Abstract
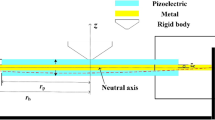
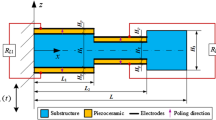
This paper presents the techniques for formulating the multiple segmented smart plate structures with different circuit connection patterns using the electromechanical finite element dynamic analysis. There are three major contributions in the proposed numerical studies. First, the electromechanical discretization has been developed for generalizing the coupled system of Kirchhoff’s smart plate structures with circuit connection patterns. Such constitutive numerical models reduced from the extended Lagrange equations can be used for the physical systems including, but not restricted to, the multiple piezoelectric and electrode segments. Second, the multiple piezoelectric or electrode segments can be arranged electrically in parallel, series, and mixed series–parallel connections with the on–off switching techniques where the electrical outputs of each connection are further connected with the standard AC–DC circuit interfaces. Third, the coupling transformation technique (CTT) has been introduced by modifying the orthonormalized global element matrices into the scalar form equations. As a result, the multimode frequency response function and time-waveform signal response equations are distinctly formulated for each circuit connection. Further parametric numerical case studies are also discussed in this paper. The benefit of using the circuit connection patterns with the on–off switching techniques is that the studies can be used for an adaptive vibration power harvester.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tzou, H.S., Tseng, C.I.: Distributed vibration control and identification of coupled elastic/piezoelectric systems: finite element formulation and applications. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 5, 215–231 (1991)
Saravanos, D.A., Heyliger, P.R., Hopkins, D.A.: Layerwise mechanics and finite element for the dynamics analysis of piezoelectric composite plate. Int. J. Solids Struct. 34, 359–378 (1996)
Lam, K.Y., Peng, X.Q., Liu, G.R., Reddy, J.N.: A finite element model for piezoelectric composite laminates. Smart Mater. Struct. 6, 583–591 (1997)
Detwiler, D.T., Shen, H.M.-H., Venkayya, V.B.: Finite element analysis of laminated composite structures containing distributed piezoelectric actuators and sensors. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 20, 87–100 (1995)
Krommer, M., Irschik, H.: A Reissner–Mindlin type plate theory including the direct piezoelectric and the pyroelectric effect. Acta Mech. 141, 51–69 (2000)
Ray, M.C., Sachade, H.M.: Finite element analysis of smart functionally graded plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43(18–19), 5468–5484 (2006)
Krommer, M.: On the correction of the Bernoulli–Euler beam theory for smart piezoelectric beams. Smart Mater. Struct. 10, 668–680 (2001)
Krommer, M., Irschik, H.: An electromechanically coupled theory for piezoelastic beams taking into account the charge equation of electrostatics. Acta Mech. 154, 141–158 (2002)
Fernandes, A., Pouget, J.: Analytical and numerical approach to piezoelectric bimorph. Int. J. Solids Struct. 40, 4331–4352 (2003)
Moita, J.M., Correia, I.F.P., Soares, C.M.M.: Active control of adaptive laminated structures with bounded piezoelectric sensors and actuators. Comput. Struct. 82(17–19), 1349–1358 (2004)
Wang, S.Y.: A finite element model for the static and dynamic analysis of a piezoelectric bimorph. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 4075–4096 (2004)
Deü, J.-F., Benjeddou, A.: Free-vibration analysis of laminated plates with embedded shear-mode piezoceramic layers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 42(7), 2059–2088 (2005)
Irschik, H., Krommer, M., Belyaev, A.K., Schlacher, A.K.: Shaping of piezoelectric sensors/actuators for vibrations of slender beams: coupled theory and inappropriate shape functions. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 9, 546–554 (1998)
Maurini, C., Dell’Isola, F., Del Vescovo, D.: Comparison of piezoelectric networks acting as distributed vibration absorbers. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 18(5), 1243–1271 (2004)
Thomas, O., Deü, J.-F., Ducarne, J.: Vibrations of an elastic structure with shunted piezoelectric patches: efficient finite element formulation and electromechanical coupling coefficients. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 8, 235–268 (2009)
Vasques, C.M.A.: Improved passive shunt vibration control of smart piezo-elastic beams using modal piezoelectric transducers with shaped electrodes. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 125003 (2012)
