Summary
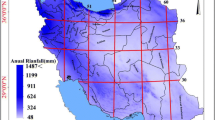
Understanding rainfall variability in the arid, rugged landscapes of Iran requires studying the climatology and spatial patterns of daily precipitation. This paper applies geostatistical and other methods to daily precipitation data from 90 stations that are distributed across Iran to calculate daily rainfall concentration and intensity and map their spatial distribution. The results show that daily precipitation tends to be irregular and intense across much of Iran and that a disproportionately large share of the annual rainfall comes from a small number of high intensity to extreme rainfall events. Analysis of daily rainfall concentration confirms that extreme events are widely distributed across the country, with more than 20% of the land area exposed to the risk of extreme rainfall. The areas experiencing the most frequent extreme events are the hot, dry southern coast and the western slopes of the main north–south range, the Zagros Mountains. Even the wettest parts of the country along the Caspian Sea coast derive a significant amount of their rain from high intensity and extreme events. A cross-validation analysis supports the reliability and accuracy of the geostatistical modeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B Alijani (1979) ArticleTitleRelation between cyclone tracks and upper level flow patterns in the Middle East Geogr Res Q 4 125–143
B Alijani (1997) Climate of Iran Payam Nour University Tehran, Iran
B Alijani (2002a) ArticleTitleVariations of 500 hPa flow patterns and their relationship with the climate of Iran Theor Appl Climatol 72 41–52 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007040200011
B Alijani (2002b) ArticleTitleIdentifying rain producing weather types of Tehran according to the vorticity computations Geogr Res Q 63&64 114–132
B Alijani G Azizi P Rezai (2004a) ArticleTitleThe effects of synoptic patterns on the floods of the southern Caspian Coast. Case study: Shafarood and Talar rivers Q J Territory 1 1–16
B Alijani JR Harman (1985) ArticleTitleSynoptic climatology of precipitation in Iran Ann Assoc Am Geogr 75 404–416 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1467-8306.1985.tb00075.x
B Alijani Z Jafarpour GJ Ghobadi (2005a) ArticleTitleAnalysis of the Droughts in the Southern coastal areas of the Caspian Sea Q J Territory 7 11–23
B Alijani Z Jafarpour H Ghaderi (2005b) ArticleTitleAnalysis and forecasting of precipitation in the Larestan area by Markov chain Q J Territory 7 1–10
B Alijani TG Parnian (2004) ArticleTitleSynoptic patterns of the flood rains of Gorgan River Q J Territory 2 1–20
B Alijani M Zahedi (2002) ArticleTitleSynoptic and statistical analysis of precipitation of Azerbaijan Geogr Res Q 65&66 202–217
A Baniwaheb B Alijani (2005) ArticleTitleStudying droughts and forecasting precipitation and temperature in Birjand area J Res Geogr 52 33–46
MC Brown (1994) ArticleTitleUsing Gini-style indices to evaluate the spatial patterns of health practitioners: theoretical considerations and an application based on Alberta data Soc Sci Med 38 1243–1256 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0277-9536(94)90189-9
M Brunetti M Maugeri T Nanni (2001) ArticleTitleChanges in total precipitation, rainy days and extreme events in northeastern Italy Int J Climatol 21 861–871 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.660
A Burgueño C Serra X Lana (2004) ArticleTitleMonthly and annual statistical distributions of daily rainfall at the Fabra Observatory (Barcelona, NE Spain) for the years 1917–1999 Theor Appl Climatol 77 57–75 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00704-003-0020-9
A Burgueño MD Martinez X Lana C Serra (2005) ArticleTitleStatistical distributions of the daily rainfall regime in Catalonia (Northeastern Spain) for the years 1950–2000 Int J Climatol 25 1381–1403 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.1197
JD Creutin C Obled (1982) ArticleTitleObjective analysis and mapping techniques for rainfall fields: an objective comparison Water Resour Res 18 413–431 Occurrence Handle10.1029/WR018i002p00413
JP Delhomme (1978) ArticleTitleKriging in the hydrosciences Adv Water Resour 1 251–266 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0309-1708(78)90039-8
Derby N (2003) Derivation of the Gini index. Statistical consulting report, Department of Biostatistics and Statistics, University of Washington
Y Dinpashoh A Fakheri-Fard M Moghaddam S Jahanbakhsh M Mirnia (2004) ArticleTitleSelection of variables for the purpose of regionalization of Iran’s precipitation climate using multivariate methods J Hydrol 294 109–123 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.04.009
