Abstract
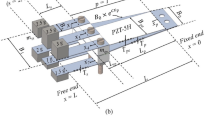
This paper presents an adaptive power harvester using a shunted piezoelectric control system with segmented electrodes. This technique has spurred new capability for widening the three simultaneous resonance frequency peaks using only a single piezoelectric laminated beam where normally previous works only provide a single peak for the resonance at the first mode. The benefit of the proposed techniques is that it provides effective and robust broadband power generation for application in self-powered wireless sensor devices. The smart structure beam with proof mass offset is considered to have simultaneous combination between vibration-based power harvesting and shunt circuit control-based electrode segments. As a result, the system spurs new development of the two mathematical methods using electromechanical closed-boundary value techniques and Ritz method-based weak-form analytical approach. The two methods have been used for comparison giving accurate results. For different electrode lengths using certain parametric tuning and harvesting circuit systems, the technique enables the prediction of the power harvesting that can be further proved to identify the performance of the system using the effect of varying circuit parameters so as to visualize the frequency and time waveform responses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roundy, S., Wright, P.K., Rabaey, J.: A study of low level vibrations as a power source for wireless sensor nodes. Comput. Commun. 26, 1131–1144 (2003)
Chao, P.C.-P.: Energy harvesting electronics for vibratory devices in self-powered sensors. IEEE Sensor J. 11, 3106–3121 (2011)
Sue, C.-Y., Tsai, N.-C.: Human powered MEMS-based energy harvest devices. Appl. Energy 93, 390–403 (2012)
Abdelkefi, A., Alothman, A., Hajj, M.R.: Performance analysis and validation of thermoelectric energy harvesters. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 095014 (2013)
Li, Y., Zeynep, C.-B., Butler, D.P.: A hybrid electrostatic micro-harvester incorporating in-plane overlap and gap closing mechanisms. J. Micromech. Microeng. 25, 035027 (2015)
Mann, B.P., Sims, N.D.: Energy harvesting from the nonlinear oscillations of magnetic levitation. J. Sound Vib. 319, 515–530 (2009)
Wang, X., Liang, X., Wei, H.: A study of electromagnetic vibration energy harvesters with different interface circuits. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 58–59, 376–398 (2015)
Roundy, S., Wright, P.K.: A piezoelectric vibration based generator for wireless electronics. Smart Mater. Struct. 13, 1131–1142 (2004)
Erturk, A.: Assumed-modes modeling of piezoelectric energy harvesters: Euler–Bernoulli, Rayleigh, and Timoshenko models with axial deformations. Comput. Struct. 106–107, 214–227 (2012)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Parametric design-based modal damped vibrational piezoelectric energy harvesters with arbitrary proof mass offset: numerical and analytical validations. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 68–69, 562–586 (2015)
Krommer, M., Irschik, H.: An electromechanically coupled theory for piezoelastic beams taking into account the charge equation of electrostatics. Acta Mech. 154, 141–158 (2002)
Krommer, M.: On the correction of the Bernoulli–Euler beam theory for smart piezoelectric beams. Smart Mater. Struct. 10, 668–680 (2001)
Irschik, H., Krommer, M., Belyaev, A.K., Schlacher, A.K.: Shaping of piezoelectric sensors/actuators for vibrations of slender beams: coupled theory and inappropriate shape functions. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 9, 546–554 (1998)
Krommer, M., Zellhofer, M., Heilbrunner, K.-H.: Strain-type sensor networks for structural monitoring of beam-type structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 20, 1875–1888 (2003)
Krommer, M., Irschik, H.: A Reissner-Mindlin-type plate theory including the direct piezoelectric and the pyroelectric effect. Acta Mech. 141, 51–69 (2000)
Krommer, M.: On the influence of pyroelectricity upon thermally induced vibrations of piezothermoelastic plates. Acta Mech. 171, 59–73 (2004)
Tzou, H.S., Tseng, C.I.: Distributed vibration control and identification of coupled elastic/piezoelectric systems: finite element formulation and applications. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 5, 215–231 (1991)
Krommer, M., Irschik, H.: Sensor and actuator design for displacement control of continuous systems. Smart Struct. Syst. 3, 147–172 (2007)
Kapuria, S., Yasin, M.Y.: Active vibration control of smart plates using directional actuation and sensing capability of piezoelectric composites. Acta Mech. 224, 1185–1199 (2013)
dell’Isola, F., Maurini, C., Porfiri, M.: Passive damping of beam vibrations through distributed electric networks and piezoelectric transducers: prototype design and experimental validation. Smart Mater. Struct. 13, 299–308 (2004)
Niederberger, D., Morari, M.: An autonomous shunt circuit for vibration damping. Smart Mater. Struct. 15, 359–364 (2006)
Schoeftner, J., Irschik, H.: Passive damping and exact annihilation of vibrations of beams using shaped piezoelectric layers and tuned inductive networks. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 125008 (2009)
Schoeftner, J., Krommer, M.: Single point vibration control for a passive piezoelectric Bernoulli-Euler beam subjected to spatially varying harmonic loads. Acta Mech. 223, 1983–1998 (2012)