Schoeftner, J., Krommer, M.: Single point vibration control for a passive piezoelectric Bernoulli–Euler beam subjected to spatially varying harmonic loads. Acta Mech. 223, 1983–1998 (2012)
Lossouarn, B., Deü, J.-F., Aucejo, M., Cunefare, K.A.: Multimodal vibration damping of a plate by piezoelectric coupling to its analogous electrical network. Smart Mater. Struct. 25, 115042 (2016)
Roundy, S., Wright, P.K.: A piezoelectric vibration based generator for wireless electronics. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 1131–1142 (2004)
Lefeuvre, E., Badel, A., Richard, C., Petit, L., Guyomar, D.: A comparison between several vibration-powered piezoelectric generators for standalone systems. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 126, 405–416 (2006)
Shu, Y.C., Lien, I.C.: Analysis of power outputs for piezoelectric energy harvesting systems. Smart Mater. Struct. 15, 1499–1512 (2006)
Shu, Y.C., Lien, I.C., Wu, W.J.: An improved analysis of the SSHI interface in piezoelectric energy harvesting. Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 2253–2264 (2007)
Lallart, M., Guyomar, D.: An optimized self-powered switching circuit for nonlinear energy harvesting with low voltage output. Smart Mater. Struct. 17, 035030 (2008)
Kim, M., Hoegen, M., Dugundji, J., Wardle, B.L.: Modeling and experimental verification of proof mass effects on vibration energy harvester performance. Smart Mater. Struct. 19, 045023 (2010)
Goldschmidtboeing, F., Woias, P.: Characterization of different beam shapes for piezoelectric energy harvesting. J. Micromech. Microeng. 18, 104013 (2008)
Dalzell, P., Bonello, P.: Analysis of an energy harvesting piezoelectric beam with energy storage circuit. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 105029 (2012)
Erturk, A.: Assumed-modes modeling of piezoelectric energy harvesters: Euler–Bernoulli, Rayleigh, and Timoshenko models with axial deformations. Comput. Struct. 106–107, 214–227 (2012)
Wang, H., Meng, Q.: Analytical modeling and experimental verification of vibration-based piezoelectric bimorph beam with a tip-mass for power harvesting. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 36, 193–209 (2013)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Analytical and experimental comparisons of electromechanical vibration response of a piezoelectric bimorph beam for power harvesting. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 36, 66–86 (2013)
Adhikari, S., Friswell, M.I., Inman, D.J.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting from broadband random vibrations. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 115005 (2009)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Parametric design-based modal damped vibrational piezoelectric energy harvesters with arbitrary proof mass offset: numerical and analytical validations. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 68, 562–586 (2016)
Tang, L., Wang, J.: Size effect of tip mass on performance of cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvester with a dynamic magnifier. Acta Mech. 228(11), 3997–4015 (2017)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Intrinsic electromechanical dynamic equations for piezoelectric power harvesters. Acta Mech. 228(2), 631–650 (2017)
Wickenheiser, A.M.: Eigensolution of piezoelectric energy harvesters with geometric discontinuities: analytical modelling and validation. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 24, 729–744 (2013)
Zhou, S., Hobeck, J.D., Cao, J., Inman, D.J.: Analytical and experimental investigation of flexible longitudinal zigzag structures for enhanced multi-directional energy harvesting. Smart Mater. Struct. 26, 035008 (2017)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Effect of shunted piezoelectric control for tuning piezoelectric power harvesting system responses–analytical techniques. Smart Mater. Struct. 24, 105029 (2015)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Electromechanical analysis of an adaptive piezoelectric energy harvester controlled by two segmented electrodes with shunt circuit networks. Acta Mech. 228(4), 1321–1341 (2017)
Lumentut, M.F., Francis, L.A., Howard, I.M.: Analytical techniques for broadband multielectromechanical piezoelectric bimorph beams with multifrequency power harvesting. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 59, 1555–1568 (2012)
Zhang, H., Afzalul, K.: Design and analysis of a connected broadband multi-piezoelectric-bimorph-beam energy harvester. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 61, 1016–1023 (2014)
Xiong, X., Oyadiji, S.O.: Modal optimization of doubly clamped base-excited multilayer broadband vibration energy harvesters. J. Intel. Mat. Syst. Struct. 26(16), 2216–2241 (2014)
