Abstract
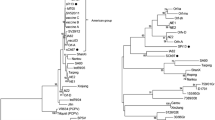
Orf virus (ORFV) is an enveloped virus with a double-stranded DNA genome, causing a contagious pustular dermatitis, mainly in goats and sheep. In this study, two strains of ORFV were isolated from sheep and goat samples in Xinjiang and Shaanxi, China. The B2L and virus interferon resistance (VIR) genes of these two isolates were sequenced and analyzed after PCR amplification. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the two isolates clustered with other ORFV strains but were separated into different subgroups. The Xinjiang strain shared the highest homology with the Gansu strain, whereas the Shaanxi strain shared higher homology with the Taiwan and Hubei strains. This is the first report of the molecular characterization of ORFV in Northwest China, and it provides new information on the genotyping of the causative agents responsible for contagious ecthyma dermatitis outbreaks in China.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nandi S, De UK, Chowdhury S (2011) Current status of contagious ecthyma or orf disease in goat and sheep-A global perspective. Small Ruminant Res 96:73–82
Hosamani M, Bhanuprakash V, Scagliarini A, Singh RK (2006) Comparative sequence analysis of major envelope protein gene (B2L) of Indian orf viruses isolated from sheep and goats. Vet Microbiol 116:317–324
Ara M, Zaballos P, Sanchez M, Querol I, Zubiri ML, Simal E, Horndler C (2008) Giant and recurrent orf virus infection in a renal transplant recipient treated with imiquimod. J Am Acad Dermatol 58:S39–S40
Zhao K, Song DG, He WQ, Lu HJ, Zhang BB, Li C, Chen KY, Gao F (2010) Identification and phylogenetic analysis of an Orf virus isolated from an outbreak in sheep in the Jilin province of China. Vet Microbiol 142:408–415
Haig DM, McInnes CJ (2002) Immunity and counter-immunity during infection with the parapoxvirus orf virus. Virus Res 88:3–16
Delhon G, Tulman ER, Afonso CL, Lu Z, de la Concha-Bermejillo A, Lehmkuhl HD, Piccone ME, Kutish GF, Rock DL (2004) Genomes of the parapoxviruses orf virus and bovine Papular stomatitis virus. J Virol 78:168–177
Sullivan JT, Mercer AA, Fleming SB, Robinson AJ (1994) Identification and characterization of an orf virus homologue of the vaccinia virus gene encoding the major envelope antigen p37 K. Virology 202:968–973
Inoshima Y, Morooka A, Sentsui H (2000) Detection and diagnosis of parapoxvirus by the polymerase chain reaction. J Virol Methods 84:201–208
Inoshima Y, Murakami K, Yokoyama T, Sentsui H (2001) Genetic heterogeneity among parapoxviruses isolated from sheep, cattle and Japanese serows (Capricornis crispus). J Gen Virol 82:1215–1220
Tikkanen MK, McInnes CJ, Mercer AA, Buttner M, Tuimala J, Hirela-Koski V, Neuvonen E, Huovilainen A (2004) Recent isolates of Parapoxvirus of Finnish reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) are closely related to bovine Pseudocowpox virus. J Gen Virol 85:1413–1418
Zhang K, Shang Y, Jin Y, Wang G, Zheng H, He J, Lu Z, Liu X (2010) Diagnosis and phylogenetic analysis of Orf virus from goats in China: a case report. Virol J 7:78–82
McInnes CJ, Wood AR, Mercer AA (1998) Orf virus encodes a homolog of the vaccinia virus interferon resistance gene E3L. Virus Genes 17:107–115
Kottaridi C, Nomikou K, Teodori L, Savini G, Lelli R, Markoulatos P, Mangana O (2006) Phylogenetic correlation of Greek and Italian orf virus isolates based on VIR gene. Vet Microbiol 116:310–316
Oem JK, Roh IS, Lee KH, Lee KK, Kim HR, Jean YH, Lee OS (2009) Phylogenetic analysis and characterization of Korean orf virus from dairy goats: case report. Virol J 6:167
Kottaridi C, Nomikou K, Lelli R, Markoulatos P, Mangana O (2006) Laboratory diagnosis of contagious ecthyma: comparison of different PCR protocols with virus isolation in cell culture. J Virol Methods 134:119–124
Torfason EG, Guonadottir S (2002) Polymerase chain reaction for laboratory diagnosis of orf virus infections. J Clin Virol 24:79–84
Liu Y, Shao H, Cheng R (2007) Establish and application of PCR detection method to contagious pustular dermatitis virus. Jilin Xu Mu Shou Yi 3:7–9
Chan KW, Lin JW, Lee SH, Liao CJ, Tsai MC, Hsu WL, Wong ML, Shih HC (2007) Identification and phylogenetic analysis of orf virus from goats in Taiwan. Virus Genes 35:705–712
Chan KW, Yang CH, Lin JW, Wang HC, Lin FY, Kuo ST, Wong ML, Hsu WL (2009) Phylogenetic analysis of parapoxviruses and the C-terminal heterogeneity of viral ATPase proteins. Gene 432:44–53
Lucinda N, Inoue-Nagata AK, Kitajima EW, Nagata T (2010) Complete genome sequence of Brugmansia suaveolens mottle virus, a potyvirus from an ornamental shrub. Arch Virol 155(10):1729–1732
Mercer AA, Ueda N, Friederichs SM, Hofmann K, Fraser KM, Bateman T, Fleming SB (2006) Comparative analysis of genome sequences of three isolates of orf virus reveals unexpected sequence variation. Virus Res. 116(1–2):146–158
Guo J, Zhang Z, Edwards JF, Ermel RW, Taylor C Jr, de la Concha-Bermejillo A (2003) Characterization of a North American orf virus isolated from a goat with persistent, proliferative dermatitis. Virus Res. 93:169–179
Guo J, Rasmussen J, Wunschmann A, de la Concha-Bermejillo A (2004) Genetic characterization of orf viruses isolated from various ruminant species of a zoo. Vet Microbiol 99:81–92
Hautaniemi M, Ueda N, Tuimala J, Mercer AA, Lahdenpera J, McInnes CJ (2010) The genome of pseudocowpoxvirus: comparison of a reindeer isolate and a reference strain. J Gen Virol 91(6):1560–1576
Inoshima Y, Ito M, Ishiguro N (2010) Spatial and temporal genetic homogeneity of orf viruses infecting Japanese serows (Capricornis crispus). J Vet Med Sci 72(6):701–707
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by National Key Technology R&D Program (2007BAD40B01), the Ministry of Science and Technology, and Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System(CARS-40-10), the Ministry of Agriculture, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Zhu, X., Zheng, Y. et al. Phylogenetic analysis of two Chinese orf virus isolates based on sequences of B2L and VIR genes. Arch Virol 158, 1477–1485 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1641-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1641-7