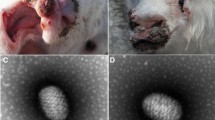
Abstract
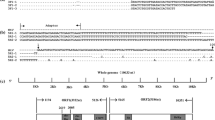
Orf virus (ORFV) is a typical member of the genus Parapoxvirus. The parapoxvirus genome consists of highly variable terminal regions and relatively conserved central regions with a high G + C content. In our previous study, a novel ORFV strain, NA1/11, was isolated from northeastern China. To fully characterize this strain, we sequenced the entire genome of NA1/11 and conducted a comparative analysis using multiple parapoxviruses. The genomic sequence of NA1/11 was found to consist of 137,080 nucleotides with a G + C content of 63.6 %, but it did not contain the terminal hairpin sequence. Alignment of ORFs from NA1/11 with NZ2, IA82 and SA00 revealed several highly variable ORFs, while the most evident ones are ORFs 001, 103, 109–110, 116 and 132. An odd phenomenon in the region of ORFs 118–120 is that the non-coding fragments are almost as long as the coding fragments. By comparative analysis of inverted terminal repeats, we identified one repeat motif and a long conserved fragment. By comparing the ITRs of SA00 with those of three other ORFVs, more clues were obtained about the correlation between ITR sequence and host adaption. Comparison of the NA1/11 genome with the sequences of other strains of ORFV revealed highly variable regions, thus providing new insights into the genetic diversity of ORFV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hosamani M, Scagliarini A, Bhanuprakash V, McInnes CJ, Singh RK (2009) Orf: an update on current research and future perspectives. Expert Rev Anti-infect Ther 7(7):879–893. doi:10.1586/eri.09.64
Bora DP, Barman NN, Das SK, Bhanuprakash V, Yogisharadhya R, Venkatesan G, Kumar A, Rajbongshi G, Khatoon E, Chakraborty A, Bujarbaruah KM (2012) Identification and phylogenetic analysis of orf viruses isolated from outbreaks in goats of Assam, a northeastern state of India. Virus Genes 45(1):98–104. doi:10.1007/s11262-012-0740-y
Kottaridi C, Nomikou K, Teodori L, Savini G, Lelli R, Markoulatos P, Mangana O (2006) Phylogenetic correlation of Greek and Italian orf virus isolates based on VIR gene. Veterinary Microbiol 116(4):310–316. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2006.04.020
Lojkic I, Cac Z, Beck A, Bedekovic T, Cvetnic Z, Sostaric B (2010) Phylogenetic analysis of Croatian orf viruses isolated from sheep and goats. Virol J 7:314. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-7-314
Oem JK, Roh IS, Lee KH, Lee KK, Kim HR, Jean YH, Lee OS (2009) Phylogenetic analysis and characterization of Korean orf virus from dairy goats: case report. Virol J 6:167. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-6-167
Venkatesan G, Balamurugan V, Bora DP, Yogisharadhya R, Prabhu M, Bhanuprakash V (2011) Sequence and phylogenetic analyses of an Indian isolate of orf virus from sheep. Veterinaria italiana 47(3):323–332
Haig DM, Mercer AA (1998) Ovine diseases. Orf. Veterinary Res 29(3–4):311–326
Li W, Ning Z, Hao W, Song D, Gao F, Zhao K, Liao X, Li M, Rock DL, Luo S (2012) Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of orf virus from the sheep herd outbreak in northeast China. BMC Veterinary Res 8:229. doi:10.1186/1746-6148-8-229
Zhao K, Song D, He W, Lu H, Zhang B, Li C, Chen K, Gao F (2010) Identification and phylogenetic analysis of an Orf virus isolated from an outbreak in sheep in the Jilin province of China. Veterinary Microbiol 142(3–4):408–415. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.10.006
Zhang K, Shang Y, Jin Y, Wang G, Zheng H, He J, Lu Z, Liu X (2010) Diagnosis and phylogenetic analysis of Orf virus from goats in China: a case report. Virol J 7:78. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-7-78