Lien, I.C., Shu, Y.C.: Array of piezoelectric energy harvesting by the equivalent impedance approach. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 082001 (2012)
Lin, H.C., Wu, P.H., Lien, I.C., Shu, Y.C.: Analysis of an array of piezoelectric energy harvesters connected in series. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 094026 (2013)
Wu, P.H., Shu, Y.C.: Finite element modeling of electrically rectified piezoelectric energy harvesters. Smart Mater. Struct. 24, 094008 (2015)
Aridogan, U., Basdogan, I., Erturk, A.: Multiple patch-based broadband piezoelectric energy harvesting on plate-based structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct 25(14), 1664–1680 (2014)
Bayik, B., Aghakhani, A., Basdogan, I., Erturk, A.: Equivalent circuit modeling of a piezo-patch energy harvester on a thin plate with AC–DC conversion. Smart Mater. Struct. 25, 055015 (2016)
Yoon, H., Youn, B.D., Kim, H.S.: Kirchhoff plate theory-based electromechanically-coupled analytical model considering inertia and stiffness effects of a surface-bonded piezoelectric patch. Smart Mater. Struct. 25, 025017 (2016)
Samanta, B., Ray, M.C., Bhatacharya, R.: Finite element model for active control of intelligent structures. AIAA J. 34(9), 1885–1893 (1996)
Liu, G.R., Dai, K.Y., Lim, K.M.: Static and vibration control composite laminates integrated with piezoelectric sensors and actuators using the radial point interpolation method. Smart Mater. Struct. 13, 1438–1447 (2004)
Kapuria, S., Yaqoob Yasin, M.: Active vibration control of smart plates using directional actuation and sensing capability of piezoelectric composites. Acta Mech. 224, 1185–1199 (2013)
Venkata, R.K., Raja, S., Munikenche Gowda, T.: Finite element modelling and vibration control study of active plate with debonded piezoelectric actuators. Acta Mech. 225, 2923–2942 (2014)
Elvin, N.G., Elvin, A.A.: Coupled finite element-circuit simulation model for analyzing piezoelectric energy generators. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 20, 587–595 (2009)
Friswell, M.I., Adhikari, S.: Sensor shape design for piezoelectric cantilever beams to harvest vibration energy. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 014901 (2010)
DeMarqui Jr., J., Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: An electromechanical finite element model for piezoelectric energy harvester plates. J. Sound Vib. 327(1–2), 9–25 (2009)
Aladwani, A., Arafa, M., Aldraihem, O., Baz, A.: Cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvester with a dynamic magnifier. J. Vib. Acoust. 134, 031004 (2012)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Electromechanical finite element modelling for dynamic analysis of a cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvester with tip mass offset under base excitations. Smart Mater. Struct. 23(9), 095037 (2014)
Tiersten, H.F.: Linear Piezoelectric Plate Vibrations. Plenum, New York (1969)
Nye, J.F.: Physical Properties of Crystals: Their Representation by Tensors and Matrices. Clarendon, Oxford (1984)
Ikeda, T.: Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity. Oxford University Press, New York (1990)
Lumentut, M.F.: Mathematical dynamics of electromechanical piezoelectric energy harvester. PhD Thesis Curtin University, Australia (2011). http://espace.library.curtin.edu.au/R/?func=dbin-jump-full&object_id=186549&local_ base=gen01-era02
Kirchhoff, G.R.: Über das Gleichgewicht und die Bewegung einer elastischen Scheibe. J. Reine Angew. Math. 40, 51–88 (1850)
Sokolnikoff, I.S.: Mathematical Theory of Elasticity, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York (1956)
Adini, A., Clough, R.W.: Analysis of plate bending by the finite element method. Report submitted to the National Science Foundation, G7337 (1960)
Melosh, R.J.: Basis for derivation of matrices for the direct stiffness method. AIAA J. 1, 1631–1637 (1963)
Petyt, M.: Introduction to Finite Element Vibration Analysis, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Ottman, G.K., Hofmann, H.F., Bhatt, A.C., Lesieutre, G.A.: Adaptive piezoelectric energy harvesting circuit for wireless remote power supply. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 17(5), 669–676 (2002)
http://www.efunda.com/materials/piezo/material_data/matdata_output.cfm?Material_ID=PZT-5A. Accessed 15 Jan 2017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lumentut, M.F., Shu, Y.C. A unified electromechanical finite element dynamic analysis of multiple segmented smart plate energy harvesters: circuit connection patterns. Acta Mech 229, 4575–4604 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-018-2249-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-018-2249-5