Abstract
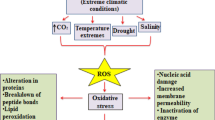
Leaf senescence is a genetically programmed decline in various cellular processes including photosynthesis and involves the hydrolysis of macromolecules such as proteins, lipids, etc. It is governed by the developmental age and is induced or enhanced by environmental stresses such as drought, heat, salinity and others. Internal factors such as reproductive structures also influence the rate of leaf senescence. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation is one of the earliest responses of plant cells under abiotic stresses and senescence. Chloroplasts are the main targets of ROS-linked damage during various environmental stresses and natural senescence as ROS detoxification systems decline with age. Plants adapt to environmental stresses through the process of acclimation, which involves less ROS production coupled with an efficient antioxidant defence. Chloroplasts are a major site of protein degradation, and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) is rapidly and selectively degraded during senescence and stress. The process of protein degradation is initiated by ROS and involves the action of proteolytic enzymes such as cysteine and serine proteases. The mechanism of Rubisco degradation still remains to be elucidated. The molecular understanding of leaf senescence was achieved through the characterization of senescence-associated genes and various senescence mutants of Arabidopsis, which is a suitable model plant showing monocarpic senescence. The regulation of senescence involves many regulatory elements composed of positive and negative elements to fine-tune the initiation and progression of senescence. This review gives an overview on chloroplast protein degradation during leaf senescence and abiotic stresses and also highlights the role of ROS management in both processes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- AsA:
-
Ascorbate
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DHAR:
-
Dehydroascorbate reductase
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GSSG:
-
Oxidized glutathione
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- MDHAR:
-
Monodehydroascorbate reductase
- MeJA:
-
Methyl jasmonate
- POX:
-
Guaiacol peroxidase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
Abreu ME, Munné-Bosch S (2008) Salicylic acid may be involved in the regulation of drought-induced leaf senescence in perennials: a case study in field-grown Salvia officinalis L. plants. Environ Exp Bot 64:105–112
Adam Z, Clarke AK (2002) Cutting edge of chloroplast proteolysis. Trends Plant Sci 7:51–456
Ahmed P, Jaleel CA, Azooz MM, Nabi G (2009) Generation of ROS and nonenzymatic antioxidants during abiotic stresses in plants. Bot Res Int 2:11–20
Anderson JA, Padhye SR (2004) Protein aggregation, radical scavenging capacity, and stability of hydrogen peroxide defense systems in heat-stressed Vinca and sweet pea leaves. J Am Soc Hort Sci 129:54–59
Atkinson D, Porter JR (1996) Temperature, plant development and crop yields. Trends Plant Sci 1:119–124
Bailey-Serres J, Mittler R (2006) The roles of reactive oxygen species in plant cells. Plant Physiol 141:311
Barth C, Moeder W, Klessig DF, Conklin PL (2004) The timing of senescence and response to pathogens is altered in the ascorbate-deficient mutant vitamin C-1. Plant Physiol 134:178–192
Bergmüller E, Porfirova E, Dörmann P (2003) Characterization of an Arabidopsis mutant deficient in γ-tocopherol methyltransferase. Plant Mol Biol 52:1181–1190
Berry J, Bjőrkman O (1980) Photosynthetic response and adaptation to temperatures in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Phyiol 31:491–493
Bhattacharjee (2005) Reactive oxygen species and oxidative burst: roles in stress, senescence and signal transduction in plants. Curr Sci 89:1113–1121
Breusegem FV, Dat JF (2006) Reactive oxygen species in plant cell death. Plant Physiol 141:384–390