Li H, Zhu X, Zheng Y, Wang S, Liu Z, Dou Y, Cai X, Luo X (2013) Phylogenetic analysis of two Chinese orf virus isolates based on sequences of B2L and VIR genes. Arch Virol 158(7):1477–1485. doi:10.1007/s00705-013-1641-7
Guo J, Zhang Z, Edwards JF, Ermel RW, Taylor C Jr, de la Concha-Bermejillo A (2003) Characterization of a North American orf virus isolated from a goat with persistent, proliferative dermatitis. Virus Res 93(2):169–179
Delhon G, Tulman ER, Afonso CL, Lu Z, de la Concha-Bermejillo A, Lehmkuhl HD, Piccone ME, Kutish GF, Rock DL (2004) Genomes of the parapoxviruses ORF virus and bovine papular stomatitis virus. J Virol 78(1):168–177
Mercer AA, Ueda N, Friederichs SM, Hofmann K, Fraser KM, Bateman T, Fleming SB (2006) Comparative analysis of genome sequences of three isolates of Orf virus reveals unexpected sequence variation. Virus Res 116(1–2):146–158. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2005.09.011
McGuire MJ, Johnston SA, Sykes KF (2012) Novel immune-modulator identified by a rapid, functional screen of the parapoxvirus ovis (Orf virus) genome. Proteome Sci 10(1):4. doi:10.1186/1477-5956-10-4
Friederichs S, Krebs S, Blum H, Wolf E, Lang H, von Buttlar H, Buttner M (2014) Comparative and retrospective molecular analysis of Parapoxvirus (PPV) isolates. Virus Res 181:11–21. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2013.12.015
Hautaniemi M, Ueda N, Tuimala J, Mercer AA, Lahdenpera J, McInnes CJ (2010) The genome of pseudocowpoxvirus: comparison of a reindeer isolate and a reference strain. J Gen Virol 91(Pt 6):1560–1576. doi:10.1099/vir.0.018374-0
Rziha HJ, Bauer B, Adam KH, Rottgen M, Cottone R, Henkel M, Dehio C, Buttner M (2003) Relatedness and heterogeneity at the near-terminal end of the genome of a parapoxvirus bovis 1 strain (B177) compared with parapoxvirus ovis (Orf virus). J Gen Virol 84(Pt 5):1111–1116
Cottone R, Buttner M, McInnes CJ, Wood AR, Rziha HJ (2002) Orf virus encodes a functional dUTPase gene. J Gen Virol 83(Pt 5):1043–1048
Fleming SB, Lyttle DJ, Sullivan JT, Mercer AA, Robinson AJ (1995) Genomic analysis of a transposition-deletion variant of orf virus reveals a 3.3 kbp region of non-essential DNA. J Gen Virol 76(12):2969–2978
Hautaniemi M, Vaccari F, Scagliarini A, Laaksonen S, Huovilainen A, McInnes CJ (2011) Analysis of deletion within the reindeer pseudocowpoxvirus genome. Virus Res 160(1–2):326–332. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2011.07.005
McInnes CJ, Wood AR, Nettleton PE, Gilray JA (2001) Genomic comparison of an avirulent strain of Orf virus with that of a virulent wild type isolate reveals that the Orf virus G2L gene is non-essential for replication. Virus Genes 22(2):141–150
Li R, Zhu H, Ruan J, Qian W, Fang X, Shi Z, Li Y, Li S, Shan G, Kristiansen K, Yang H, Wang J (2010) De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequencing. Genome Res 20(2):265–272. doi:10.1101/gr.097261.109
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Cottone R, Buttner M, Bauer B, Henkel M, Hettich E, Rziha HJ (1998) Analysis of genomic rearrangement and subsequent gene deletion of the attenuated Orf virus strain D1701. Virus Res 56(1):53–67
Ball LA (1987) High-frequency homologous recombination in vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol 61(6):1788–1795
Fraser KM, Hill DF, Mercer AA, Robinson AJ (1990) Sequence analysis of the inverted terminal repetition in the genome of the parapoxvirus, orf virus. Virology 176(2):379–389
Dwivedi B, Gadagkar SR (2009) Phylogenetic inference under varying proportions of indel-induced alignment gaps. BMC Evol Biol 9:211. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-9-211