M Domroes M Kaviani D Schaefer (1998) ArticleTitleAn analysis of regional and intra-annual precipitation variability over Iran using multivariate statistical methods Theor Appl Climatol 61 151–159 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007040050060
DR Easterling JL Evans P Ya Groisman TR Karl KE Kunkel P Ambenje (2000) ArticleTitleObserved variability and trends in extreme climate events: a brief review Bull Amer Meteor Soc 81 417–425 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0477(2000)081<0417:OVATIE>2.3.CO;2
JJ Egozcue C Ramis (2001) ArticleTitleBayesian hazard analysis of heavy precipitation in eastern Spain Int J Climatol 26 1263–1279 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.688
HJ Fowler CG Kilsby (2003) ArticleTitleA regional frequency analysis of United Kingdom extreme rainfall from 1961 to 2000 Int J Climatol 23 1313–1334 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.943
P Goovaerts (2000) ArticleTitleGeostatistical approaches for incorporating elevation into the spatial interpolation of rainfall J Hydrol 228 113–129 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00144-X
PY Groisman TR Karl DR Easterling RW Knight PF Jamason KJ Hennessy R Suppiah CM Page J Wibig K Fortuniak VN Razuvaev A Douglas EJ Forland P Zhai (1999) ArticleTitleChanges in probability of heavy precipitation: important indicators of climate change Climate Change 42 243–283 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005432803188
EH Issaks RM Srivastava (1989) An introduction to applied geostatistics Oxford University Press Oxford
X Lana MD Martinez C Serra A Burgueno (2005) ArticleTitlePeriodicities and irregularities of indices describing the daily pluviometric regime of the Fabra Observatory (NE Spain) for the years 1917–1999 Theor Appl Climatol 82 183–198 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00704-005-0127-2
B Liebmann C Jones LM DeCarvalho (2001) ArticleTitleInter-annual variability of daily extreme precipitation events in the State of Sao Paulo, Brazil J Climate 14 208–218 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<0208:IVODEP>2.0.CO;2
J Martin-Vide (2004) ArticleTitleSpatial distribution of a daily precipitation concentration index in peninsular Spain Int J Climatol 24 959–971 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.1030
GA Meehl T Karl DR Easterling S Changnon R Pielke SuffixJr D Changnon J Evans PY Groisman TR Knutson KE Kunkel LO Mearns C Parmesan R Pulwarty T Root RT Sylves P Whetton F Zwiers (2000) ArticleTitleAn introduction to trends in extreme climate and weather events observations, socioeconomic impacts, terrestrial ecological impacts and model projections Bull Amer Meteor Soc 81 413–416 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0477(2000)081<0413:AITTIE>2.3.CO;2
M Mehdizadeh MH Mahdian H Hajjam (2006) ArticleTitleThe efficiency of geostatistics in regionalizing the climate of the Oroomieh watershed, Iran J Phys Space 32 103–116
A Moberg PD Jones (2005) ArticleTitleTrends in indices for extremes in daily temperature and precipitation in Central and Western Europe Int J Climatol 25 1149–1171 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.1163
TJ Osborn M Hulme PD Jones TA Basnett (2000) ArticleTitleObserved trends in the daily intensity of United Kingdom precipitation Int J Climatol 20 347–364 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(20000330)20:4<347::AID-JOC475>3.0.CO;2-C
D Peñarrocha MJ Estrela M Millan (2002) ArticleTitleClassification of daily rainfall patterns in a Mediterranean area with extreme intensity levels: the valencia region Int J Climatol 22 677–695 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.747
M Perry D Hollis (2005) ArticleTitleThe generation of monthly gridded datasets for a range of climatic variables over the UK Int J Climatol 25 1041–1054 Occurrence Handle10.1002/joc.1161
C Prudhomme DW Reed (1999) ArticleTitleMapping extreme rainfall in a mountainous region using geostatistical techniques: a case study in Scotland Int J Climatol 19 1337–1356 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(199910)19:12<1337::AID-JOC421>3.0.CO;2-G
W Tobler (1970) ArticleTitleA computer movie simulating urban growth in detroit region Econ Geogr 46 234–240 Occurrence Handle10.2307/143141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Correspondence: Professor Brent Yarnal, Department of Geography and Center for Integrated Regional Assessment, 302 Walker Building, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802, USA
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alijani, B., O’Brien, J. & Yarnal, B. Spatial analysis of precipitation intensity and concentration in Iran. Theor Appl Climatol 94, 107–124 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-007-0344-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-007-0344-y