Brugière N, Dubois F, Masclaux C, Sangwan RS, Hirel B (2000) Immunolocalization of glutamine synthetase in senescing tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) leaves suggests that ammonia assimilation is progressively shifted to the mesophyll cytosol. Planta 211:519–527
Büchert AM, Civello PM, Martínez GA (2011) Chlorophyllase versus pheophytinase as candidates for chlorophyll dephytilation during senescence of broccoli. J Plant Physiol 168:337–343
Chauhan S (2005) Physiological and molecular basis of heat tolerance with emphasis on oxidative stress metabolism in wheat. PhD thesis, HNB Garhwal University, Srinagar, Uttaranchal, India
Chauhan S, Srivalli S, Nautiyal AR, Khanna-Chopra R (2009) Wheat cultivars differing in heat tolerance show a differential response to monocarpic senescence under high temperature stress and the involvement of serine proteases. Photosynthetica 47:536–547
Chen W, Provart NJ, Glazebrook J, Katagiri F, Chang HS, Eulgen T, Mauch F, Luan S, Zou G, Whittham SA, Budworth PR, Tao Y, Xie Z, Chen X, Lam S, Kreps JA, Harper JF, Si-Ammour A, Mauch-Mani B, Heinlein M, Kobayashi K, Hohn T, Dangl JL, Wang X, Zhu T (2002) Expression profile matrix of Arabidopsis transcription factor genes suggests their putative functions in responseto environmental stresses. Plant Cell 14:559–574
Dalling MJ, Boland G, Wilson JH (1976) Relation between acid proteinase activity and redistribution of nitrogen during grain development in wheat. Aust J Plant Physiol 3:721–730
Dat JF, Lopez-Delgado H, Foyer CH, Scott IM (1998) Parallel changes in H2O2 and catalse during thermotolerance induced by salicylic acid or heat acclimation in mustard seedlings. Plant Physiol 116:1351–1357
Davletova S, Rizhsky L, Liang H, Shengqiang Z, Oliver DJ, Coutu J, Shulaev V, Schlauch K, Mittler R (2005) Cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase 1 is a central component of the reactive oxygen gene network of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:268–281
Delledonne M, Xia Y, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998) Nitric oxide functions as a signal in plant disease resistance. Nature 394:585–588
Demirevska-Kepova K, Hölzer R, Simova-Stoilova L, Feller U (2005) Heat stress effecects on Rubisco, Rubisco binding protein and Rubisco activase in wheat leaves. Biol Plant 49:521–525
Dhindsa RJ, Dhindsa PP, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased level of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation and decreased level of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32:93–101
El Yahyaoui F, Kuster HK, Amor BB, Hohnjec N, Puhler A, Becker A, Gouzy J, Vernie T, Gough C, Niebel A, Godiard L, Gamas P (2004) Expression profiling in Medicago truncatula identifies more than 750 genes differentially expressed during nodulation, including many potential regulators of the symbiotic program. Plant Physiol 136:3159–3176
Feller U, Anders I, Mae T (2008a) Rubiscolytics: fate of Rubisco after its enzymatic function in a cell is terminated. J Exp Bot 59:1615–1624
Feller U, Anders I, Demirevska K (2008b) Degradation of Rubisco and other chloroplast proteins under abiotic stresses. Gen Appl Plant Physiol 34:5–18
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2005) Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signalling: a metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell 17:1866–1875
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2009) Redox regulation in photosynthetic organisms: signaling, acclimation, and practical implications. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:861–905
Fryer MJ, Andrews JR, Oxborough K, Blowers DA, Baker NR (1998) Relationship between CO2 assimilation, photosynthetic electron transport and active O2 metabolism in leaves of maize in the field during periods of low temperature. Plant Physiol 116:571–580
Gadjev I, Vanderauwera S, Gechev TS, laloi C, Minkov IN, Shulaev V, Apel K, Inze D, Mittler R, Van Breusegem F (2006) Transcriptomic footprints disclose specificity of reactive oxygen species signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141:436–445