Nozaki Y, Bellgard M (2005) Statistical evaluation and comparison of a pairwise alignment algorithm that a priori assigns the number of gaps rather than employing gap penalties. Bioinformatics 21(8):1421–1428. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti198
McKelvey TA, Andrews SC, Miller SE, Ray CA, Pickup DJ (2002) Identification of the orthopoxvirus p4c gene, which encodes a structural protein that directs intracellular mature virus particles into A-type inclusions. J Virol 76(22):11216–11225
McIntosh AA, Smith GL (1996) Vaccinia virus glycoprotein A34R is required for infectivity of extracellular enveloped virus. J Virol 70(1):272–281
Roper RL, Payne LG, Moss B (1996) Extracellular vaccinia virus envelope glycoprotein encoded by the A33R gene. J Virol 70(6):3753–3762
Meyer M, Clauss M, Lepple-Wienhues A, Waltenberger J, Augustin HG, Ziche M, Lanz C, Buttner M, Rziha HJ, Dehio C (1999) A novel vascular endothelial growth factor encoded by Orf virus, VEGF-E, mediates angiogenesis via signalling through VEGFR-2 (KDR) but not VEGFR-1 (Flt-1) receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J 18(2):363–374. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.2.363
Savory LJ, Stacker SA, Fleming SB, Niven BE, Mercer AA (2000) Viral vascular endothelial growth factor plays a critical role in orf virus infection. J Virol 74(22):10699–10706
Wise LM, Ueda N, Dryden NH, Fleming SB, Caesar C, Roufail S, Achen MG, Stacker SA, Mercer AA (2003) Viral vascular endothelial growth factors vary extensively in amino acid sequence, receptor-binding specificities, and the ability to induce vascular permeability yet are uniformly active mitogens. J Biol Chem 278(39):38004–38014. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301194200
Resch W, Weisberg AS, Moss B (2009) Expression of the highly conserved vaccinia virus E6 protein is required for virion morphogenesis. Virology 386(2):478–485. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2009.01.009
Diel DG, Luo S, Delhon G, Peng Y, Flores EF, Rock DL (2011) A nuclear inhibitor of NF-kappaB encoded by a poxvirus. J Virol 85(1):264–275. doi:10.1128/JVI.01149-10
Ning Z, Zheng Z, Hao W, Duan C, Li W, Wang Y, Li M, Luo S (2013) The N terminus of orf virus-encoded protein 002 inhibits acetylation of NF-kappaB p65 by preventing Ser(276) phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 8(3):e58854. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058854
Diel DG, Delhon G, Luo S, Flores EF, Rock DL (2010) A novel inhibitor of the NF-{kappa}B signaling pathway encoded by the parapoxvirus orf virus. J Virol 84(8):3962–3973. doi:10.1128/JVI.02291-09
Diel DG, Luo S, Delhon G, Peng Y, Flores EF, Rock DL (2011) Orf virus ORFV121 encodes a novel inhibitor of NF-kappaB that contributes to virus virulence. J Virol 85(5):2037–2049. doi:10.1128/JVI.02236-10
Westphal D, Ledgerwood EC, Hibma MH, Fleming SB, Whelan EM, Mercer AA (2007) A novel Bcl-2-like inhibitor of apoptosis is encoded by the parapoxvirus ORF virus. J Virol 81(13):7178–7188. doi:10.1128/JVI.00404-07
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants (No. 31070138 and No. 31170147) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) and Special Funds for Colleges and Universities Talents by Guangdong Province (2011) and Scientific Research Foundation of Introducing Talents of Southern Medical University (2010). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Hao, W., Peng, Y. et al. Comparative genomic sequence analysis of Chinese orf virus strain NA1/11 with other parapoxviruses. Arch Virol 160, 253–266 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2274-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2274-1