Abstract
The concentration index (CI) has been widely used in recent years to analyze the statistical structure of daily precipitation. This index was proposed by Martin-Vide Int J Climatol 24:959–971 (2004) to explore the contribution of the days of the greatest rainfall to the total amount. However, sometimes, the interpretation of the concentration index could be confusing because depending on the research work consulted, it could be categorized into different levels of concentration. The differences observed in the classifications are due to the distribution of the CI values within each of the regions under study, that is, it is due to local classification. Under these circumstances, it is important to differentiate between the global and local behavior of this index in order to make comparable the results of different research work. According to their definition, the concentration index could be classified intuitively on global manner as: very low concentration (0–0.2), low concentration (0.2–0.4), moderate concentration (0.4–0.6), high concentration (0.6–0.8), and very high concentration (0.8–1). The results show that the observed range of the CI values at a global scale of the countries considered in this work is between moderate and high. On the other hand, at the local scale, the methodologies proposed for the classification of the concentration index show a good performance. The local classification allows for knowing within the range of local variation the conditions of concentration of the precipitation at this scale.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alijani B, O’Brien J, Yarnal B (2008) Spatial analysis of precipitation intensity and concentration in Iran. Theor Appl Climatol 94:107–124
Benhamrouche A, Martín-Vide J (2012) Methodological advances in the analysis of the daily concentration of rainfall in mainland Spain. An Geografía 32-1:11–27
Benhamrouche A, Boucherf D, Hamadache R, Bendahmane L, Martin-Vide J, Teixeira J (2015) Spatial distribution of the daily precipitation concentration index in Algeria. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 15:617–625
Brooks C, Carruthers N (1953) Handbook of statistical methods in meteorology. Meteorological Office, London
Brugnara Y, Brunetti M, Maugeri M, Nanni T, Simolo C (2012) High resolution analysis of daily precipitation trends in the central Alps over the last century. Int J Climatol 32:1406–1422
Cortesi N, Gonzalez-Hidalgo JC, Brunetti M, Martin-Vide J (2012) Daily precipitation concentration across Europe 1971-2010. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12:2799–2810
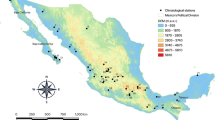
García E (2003) Distribución de la precipitación en la República Mexicana. Investigaciones Geográficas 50:67–76. https://doi.org/10.14350/rig.30432
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Li X, Jiang F, Li L, Wang G (2011) Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation concentration index, concentration degree and concentration period in Xinjiang, China. Int J Climatol 31:1679–1693
Liu Y, Yan J, Cen M (2016) The relationship between precipitation heterogeneity and meteorological drought/flood in China. J Meteorol Res 30:758–770
Llano MP (2018) Spatial distribution of the daily rainfall concentration index in Argentina: comparison with other countries. Theor Appl Climatol 133:997–1007
Martin-Vide J (2004) Spatial distribution of a daily precipitation concentration index in peninsular Spain. Int J Climatol 24:959–971
Mayer P, Marzol M (2014) La concentración pluviométrica diaria y las secuencias lluviosas en Canarias: dos factores de peligrosidad. Bol AGE 65:231–247
Mayer P, Marzol MV, Perreño JM (2017) Precipitation trends and a daily precipitation concentration index for the mid-eastern Atlantic (Canary Islands, Spain). Geogr Res Lett 43(1):255–268
Monjo R, Martin-Vide J (2016) Daily precipitation concentration around the world according to several indices. Int J Climatol 36:3828–3838. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4596
NMS (2018) Climatological information from the National Meteorological Service. March 19, 2018. In: URL http://smn.cna.gob.mx/es/?option=com_content&view=article&id=42&itemid=75
Oliver J (1980) Monthly precipitation distribution: a comparative index. Prof Geogr 32(3):300–309
Patel NR, Shete DT (2015) Analyzing precipitation using concentration indices for North Gujarat Agro Climatic Zone, India. Aquat Procedia 4:917–924
Serrano-Notivoli R, Martin-Vide J, Saz MA, Longares LA, Beguer ́ıa S, Sarricolea P, Meseguer-Ruiz O, de Luis M (2017) Spatio- temporal variability of daily precipitation concentration in Spain based on a high-resolution gridded data set. Int J Climatol 38:e518–e530. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5387
Shi W, Yu X, Liao W, Wang Y, Jia B (2013) Spatial and temporal variability of daily precipitation concentration in the Lancang River basin, China. J Hydrol 495:197–207
Shi P, Qiao X, Chen X, Zhou M, Qu S, Ma X, Zhang Z (2014) Spatial distribution and temporal trends in daily and montly precipitation concentration indices in the upper reaches of the Huai River, China. Stoch Env Res Risk A 28:201–212
Suhaila J, Jemain A (2012) Spatial analysis of daily rainfall intensity and concentration index in peninsular Malaysia. Theor Appl Climatol 108:235–245
Trenberth KE, Jones PD, Ambenje P, Bojariu R, Easterling D, Klein TA, Parker D, Rahimzadeh F, Renwick JA, Rusticucci M, Soden B, Zhai P (2007) Observations: surface and atmospheric climate change. In: Solomon S et al (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Vyshkvarkova E, Voskresenskaya E, Martin-Vide J (2018) Spatial distribution of the daily precipitation concentration index in southern Russia. Atmos Res 203:36–43
Wang X, Chen H, Wu Y, Feng Y, Pu Q (2010) New techniques for detection and adjustment of shifts in daily precipitation data series. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 49:2416–2436
Wilks DS (2006) Statistical methods in the atmospheric sciences, second edition, vol 91. Academic Press, London
Yesilırmak E, Atatanır L (2016) Spatiotemporal variability of precipitation concentration in Western Turkey. Nat Hazards 81:687–704
Zhang L, Qian Y (2003) Annual distribution features of precipitation in China and their interannual variations. Acta Meteorol Sin 17:146–163
Zhang Q, Xu C, Gemmer M, Chen YD, Liu C (2009) Changing properties of precipitation concentration in the Pearl River basin, China. Stoch Env Res Risk A 23:377–385
Zubieta R, Saavedra M, Silva Y, Giráldez L (2017) Spatial analysis and temporal trends of daily precipitation concentration in the Mantaro River basin: Central Andes of Peru. Stoch Env Res Risk A 31(6):1305–1318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Núñez-González, G. Comparison of the behavior of the precipitation concentration index on global and local scale. Theor Appl Climatol 139, 631–638 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-02996-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-02996-5