Giacomelli L, Masi A, Ripoll DR, Lee MJ, van Wijk KJ (2007) Arabidopsis thaliana deficient in two chloroplast ascorbate peroxidases shows accelerated light-induced necrosis when levels of cellular ascorbate are low. Plant Mol Biol 65:627–644
Groten K, Dutilleul C, van Heerden PDR, Vanacker H, Bernard S, Finkemeier I, Dietz KJ, Foyer CH (2006) Redoxregulation of peroxiredoxin and proteinases by ascorbate and thiols during pea root nodule senescence. FEBS Lett 580:1269–1276
Guiamét JJ, Pichersky E, Nooden LD (1999) Mass exodus from senescing soybeans chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 40:986–992
Guo FQ, Crawford NM (2005) Arabidopsis nitric-oxide synthase1 is targeted to mitochondria and protects against oxidative damage and dark-induced senescence. Plant Cell 17:3436–3450
He Y, Fukushige H, Hildebrand DF, Gan S (2002) Evidence supporting a role of jasmonic acid in Arabidopsis leaf senescence. Plant Physiol 128:876–884
Hörtensteiner S (2006) Chlorophyll degradation during senescence. Ann Rev Plant Biol 57:55–77
Hörtensteiner S, Feller U (2002) Nitrogen metabolism and remobilization during senescence. J Exp Bot 53:927–937
Hung KT, Kao CH (2003) Nitric oxide counteracts the senescence of rice leaves induced by abscisic acid. J Plant Physiol 160:871–879
Hung KT, Kao CH (2004) Hydrogen peroxide is necessary for abscisic acid-induced senescence of rice leaves. J Plant Physiol 161:1347–1357
Izumi M, Wada S, Makino A, Ishida H (2010) The autophasic degradation of chloroplasts via Rubisco containing bodies is specifically linked to leaf carbon status but not nitrogen status in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 154:1196–1209
Jiménez A, Hernandez JA, Pastori G, del Rio LA, Sevilla F (1998) Role of the ascorbate–glutathione cycle of mitochondria and peroxisomes in the senescence of pea leaves. Plant Physiol 118:1327–1335
Jing H-C, Hebelar R, Oeljeklaus S, Sitek B, Stühler K, Meyer HE, Sturre MJG, Hille J, Warscheid B, Dijkwel PP (2008) Early leaf senescence is associated with an altered cellular redox balance in Arabidopsis crp5/old1 mutants. Plant Biol 10:85–98
Jing H-C, Schippers JHM, Hiller J, Djikwel DP (2005) Ethylene-induced leaf senescence depends on age-related changes and OLD genes in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 56:2915–2923
Jubany-Marí T, Munné-Bosch S, Alegre L (2010) Redox regulation of water stress responses in field-grown plants: role of hydrogen peroxide and ascorbate. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:351–358
Khanna-Chopra R (1983) Effects of temperature on the in vivo assay of nitrate reducatse in some C3 and C4 species. Ann Bot 51:31–34
Khanna-Chopra R, Jajoo A, Semwal VK (2011) Chloroplasts and mitochondria have multiple heat tolerant isozymes of SOD and APX in leaf and inflorescence in Chenopodium album. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.179
Khanna-Chopra R, Sabarinath S (2004) Heat stable chloroplastic Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase in Chenopodium murale. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 320:1187–1192
Khanna-Chopra R, Selote DS (2007) Acclimation to drought stress generates oxidative stress tolerance in drought-resistant than -susceptible wheat cultivar under field conditions. Environ Exp Bot 60:276–283
Khanna-Chopra R, Srivalli B, Ahlawat YS (1999) Drought induces many forms of cysteine proteases not observed during natural senescence. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 225:324–327
Khanna-Chopra R, Srivalli S (2008) Interaction of reproductive sink and abiotic stress with monocarpic senescence: molecular analysis. Indian Agriculturist 52:135–149
Kong Z, Li M, Yang W, Xu W, Xue Y (2006) A novel nuclear-localized CCCH-type zinc finger protein, OsDOS, is involved in delaying leaf senescence in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physol 141:1376–1388
Kukavica B, Veljovic-Jovanovic S (2004) Senescence-related changes in the antioxidant status of ginkgo and birch leaves during autumn yellowing. Physiol Plant 122:321–327
