1154. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna20195254
Wani SH, Tripathi P, Zaid A, Challa GS, Kumar A, Kumar V, Upadhyay J, Joshi R, Bhatt M (2018) Transcriptional regulation of osmotic stress tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Mol Biol 97:469–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0761-6
Wani SH, Anand S, Singh B, Bohra A, Joshi R (2021) WRKY transcription factors and plant defense responses: latest discoveries and future prospects. Plant Cell Rep 40:1071–1085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02691-8
Waqas M, Azhar MT, Rana IA, Azeem F, Ali MA, Nawaz MA, Chung G, Atif RM (2019) Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of WRKY transcription factor family members from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) reveal their role in abiotic stress-responses. Genes Genom 41:467–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-00780-9
Wei W, Zhang Y, Han L, Guan Z, Chai T (2008) A novel WRKY transcriptional factor from Thlaspi caerulescens negatively regulates the osmotic stress tolerance of transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 27:795–803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0499-0
Wei W, Hu Y, Han YT, Zhang K, Zhao FL, Feng JY (2016) The WRKY transcription factors in the diploid woodland strawberry Fragaria vesca: identification and expression analysis under biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 105:129–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.014
Wu X, Shiroto Y, Kishitani S, Ito Y, Toriyama K (2009) Enhanced heat and drought tolerance in transgenic rice seedlings overexpressing OsWRKY11 under the control of HSP101 promoter. Plant Cell Rep 28:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0614-x
Wu B, Li MY, Xu ZS, Wang F, Xiong AS (2018) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors and their response to abiotic stress in celery (Apium graveolens L.). Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 32:293–302. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2017.1413954
Xiao Y, Zhou L, Lei X, Cao H, Wang Y, Dou Y, Tang W, Xia W (2017) Genome-wide identification of WRKY genes and their expression profiles under different abiotic stresses in Elaeis guineensis. PLoS ONE 12:e0189224. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189224
Xie Y, Huhn K, Brandt R et al (2014) REVOLUTA and WRKY53 connect early and late leaf development in Arabidopsis. Dev 141:4772–4783. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.117689
Xie T, Chen C, Li C, Liu J, Liu C, He Y (2018) Genome-wide investigation of WRKY gene family in pineapple: evolution and expression profiles during development and stress. BMC Genom 19:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4880-x
Xin PF, Gao CS, Cheng CH, Tang Q, Dong ZX, Zhao LN, Zang GG (2016) Identification and characterization of hemp WRKY transcription factors in response to abiotic stresses. Biol Plant 60:489–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0621-7
Xiong W, Xu X, Zhang L, Wu P, Chen Y, Li M, Jiang H, Wu G (2013) Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY gene family in physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.). Gene 524:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.04.047
Xu H, Watanabe KA, Zhang L, Shen QJ (2016) WRKY transcription factor genes in wild rice Oryza nivara. DNA Res 23:311–323. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsw025
Xu YH, Sun PW, Tang XL, Gao ZH, Zhang Z, Wei JH (2020a) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors in Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg. Sci Rep 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59597-w
Xu Y-p, Xu H, Wang B, Su X-D (2020b) Crystal structures of N-terminal WRKY transcription factors and DNA complexes. Protein Cell 11:208–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-019-00670-0
Xue C, Li H, Liu Z, Wang L, Zhao Y, Wei X, Fang H, Liu M, Zhao J (2019) Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY gene family and their positive responses to phytoplasma invasion in Chinese jujube. BMC Genom 20:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5789-8
Yan H, Li M, Xiong Y, Wu J, Teixeira da Silva JA, Ma G (2019) Genome-wide characterization, expression profile analysis of WRKY family genes in Santalum album and functional identification of their role in abiotic stress. Int J Mol Sci 20:5676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225676
Yang Y, Liang T, Zhang L, Shao K, Gu X, Shang R, Shi N, Li X, Zhang P, Liu H (2018) UVR8 interacts with WRKY36 to regulate HY5 transcription and hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 4:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-017-0099-0
Yang X, Zhou Z, Fu M, Han M, Liu Z, Zhu C, Wang L, Zheng J, Liao Y, Zhang W (2020a) Transcriptome-wide identification of WRKY family genes and their expression profiling toward salicylic acid in Camellia japonica. Plant Signal Behav 16:1844508. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2020.1844508
Yang Y, Liu J, Zhou X, Liu S, Zhuang Y (2020b) Identification of WRKY gene family and characterization of cold stress-responsive WRKY genes in eggplant. PeerJ 8:e8777. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8777