Vasques, C.M.A.: Improved passive shunt vibration control of smart piezo-elastic beams using modal piezoelectric transducers with shaped electrodes. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 125003 (2012)
Shu, Y.C., Lien, I.C.: Analysis of power outputs for piezoelectric energy harvesting systems. Smart Mater. Struct. 15, 1499–1512 (2006)
Guyomar, D., Badel, A., Lefeuvre, E., Richard, C.: Toward energy harvesting using active materials and conversion improvement by nonlinear processing. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 52, 584–595 (2005)
Shu, Y.C., Lien, I.C., Wu, W.J.: An improved analysis of the SSHI interface in piezoelectric energy harvesting. Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 2253–2264 (2007)
Wang, X., Lin, L.: Dimensionless optimization of piezoelectric vibration energy harvesters with different interface circuits. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 1–20 (2013)
Liao, Y., Sodano, H.: Modeling and comparison of bimorph power harvesters with piezoelectric elements connected in parallel and series. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 21, 149–159 (2010)
Kim, M., Hoegen, M., Dugundji, J., Wardle, B.L.: Modeling and experimental verification of proof mass effects on vibration energy harvester performance. Smart Mater. Struct. 19, 045023 (2010)
Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: An experimentally validated bimorph cantilever model for piezoelectric energy harvesting from base excitations. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 025009 (2009)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Analytical and experimental comparisons of electromechanical vibration response of a piezoelectric bimorph beam for power harvesting. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 36, 66–86 (2013)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Analytical modeling of self-powered electromechanical piezoelectric bimorph beams with multidirectional excitation. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2, 134–175 (2011)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Electromechanical piezoelectric power harvester frequency response modelling using closed-form boundary value methods. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 19, 32–44 (2014)
Wickenheiser, A.M.: Eigensolution of piezoelectric energy harvesters with geometric discontinuities: Analytical modelling and validation. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 24, 729–744 (2013)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Electromechanical finite element modelling for dynamic analysis of a cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvester with tip mass offset under base excitations. Smart Mater. Struct. 23, 095037 (2014)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Intrinsic electromechanical dynamic equations for piezoelectric power harvesters. Acta Mech. (2016). doi:10.1007/s00707-016-1726-y
Lumentut, M.F., Francis, L.A., Howard, I.M.: Analytical techniques for broadband multielectromechanical piezoelectric bimorph beams with multifrequency power harvesting. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 59, 1555–1568 (2012)
Lien, I.C., Shu, Y.C.: Array of piezoelectric energy harvesting by the equivalent impedance approach. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 082001 (2012)
Xiong, X., Oyadiji, S.O.: Modal optimization of doubly clamped base-excited multilayer broadband vibration energy harvesters. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 26, 2216–2241 (2015)
Wu, P.H., Shu, Y.C.: Finite element modeling of electrically rectified piezoelectric energy harvesters. Smart Mater. Struct. 24, 094008 (2015)
Giorgio, I., Culla, A., Del Vescovo, D.: Multimode vibration control using several piezoelectric transducers shunted with a multiterminal network. Arch. Appl. Mech. 79, 859–879 (2009)
Thomas, O., Ducarne, J., Deu, J.-F.: Performance of piezoelectric shunts for vibration reduction. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 015008 (2012)
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M.: Effect of shunted piezoelectric control for tuning piezoelectric power harvesting system responses—analytical techniques. Smart Mater. Struct. 24, 105029 (2015)
Ikeda, T.: Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity. Oxford University Press, New York (1990)
Tichý, J., Erhart, J., Kittinger, E., Prívratská, J.: Fundamentals of Piezoelectric Sensorics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2010)
Antoniou, A.: Gyrators using operational amplifiers. Electron. Lett. 3, 350–352 (1967)
Riordan, R.H.S.: Simulated inductors using differential amplifiers. Electron. Lett. 3, 50–51 (1967)
Moheimani, S.O.R., Fleming, A.J.: Piezoelectric Transducers for Vibration Control and Damping. Springer, London (2006)
Ritz, W.: Über eine neue Methode zur Lösung gewisser Variationsprobleme der mathematischen Physik. J. Reine Angew. Math. 135, 1–61 (1909)
Courant, R., Hilbert, D.: Methoden der mathematischen Physik (Methods of mathematical physics). Interscience Publishers, vol. 1–2, New York, (1953–1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lumentut, M.F., Howard, I.M. Electromechanical analysis of an adaptive piezoelectric energy harvester controlled by two segmented electrodes with shunt circuit networks. Acta Mech 228, 1321–1341 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-016-1775-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-016-1775-2