Larkindale J, Huang B (2004) Thermotolerance and antioxidant systems in Agarostis stolonifera: involvement of salicyclic acid, abscisic acid, calcium, hydrogen peroxide and ethylene. J Plant Physiol 161:405–413
Larkindale J, Knight MR (2002) Protection against heat stress-induced oxidative damage in Arabidopsis involves calcium, abscisic acid, ethylene, and salicylic acid. Plant Physiol 128:682–695
Lim PO, Kim HJ, Nam HG (2007) Leaf senescence. Ann Rev Plant Biol 58:115–136
Lohman KN, Gan S, Manorama CJ, Amasino R (1994) Molecular analysis of natural leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol Plant 92:322–328
Marín-Navarro J, Moreno J (2006) Cysteines 449 and 459 modulate the reduction–oxidation conformational changes of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and the translocation of the enzyme to membranes during stress. Plant Cell Environ 29:898–908
Mariya K, Courtney S, Qian W, Imara YP, Wendy FB, Christopher SB, Heike WS (2010) Increasing inositol(1,4,5)-triphosphate metabolism affects drought tolerance, carbohydrate metabolism and phosphate-sensitive biomass increases in tomato. Plant Biotech J 8:170–183
Martínez DE, Bartoli CG, Grbic V, Guiamet JJ (2007) Vacuolar cysteine proteases of wheat (Triticum astivum L.) are common to leaf senescence induced by different factors. J Exp Bot 58:1099–1107
Mittler R (2006) Abiotic stresses, the field environment and stress combination. Trends Plant Sci 11:15–19
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery, Van Breusegem F (2004) The reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498
Moreno J, Penarubbia L, Gracia-Ferris C (1995) The mechanism of redox regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase turnover. A hypothesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 33:121–127
Munné-Bosch S, Alegre L (2002) Plant ageing increases oxidative stress in chloroplasts. Planta 214:608–615
Müntz K (2007) Protein dynamics and proteolysis in plant vacuoles. J Exp Bot 58:2391–2407
Navabpour S, Morris K, Allen R, Harrison E, AH-Mackerness S, Buchanan-Wollaston V (2003) Expression of senescence-enhanced genes in response to oxidative stress. J Exp Bot 54:2285–2292
Navari-Izzo F, Pinzino C, Quartacci MF, Sgherri CLM (1999) Superoxide and hydroxyl radical generation, and superoxide dismutase in PS II membrane fragments from wheat. Free Radic Res 31:S3–S9
Noctor G, Veljovic-Jovanovic S, Foyer CH (2000) Peroxide processing in photosynthesis: antixoxidant coupling and redox signalling. Phil Trans Roy Soc B 355:1465–1475
Noctor G, Queval G, Gakière B (2006) NAD (P) synthesis and pyridine nucleotide cycling in plants and their potential importance in stress conditions. J Exp Bot 57:1603–1620
Oberhuber M, Breghold J, Breuker K, Hörtensteiner S, Kräutler B (2003) Breakdown of chlorophyll: a nonenzymatic reaction accounts of the formation of colourless “nonfluorescent” chlorophyll catabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6910–6915
Orendi G, Zimmermann P, Baar C, Zentgraf U (2001) Loss of stress-induced expression of catalase3 during leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana is restricted to oxidative stress. Plant Sci 161:301–314
Otegui MS, Noh Y-S, Martínez DE, Petroff MGV, Staehelin LA, Amasino RM, Guiamet JJ (2005) Senescence-associated vacuoles with intense proteolytic activity develop in leaves of Arabidopsis and soybean. Plant J 41:831–844
Overmyer K, Tuominen H, Kettunen R, Betz C, Langebartels C, Sandermann H Jr, Kangasjärvi J (2000) Ozone-sensitive Arabidopsis rcd1 mutant reveals opposite roles for ethylene and jasmonate signaling pathways in regulating superoxide-dependent cell death. Plant Cell 12:1849–1862
Pavet V, Olmos E, Kiddle G, Mowla S, Kumar S, Antoniw J, Alvarez ME, Foyer CH (2005) Ascorbic acid deficiency activate cell death and disease resistance responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:1291–1303