Yang Z, Chi X, Guo F, Jin X, Luo H, Hawar A, Chen Y, Feng K, Wang B, Qi J, Yang Y, Sun B (2020c) SbWRKY30 enhances the drought tolerance of plants and regulates a drought stress-responsive gene, SbRD19, in sorghum. J Plant Physiol 246:153142. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjplph2020153142
Yu S, Ai C-r, Jing S-j, Yu D-q (2010) Research progress on functional analysis of rice WRKY genes. Rice Sci 17:60–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6308(08)60105-5
Yue H, Wang M, Liu S, Du X, Song W, Nie X (2016) Transcriptome-wide identification and expression profiles of the WRKY transcription factor family in Broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.). BMC Genom 17:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2677-3
Zhang Y (2014) Identification and characterization of the grape WRKY family. BioMed Res Int 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/787680
Zhang Y, Wang L (2005) The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants. BMC Evol Biol 5:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-5-1
Zhang Q, Zhu J, Ni Y, Cai Y, Zhang Z (2012) Expression profiling of HbWRKY1, an ethephon-induced WRKY gene in latex from Hevea brasiliensis in responding to wounding and drought. Trees 26:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-011-0623-1
Zhang Y, Yu H, Yang X, Li Q, Ling J, Wang H, Gu X, Huang S, Jiang W (2015) CsWRKY46, a WRKY transcription factor from cucumber, confers cold resistance in transgenic-plant by regulating a set of cold-stress responsive genes in an ABA-dependent manner. Plant Physiol Biochem 108:478–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.08.013
Zhang C, Wang D, Yang C, Kong N, Shi Z, Zhao P, Nan Y, Nie T, Wang R, Ma H (2017a) Genome-wide identification of the potato WRKY transcription factor family. PLoS ONE 12:e0181573. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181573
Zhang T, Tan D, Zhang L, Zhang X, Han Z (2017b) Phylogenetic analysis and drought-responsive expression profiles of the WRKY transcription factor family in maize. Agri Gene 3:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aggene.2017.01.001
Zhang L, Wan X, Xu Y, Niyitanga S, Qi J, Zhang L (2020) De novo assembly of transcriptome and genome-wide identification reveal GA3 stress-responsive WRKY transcription factors involved in fiber formation in jute (Corchorus capsularis). BMC Plant Biol 20:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02617-8
Zhang H, Zhang L, Wu S, Chen Y, Yu D, Chen L (2021) AtWRKY75 positively regulates age-triggered leaf senescence through gibberellin pathway. Plant Divers 43:331–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pld.2020.10.002
Zhao N, He M, Li L, Cui S, Hou M, Wang L, Mu G, Liu L, Yang X (2020) Identification and expression analysis of WRKY gene family under drought stress in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). PloS One 15:e0231396. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231396
Zhou QY, Tian AG, Zou HF, Xie ZM, Lei G, Huang J, Wang CM, Wang HW, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2008) Soybean WRKY-type transcription factor genes, GmWRKY13, GmWRKY21, and GmWRKY54, confer differential tolerance to abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6:486–503. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00336.x
Zhou H, Li Y, Zhang Q, Ren S, Shen Y, Qin L, Xing Y (2016) Genome-wide analysis of the expression of WRKY family genes in different developmental stages of wild strawberry (Fragaria vesca) fruit. PLoS ONE 11:e0154312. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154312
Zhou P, Pu T, Gui C, Zhang X, Gong L (2020) Transcriptome analysis reveals biosynthesis of important bioactive constituents and mechanism of stem formation of Dendrobium huoshanense. Sci Rep 10:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59737-2
Zou Z, Yang L, Wang D, Huang Q, Mo Y, Xie G (2016) Gene structures, evolution and transcriptional profiling of the WRKY gene family in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). PloS One 11:e0148243. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148243
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the grant (SERB/SB/SO/PS/90/2013) from the Science and Engineering Research Board, India, for funding. PG acknowledges the University Grant Commission for Senior Research Fellowship and Guru Nanak Dev University for registration; BV acknowledges the University Grant Commission and the Academy of Scientific and Innovative Research; and RD, SH, and RT acknowledge the Council for Scientific & Industrial Research. The Academy of Scientific and Innovative Research, CSIR-HRDC Campus, Sector-19, Ghaziabad, U.P., India, is also acknowledged. All the authors acknowledge the director, CSIR-IIIM, for providing all the necessary facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Handling Editor: Pengguo Xia
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, P., Devi, R., Verma, B. et al. WRKY transcription factors: evolution, regulation, and functional diversity in plants. Protoplasma 260, 331–348 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-022-01794-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-022-01794-7