Pell EJ, Schlagnhaufer CD, Arteca RN (1997) Ozone-induced oxidative stress: mechanisms of action and reaction. Physiol Plant 100:264–273
Prasad TK, Anderson MD, Martin BA, Stewart CR (1994) Evidence for chilling-induced oxidative stress in maize seedlings and a regulatory role for hydrogen peroxide. Plant Cell 6:65–74
Prins A, van Heerden PDR, Olmos E, Kunert KJ, Foyer CH (2008) Cysteine proteinases regulate chloroplast protein content and composition in tobacco leaves: a model for dynamic interactions with ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) vesicular bodies. J Exp Bot 59:1935–1950
Queval G, Noctor G (2007) A plate-reader method for the measurement of NAD, NADP, glutathione and ascorbate in tissue extracts. Application to redox profiling during Arabidopsis rosette development. Anal Biochem 363:58–69
Revero RM, Ruiz JM, Remero LM (2004) Importance of N source on heat stress tolerance due to the accumulation of proline and quaternary ammonium compounds in tomato plants. Plant Biol 6:702–707
Rosenwasser S, Rot I, Sollner E, Meyer AJ, Smith Y, Leviatan N, Fluhr R, Friedman H (2011) Organelles contribute differentially to ROS-related events during extended darkness. Plant Physiol 156:185–201. doi:10.1104/pp.110.169797
Rosenvasser S, Mayak S, Friedman H (2006) Increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) and in senescence-associated gene transcript (SAG) levels during dark-induced senescence of Pelargonium cuttings, and the effect of gibberellic acid. Plant Sci 170:873–879
Roulin S, Feller U (1998) Dithiothreitol triggers photooxidative stress and fragmentation of the large subunit of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in intact pea chloroplasts. Plant Physiol Biochem 36:849–856
Schaffer MA, Fischer RL (1988) Analysis of mRNAs that accumulate in response to low temperature identifies a thiol protease gene in tomato. Plant Physiol 87:431–436
Schelbert S, Aubry S, Burla B, Agne B, Kessler F, Krupinska K, Hörtensteiner S (2009) Pheophytin pheophorbide hydrolase (pheophytinase) is involved in chlorophyll breakdown during leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:767–785
Selote DS, Khanna-Chopra R (2004) Drought induced spikelet sterility is associated with an inefficient antioxidant defense in rice panicle. Physiol Plant 121:462–471
Selote DS, Khanna-Chopra R (2006) Drought-acclimation confers oxidative stress tolerance by inducing coordinated antioxidant defense at cellular and sub-cellular level in leaves of wheat seedlings. Physiol Plant 127:494–506
Srivalli B, Bharti S, Khanna-Chopra R (2001) Vacuolar cysteine proteases and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase degradation during monocarpic senescence in cowpea leaves. Photosynthetica 39:87–93
Srivalli B, Sharma G, Khanna-Chopra R (2003) Antioxidative defense system in an upland rice cultivar subjected to increasing intensity of water stress followed by recovery. Physiol Plant 119:503–512
Srivalli S, Khanna-Chopra R (2006) Drought stress during pod development in cowpea induces loss in ribulose-1,5 bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and an increase in cysteine proteases. J Plant Biol 33:22–31
Srivalli S, Khanna-Chopra R (2009) Delayed wheat flag leaf senescence due to removal of spikelets is associated with increased activities of leaf antioxidant enzymes, reduced glutathione/oxidized glutathione ratio and oxidative damage to mitochondrial proteins. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:663–670
Stone SL, Hauksdottir H, Troy A, Herschleb J, Kraft E, Cullis J (2005) Functional analysis of the RING-type ubiquitin ligase family of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 137:317–327
Suzuki N, Mittler R (2006) Reactive oxygen species and temperature stresses: a delicate balance between signaling and destruction. Physiol Plant 126:45–51
Tamaoki M, Matsuyama T, Kanna M, Nakajima N, Kubo A, Aono M, Saji H (2003) Differential ozone sensitivity among Arabidopsis accessions and its relevance to ethylene synthesis. Planta 216:552–560
Theriault A, Wang Q, Van Iderstine SC, Chen B, Frankee AA, Adeli K (2000) Modulation of hepatic lipoprotein synthesis and secretion by taxifolin, a plant flavonoid. J Lipid Res 41:1969–1979
Thoenen M, Feller U (1998) Degradation of glutamine synthetase in intact chloroplasts isolated from pea (Pisum sativum) leaves. Aust J Plant Physiol 25:279–286
Thoenen M, Herrmann B, Feller U (2007) Senescence in wheat leaves: is a cysteine endopeptidase involved in the degradation of the large subunit of Rubisco? Acta Physiol Plant 29:339–350
Thomas H, Ougham H, Canter P, Donnison I (2002) What stay-green mutants tell us about nitrogen remobilization in leaf senescence. J Exp Bot 53:801–808
Vacca RA, de Pinto MC, Valenti D, Passarella S, Marra E, De Gara L (2004) Production of reactive oxygen species, alteration of cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase and impairment of mitochondrial metabolism are early events in heat shock induced programmed cell death in tobacco Bright-Yellow 2 cells. Plant Physiol 134:1100–1112
Vanacker H, Sandalio LM, Jimenez A, Palma JM, Corpas FJ, Meseguer V, Gomez M, Sevilla F, Leterrir M, Foyer CH, del Rio LA (2006) Role of redox regulation in leaf senescence of pea plants grown in different sources of nitrogen nutrition. J Exp Bot 57:1735–1745
Vinocur B, Altman A (2005) Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stresses: achievements and limitations. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:123–132
Wada S, Ishida H, Izumi M, Yoshimoto K, Ohsumi Y, Mae T, Makino A (2009) Autophagy plays a role in chloroplast degradation during senescence in individually darkened leaves. Plant Physiol 149:885–893
Wise RR (1995) Chilling-enhanced photooxidation: the production, action and study of reactive oxygen species produced during chilling in the light. Photosyn Res 45:79–97
Woo HR, Goh CH, Park JH, de la Serve BT, Kim JH, Park YI, Nam HG (2002) Extended leaf longevity in the ore4-1mutant of Arabidopsis with a reduced expression of plastid ribosomal protein gene. Plant J 31:331–340
Woo HR, Kim JH, Nam HG, Lim PO (2004) The delayed leaf senescence mutants of Arabidopsis, ore1, ore3, and ore9 are tolerant to oxidative stress. Plant Cell Physiol 45:923–932
Xu S, Li J, Zhang X, Wei H, Cui L (2006) Effects of heat acclimation pretreatment on changes of membrane lipid peroxidation, antioxidant metabolites, and ultrastructure of chloroplasts in two cool-season turfgrass species under heat stress. Environ Exp Bot 53:274–285
Xue-Xuan X, Hong-Bo S, Yuan-Yuan S, Gang X, Jun-Na S, Dong-Gang G, Cheng-Jiang R (2010) Biotechnological implications from abscisic acid (ABA) roles in cold stress and leaf senescence as an important signal for improving plant sustainable survival under abiotic stressed conditions. Critical Rev in Biotech 30(3):222–230
Xing D, Zhang L (2008) Methyl jasmonate induces production of reactive oxygen species and alterations in mitochondrial dynamics that precede photosynthetic dysfunction and subsequent cell death. Plant Cell Physiol 49(7):1092–1111
Ying W (2008) NAD/NADH and NADP/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death: regulation and biological consequences. Antiox Red Signal 10:179–206
Zimmermann P, Zentgraf U (2005) The correlation between oxidative stress and leaf senescence during plant development. Cell Mol Biol Lett 10:515–534
Zimmermann P, Heinlein C, Orendi G, Zentgraf U (2006) Senescence-specific regulation of catalase in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Cell Environ 29:1049–1056
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the grants of the National Fellow and ICAR-NPTC scheme of Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, India.
Conflict of interest
The author has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khanna-Chopra, R. Leaf senescence and abiotic stresses share reactive oxygen species-mediated chloroplast degradation. Protoplasma 249, 469–481 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-011-0308-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-011-0308-z